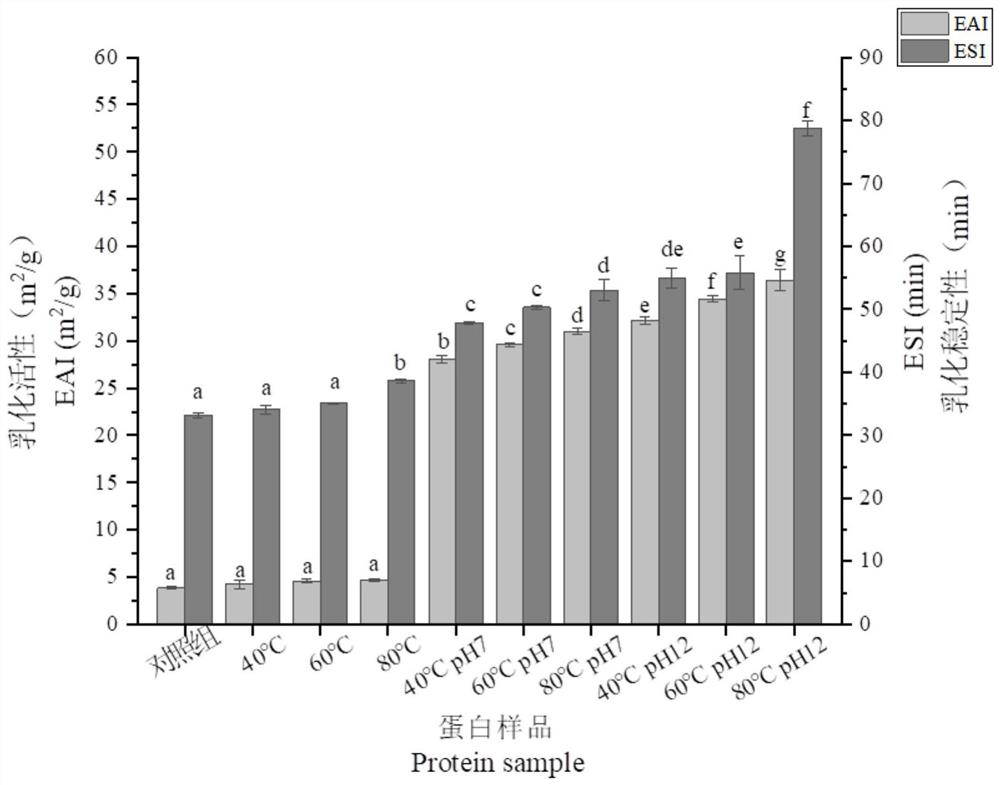
Treatment method and application of gluten protein
A processing method and technology of gluten protein, applied in the fields of application, plant protein processing, packaging, etc., can solve the problems of poor water solubility, unsatisfactory functional properties, hindering the application of gluten protein, etc., to achieve improved solubility and emulsification properties, and enhance solubility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Protein sample preparation:
[0036] At room temperature, gluten protein was dissolved in distilled water to prepare a gluten protein aqueous solution with a protein concentration of 5 mg / mL.
[0037]Among them, the gluten protein aqueous solution without any treatment was used as the control group. Take three gluten protein aqueous solutions for heat treatment only: heat treatment at 40°C, 60°C, and 80°C for 30 min, and stir at room temperature for 1 h; adjust the pH to 12.0 with 1M NaOH solution, and the three gluten protein aqueous solutions are respectively heated at 40°C, 60°C , heat treatment at 80°C for 30 min, stir at room temperature for 1 h, then adjust the pH to 7.0 with 1M HCl solution (pH cycle method), and continue stirring at room temperature for 1 h. At the same time, three gluten protein aqueous solutions were taken and heat-treated at 40° C., 60° C., and 80° C. for 30 min, respectively, and stirred for 1 h at room temperature. All processed gluten pr...
