Method for planting under-forest konjak in sunshade net-circle planting mode
A technology of sunshade net and konjac, which is applied in the field of crop cultivation, can solve problems affecting production efficiency, lack of artificial labor, economic loss of taro farmers, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing large-scale outbreaks, promoting better health, and reducing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Interplanting konjac under walnut forest
[0023] Konjac is planted under fruit forests with low tree shape and dense branches and leaves, such as walnut trees and chestnut trees. Low forests often cause poor ventilation and air permeability between konjac rows, causing local high temperature or long-term excessive humidity, which induces konjac root rot or The occurrence of stem rot, etc. In addition, due to diseases, inadequate manual management, and bird pecking, fruit drop usually occurs at the end of July or early August. Move between the lines, and then cause further damage to the konjac. Therefore, the present embodiment provides a kind of method that utilizes sunshade net-circle planting mode to plant konjac under a kind of walnut forest.
[0024] (1) The plot is located under the walnut forest at an altitude of 980 meters in the mountainous area of southern Shaanxi. It is a gentle slope land with loose soil and rich organic matter. Animals in this area are...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Same as Example 1, the only difference is that in the present embodiment, during the planting process, the crown crown width of the control tree is 2.3-2.5m; the ridge width is 80cm, the ridge height is 15cm, and the ditch width is 20cm. 3 rows of commercial taro are planted in each ridge, and the plant The line spacing is 25cm*40cm. The height of the traveler from the ground is set to 0.4m, the number of turns of the traveler is 4, and the distance between the traveler is 10cm; the shading degree of the sunshade net is 40-45%, and the height of the sunshade net from the ground is 2.2- 2.5m.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Same as Example 1, the only difference is that in the present embodiment, during the planting process, the crown width of the control tree is 2.4-2.6m; the ridge width is 90cm, the ridge height is 17cm, and the ditch width is 24cm. 4 rows of commercial taro are planted in each ridge. The line spacing is 20cm*40cm. The height of the traveler from the ground is set to 0.7m, the number of turns of the traveler is 6, and the distance between the traveler is 12cm; the shading degree of the sunshade net is 45-50%, and the height of the sunshade net from the ground is 2.3- 2.4m.
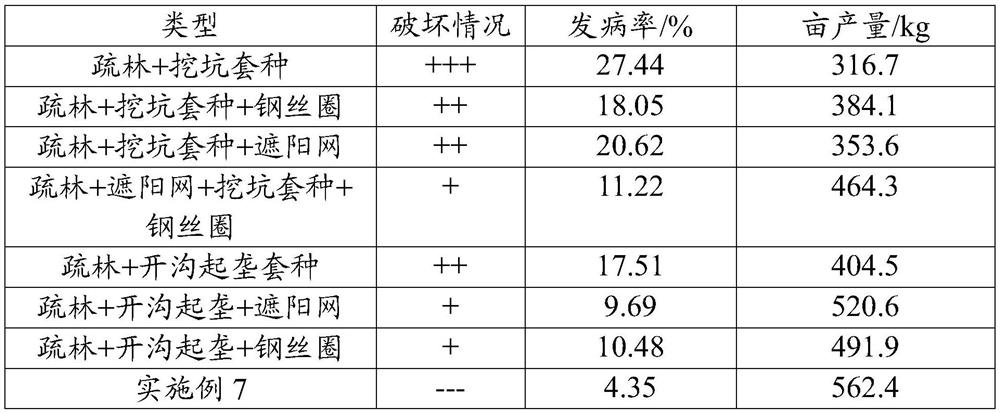
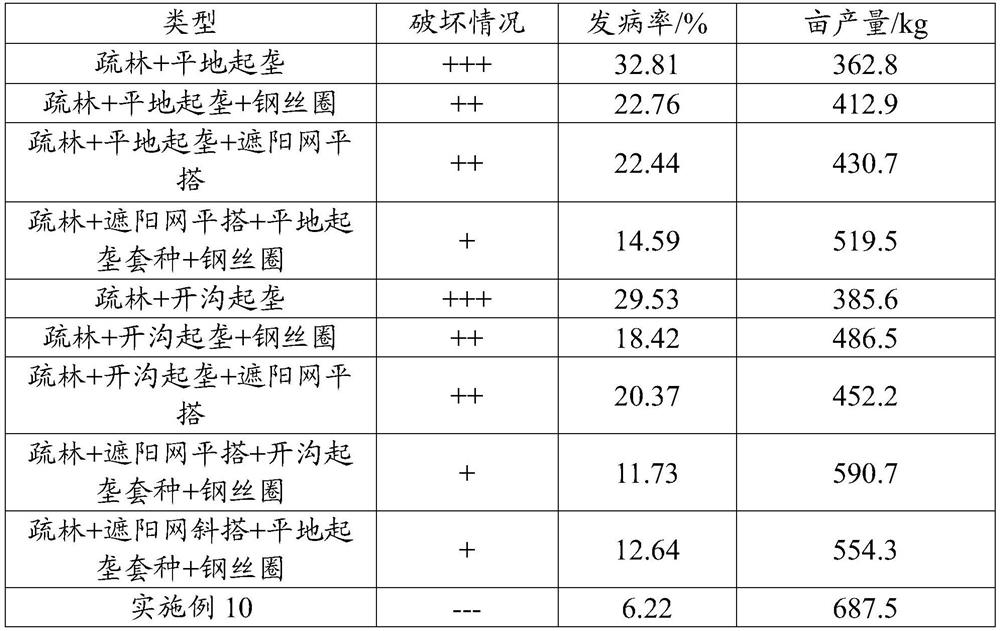
[0036] Table 1 Comparison of disease incidence and yield of commercial varieties of taro
[0037] Types of damage Incidence rate / % Yield per mu / kg direct interplanting +++ 27.63 1116.3 Direct interplanting + steel traveler ++ 21.16 1277.5 Interplanting after sparse forest +++ 30.75 1043.2 Sparse forest + traveler ++ 23.41 1230.4 Sparse forest + sha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height above ground | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height above ground | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height above ground | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com