Peptides as inhibitors of fibrotic matrix accumulation
A cyclic peptide and sequence technology, applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, peptides, cyclic peptide components, etc., can solve problems such as little knowledge of risks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
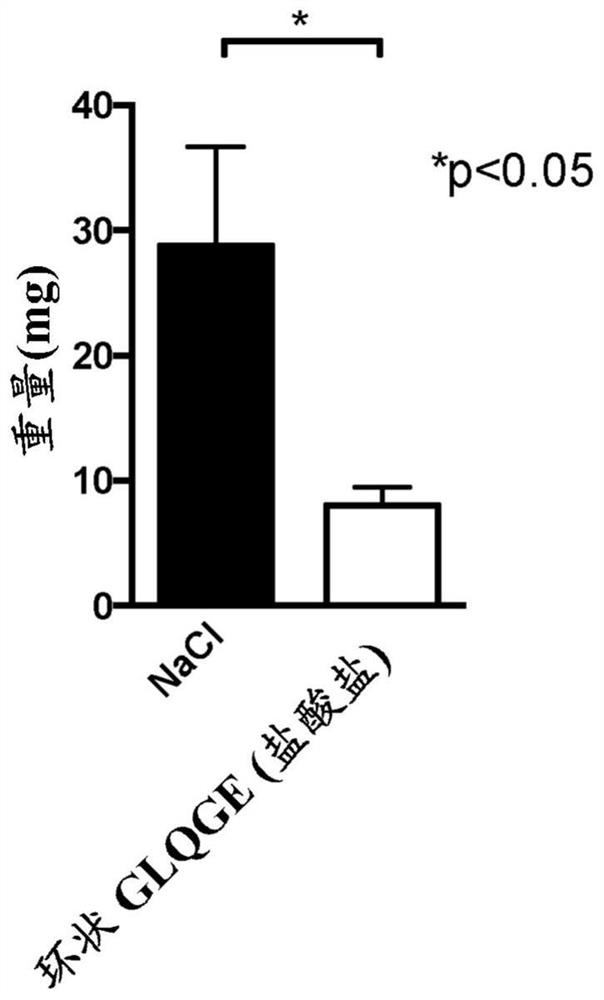
[0143] Example 1: Peptide Synthesis
[0144] Synthesis of the peptide Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu (GLQGE) in linear form as Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu-NH 2 (Also known as Linear GLQGE-NH 2 ), and in linear form as acetic acid-Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu (also known as linear Ac-GLQGE), and in cyclic form as cyclic Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu (also known as is a cyclic GLQGE with no C-terminal amide and no N-terminal acetate). The peptide Pro-Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu (also known as cyclic PGLQGE) was synthesized only in cyclic form. The control peptides Gly-Leu-Asn-Gly-Glu (also known as linear CT1 (linear GLNGE)) and Gly-Leu-Hyp-Gly-Glu (also known as linear CT2 (linear GLOGE)) are both characterized by having a C-terminal amide Chemical (GLNGE-NH 2 and GLOGE-NH 2 ) and N-terminal acetylation (Ac-GLNGE and Ac-GLOGE), can also be synthesized in a cyclic form with and without proline (cyclic GLNGE or cyclic PGLNGE and cyclic GLOGE or cyclic PGLOGE )synthesis. Table 1 lists the names of all peptides used i...
Embodiment 2
[0180] Example 2: Effect of cyclic and amidated linear peptides with proline on chemically induced liver fibrosis in mice.
[0181] Inject mice with CCl 4 6 weeks to induce liver fibrosis. Starting on day 32, mice received daily intraperitoneal injections of the peptide at a final dose of 25 mg / kg / mouse / day (diluted in 0.9% NaCl) for 10 days. In these experiments, the following peptides were tested: cyclic peptide Pro-Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu, cyclic peptide Pro-Gly-Leu-Asn-Gly-Glu, cyclic peptide Pro-Gly-Leu-Hyp-Gly- Glu, linear peptide Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu-NH 2 , linear peptide Gly-Leu-Asn-Gly-Glu-NH 2 , linear peptide Gly-Leu-Hyp-Gly-Glu-NH 2 .