Embodiment 2
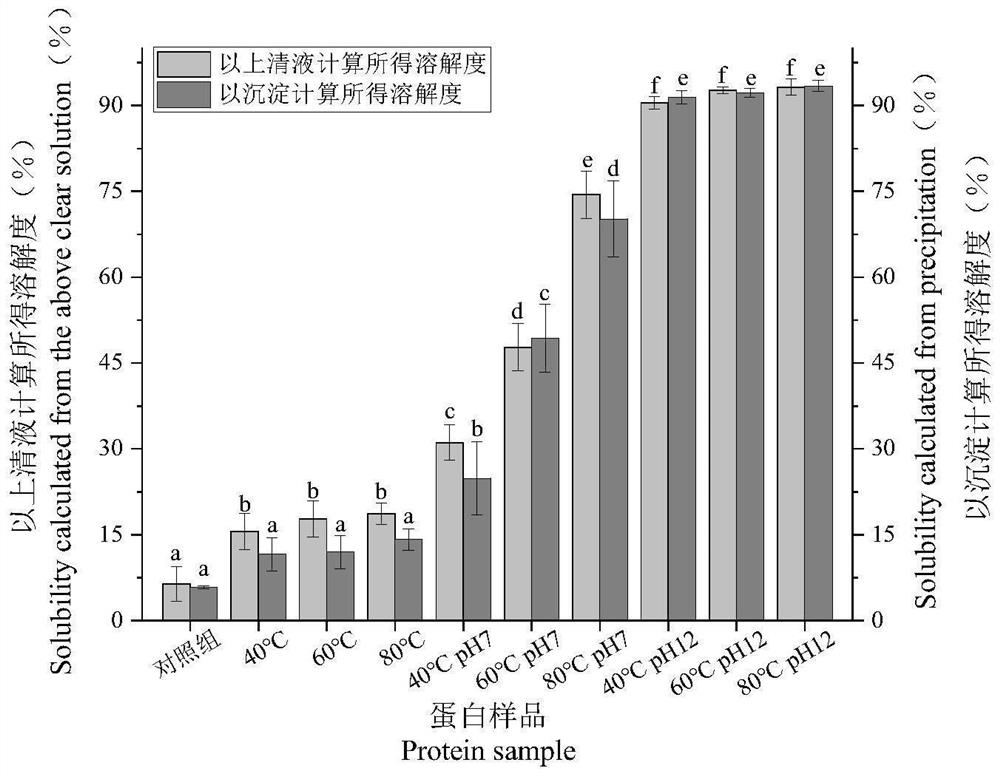
[0039] Solubility determination
[0040] Pour the centrifuged gluten protein supernatant into a petri dish, keep the precipitate in a centrifuge tube, and dry it in a 55°C oven overnight. After drying, weigh the centrifuge tube and the precipitate together, and subtract the original centrifuge tube from the obtained mass. The mass is the precipitation mass, and the gluten protein solubility calculated from the obtained gluten protein precipitation mass is Solubility 1. After 48h freeze-drying of the gluten protein supernatant, the gluten protein freeze-dried sample was carefully taken out and weighed, and the gluten protein solubility calculated according to the mass of the obtained gluten protein supernatant sample was solubility 2.
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] like figure 1 As shown, all 9 treatments had some effect on the solubility of gluten protein. Among them, compared with the control, the improvement of the solubility of gluten protein by single heat treatment wa...
Embodiment 3
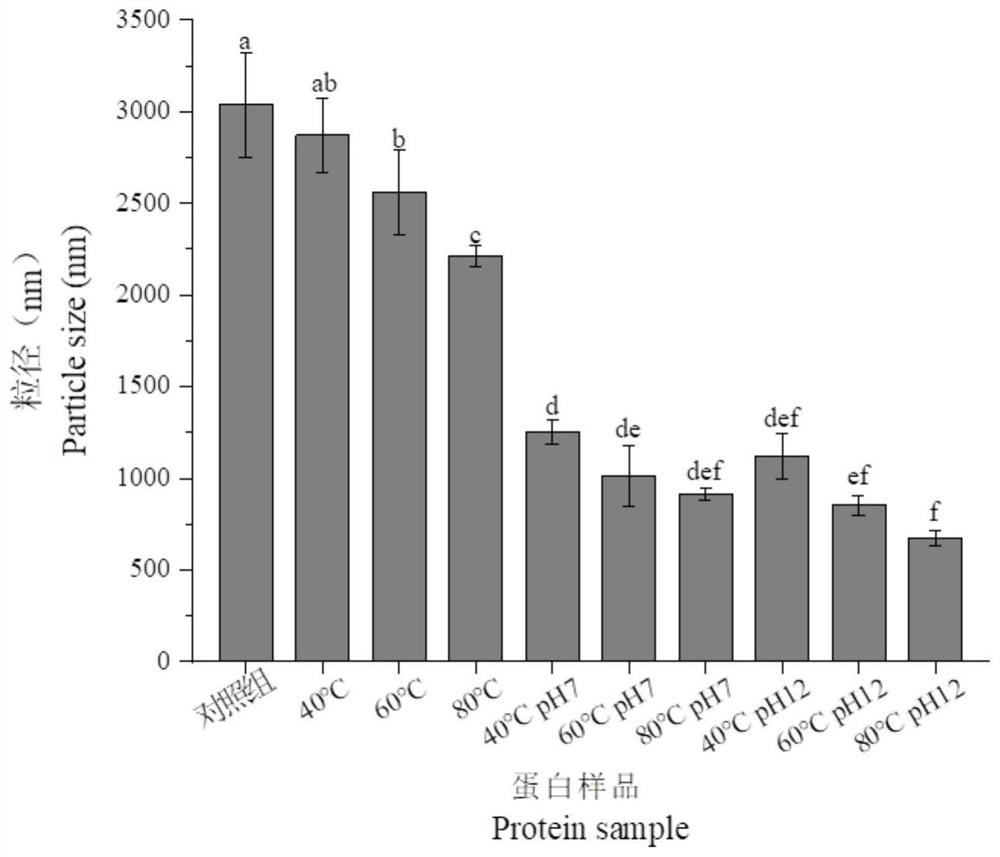
[0047] Determination of average particle size of emulsions
[0048] To measure the average particle size of protein molecules, choose a dynamic laser light scattering (DLS) with a λ=633nm He / Ne laser particle size potential analyzer and set the scattering angle to 173°. Pipette 1 mL of different gluten protein sample solutions with a concentration of 5 mg / mL into a special material cuvette (polystyrene) (refractive index 1.33) to determine the average particle size. The measurement temperature is set at 25±0.1°C, and the temperature is kept for 3 minutes. Three parallel experiments were performed for each protein sample, each parallel sample was scanned three times, and the final results were averaged.
[0049] The size of protein particle size has a great influence on protein structure and functional properties, and has important application value for improving the utilization rate of protein resources.
[0050] like figure 2 As shown, all 9 treatments had a certain effec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com