Vaccines for plague
A plague and vaccine technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, antibody mimics/scaffolds, bacterial antigen components, etc., can solve problems that are not suitable for large-scale immunization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
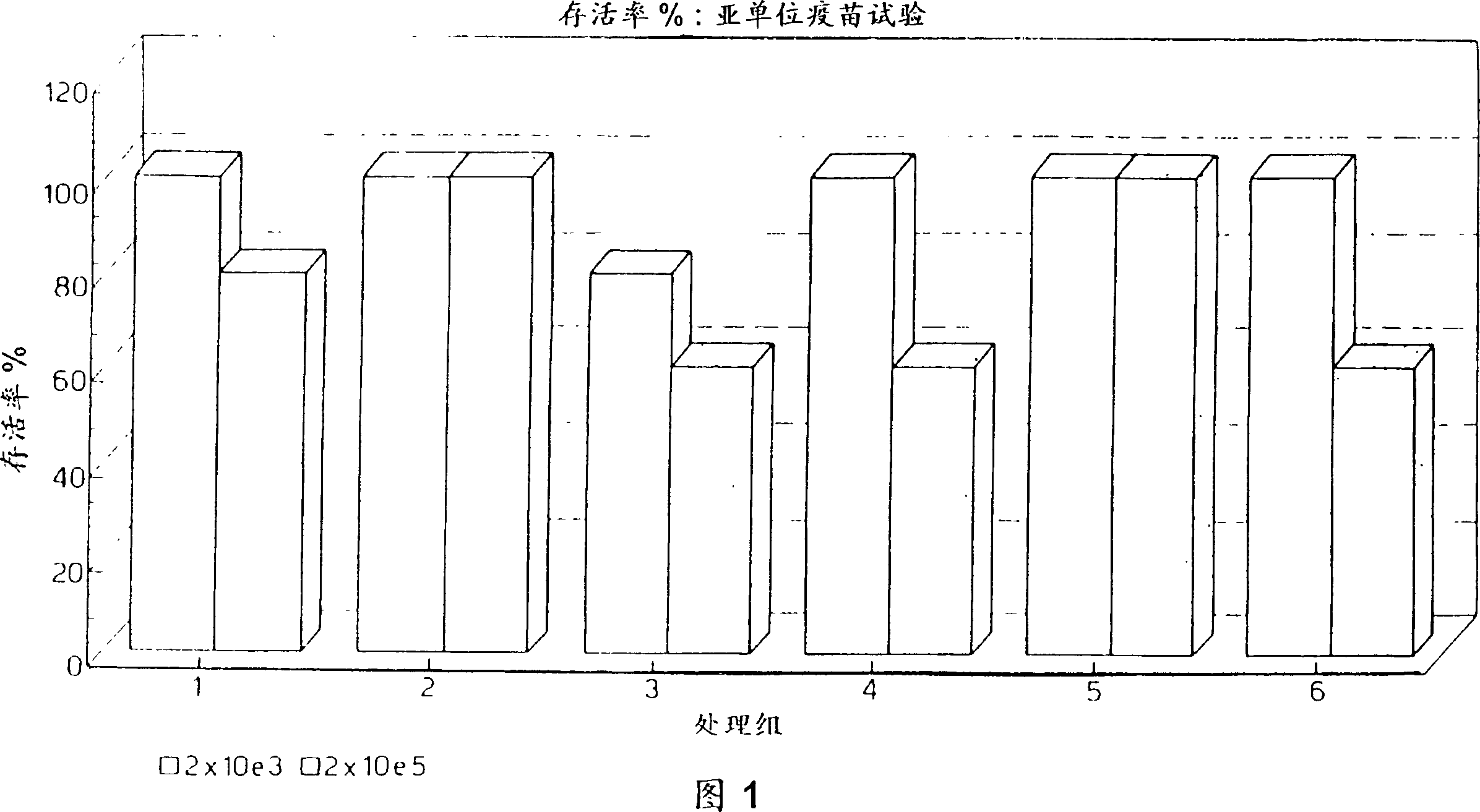
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0157] Example 1: To construct a DNA vaccine expressing V antigen, the vector plasmid pCMV was digested with restriction endonuclease Not 1 to remove the coding sequence of the Lac Z gene. The digested plasmid is treated with Klenow enzyme to generate blunt-ended vector DNA. The ssp1 restriction fragment containing the fusion protein coding sequence of V antigen and glutathione S transferase was isolated from the recombinant plasmid pVG100 and ligated with the vector DNA. The V sequence used here is the sequence described in Example Seq ID No 3. The recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli Nova Blue, and the purified plasmid was inoculated into Balb / c mice by intramuscular injection. Immunoglobulin responses to the V antigen were detected in the sera of vaccinated animals.
Embodiment 2
[0158] Example 2: In order to construct a DNA vaccine expressing F1 antigen, PCR primers were designed to amplify the full-length caf 1 open reading frame. This reading frame encodes the signal peptide for the secretion of F1 and the leader protein from bacterial cells. The PCR primers used have a "tail" containing a restriction enzyme recognition site at their 5' end, allowing the amplified product to be directly inserted into the vector plasmid. The sequences of PCR primers 5'FAB2 and 3'FBAM are shown in Seq ID No 18 and Seq ID No 19, respectively.
[0159]Using 5'FAB2 and 3'FBAM to amplify a PCR fragment, the sequence of this PCR fragment is shown in Seq ID no 20. This PCR fragment was digested with restriction enzymes NheI and BamHI and cloned into pBKCMV plasmid digested with the same enzymes. The resulting recombinant plasmid pFlAB was transformed into Escherichia coli Nova Blue, and the purified plasmid was inoculated into Bal b / c mice by intramuscular injection. Imm...
Embodiment 3
[0160] Example 3: In order to construct a DNA vaccine expressing F1 and V simultaneously, the V antigen coding sequence was inserted into the DNA vaccine expressing F1 introduced in Example 2. There is a connecting region encoding 6 amino acids between the coding sequences of F1 and V, so that the two proteins can independently form their respective configurations. The sequence encoding the junction region-V was obtained by digesting the recombinant plasmid placFV6 with BamHI and HindIII, and the sequence encoding the junction region-V was ligated with the plasmid pFIAB digested with the same restriction enzymes. The resulting plasmid pFVAB was transformed into E. coli Nova Blue. Plasmids were purified for later use. See Seq ID No 22 for the fused F1 / V sequence and deduced amino acid sequence.
[0161] Examples of fusion proteins containing F1 and V antigens are described below.
[0162] Enzymes and Reagents
[0163] Materials used to prepare media were obtained from Oxoid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com