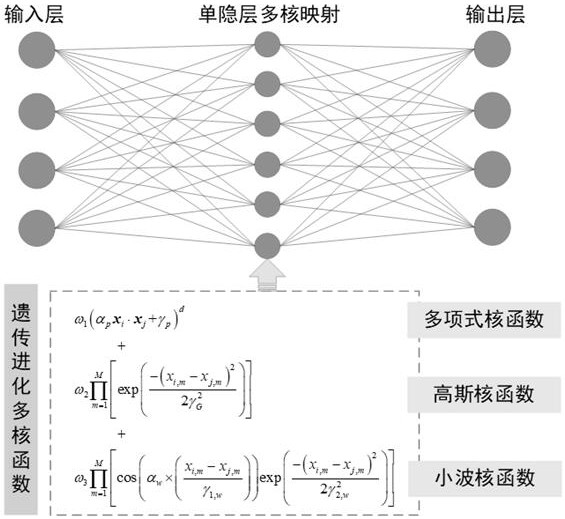
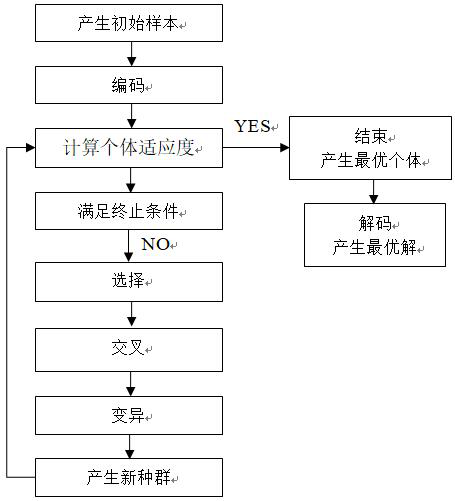
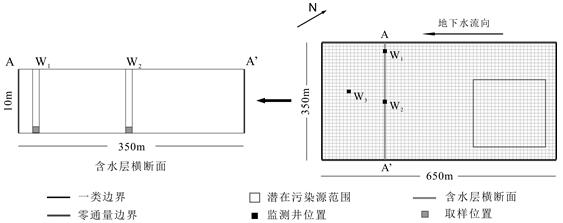
Organic pollutant migration numerical model substitution method based on multi-core extreme learning machine
An extreme learning machine and organic pollutant technology, which is applied in the combined application field of artificial intelligence and groundwater numerical simulation to achieve efficient solutions, strong learning and generalization capabilities, and improved computing efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Example 1: A hypothetical organic-polluted phreatic aquifer can be generalized into a homogeneous and isotropic three-dimensional multiphase flow model. There is no natural boundary near the polluted site, and the boundary is defined at a position where the impact of pollutant migration is negligible. Among them, the northeast boundary and southwest boundary are generalized as a type of boundary; the southeast boundary and northwest boundary are composed of flow surfaces, which can be generalized as zero-flux boundaries; the lower part of the calculation simulation area is an aquifer, which can be generalized as zero-flux The upper part of the boundary is the water table, which is the boundary of water exchange. Because the thickness of the aquifer changes slowly along the direction of groundwater flow, it is generalized as an aquifer of equal thickness. The physical and chemical parameters of water and organic pollutant chlorobenzene are shown in Table 1.
[0086] Tab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com