[0182] The results showed that using CCl 4 Treatment with Glycine significantly induced collagen production (a marker of matrix accumulation) in the liver, and the cyclic peptide Pro-Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu was able to significantly reduce collagen accumulation. Linear peptide GLQGE-NH 2 Also able to significantly reduce CCl 4 In...
Embodiment 3
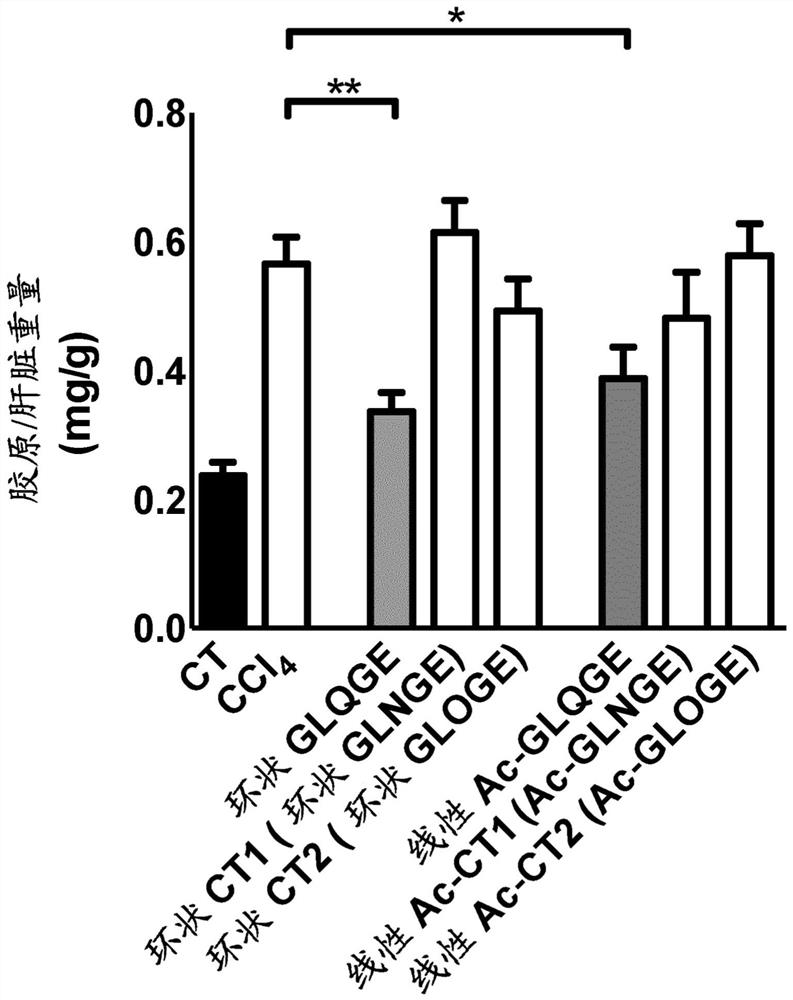
[0183] Example 3: Effects of cyclic peptides (without proline) and acetylated linear peptides on chemically induced liver fibrosis in mice use.
[0184] Inject mice with CCl 4 6 weeks to induce liver fibrosis. Starting on day 32, mice received daily intraperitoneal injections of the peptide at a final dose of 25 mg / kg / mouse / day (diluted in 0.9% NaCl) for 10 days. In these experiments, the following peptides were tested: cyclic peptide Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu, cyclic peptide Gly-Leu-Asn-Gly-Glu, cyclic peptide Gly-Leu-Hyp-Gly-Glu, linear peptide Ac- Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu, linear peptide Ac-Gly-Leu-Asn-Gly-Glu, linear peptide Ac-Gly-Leu-Hyp-Gly-Glu.
[0185] The results showed that using CCl 4 Treatment with ® significantly induced collagen production (a marker of matrix accumulation) in the liver, and the cyclic peptide Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu was able to significantly reduce collagen accumulation. In addition, the linear peptide Ac-Gly-Leu-Gln-Gly-Glu was able to significantly ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com