Enterobacter adamsii and application of enterobacter adamsii in prevention and treatment of plant bacterial soft rot
A kind of Enterobacteriaceae, bacterial technology, applied in the field of Enterobacteriaceae and its application in the prevention and treatment of plant bacterial soft rot, can solve the problems of limitation, unstable chemical properties of sensing signals, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Isolation and screening of bacterial strain L95
[0031] 1. Strain isolation
[0032] Soil sample collection: In November 2020, the rhizosphere soil of rice was collected from the paddy fields of Xiaogan City, Hubei Province. The soil at the surface and below 5cm deep was collected in bags for storage, and brought back to the laboratory as a microbial source for strain isolation.
[0033] Bacterial strain isolation: separation and purification were carried out by dilution, plate coating and streaking. Specifically, after fully mixing the collected field soil samples, 5.0 g was weighed and placed in a sterilized centrifuge tube filled with 15 mL of fresh LB liquid medium, shaken at 28°C and 200 rpm for 15 minutes, and allowed to stand until the soil Particles sink to the bottom of the centrifuge tube, the supernatant is diluted with sterile water, and 100 μL of 10 -5 、10 -6 、10 -7 The diluted solution was spread on the LB plate, placed upside down in a con...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Flow cytometry verification of the quenching effect of strain L95 on VFM
[0037] The VR2 reporter strain was activated by streaking with LB+Kan solid medium, and a single colony was picked and placed in LB+Kan liquid medium, and cultured on a shaker at 28°C and 200rpm until the bacterial liquid OD 600 = 1.0, the reporter strain VR2 and bacterial strain L95 (quenched bacteria) were equally inoculated and mixed cultured, and the reporter strain VR2 was only inoculated as a control, and the fluorescence intensity MFI of the sample was measured every four hours. From figure 2 It can be seen that when the strain is cultivated for 4-8 hours, the strain L95 can significantly quench the VFM signal produced by VR2, and when the strain is cultivated for 12 hours, the quenching gene of VR2 can degrade the VFM signal in the system. And without adding strain L95, the VFM signal value of the reporter system response decreased sharply compared with the original.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Identification of strain L95
[0039] 1. Morphological identification
[0040] Strain L95 is Gram-negative; the colonies on LB nutrient medium are milky white, translucent, round, raised, smooth, easy to pick up, and have neat edges.
[0041] 2. Molecular identification
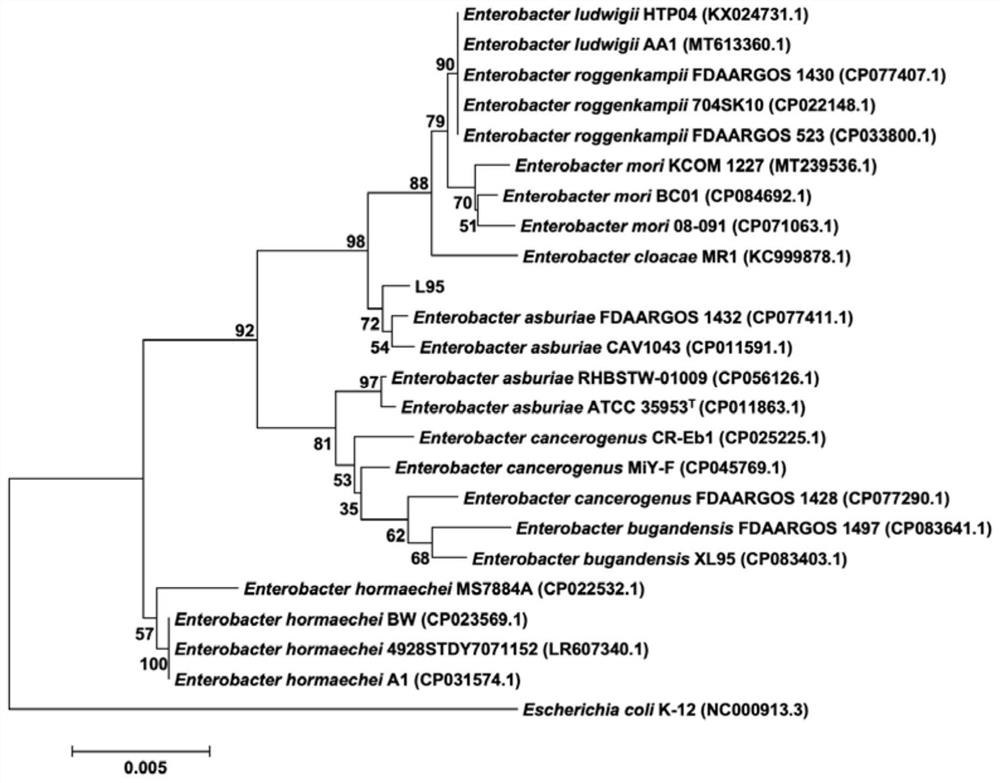
[0042] In order to clarify the taxonomic status of the strain L95 obtained in Example 1, we identified the strain L95 using the method of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) combined with phylogenetic analysis (Phylogenetic analysis).
[0043] 16S rDNA sequence analysis is a molecular biological identification method for bacterial identification. By analyzing the 16S rDNA sequence (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1), combined with the conserved housekeeping gene gyrB (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2) and the rpoD sequence (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3), the MEGA 6.0 software was used to construct a phylogenetic tree using the Neighbor-joini...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com