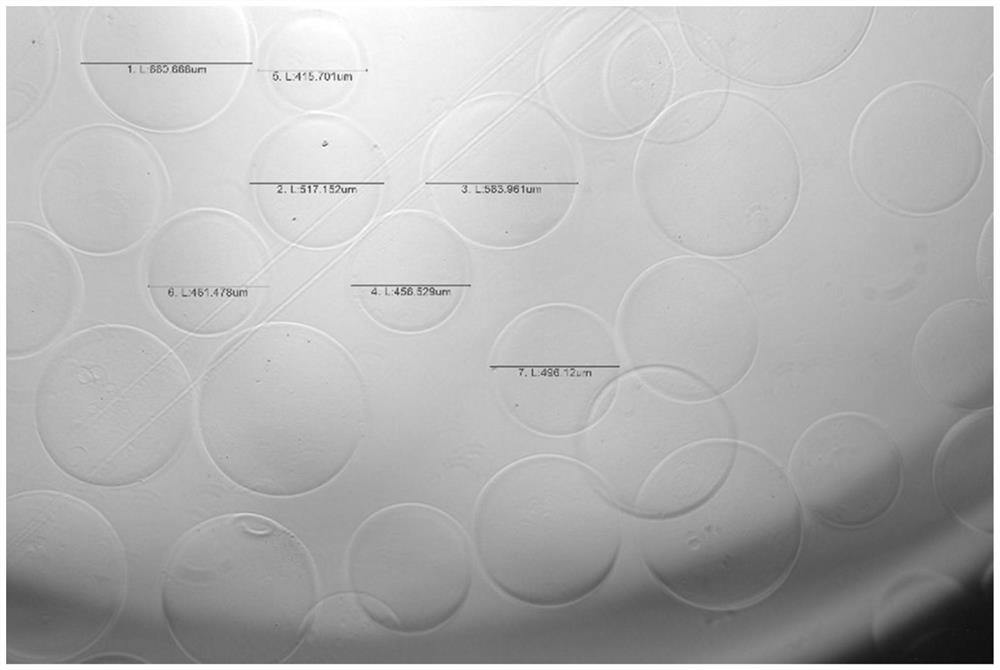
X-ray developable molecule, embolism microsphere and preparation method of X-ray developable molecule
An X-ray and molecular technology, applied in the fields of X-ray developable molecules, embolizing microspheres and their preparation, can solve problems such as harsh conditions, and achieve the effects of short reaction time, high yield, and easy intraoperative operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
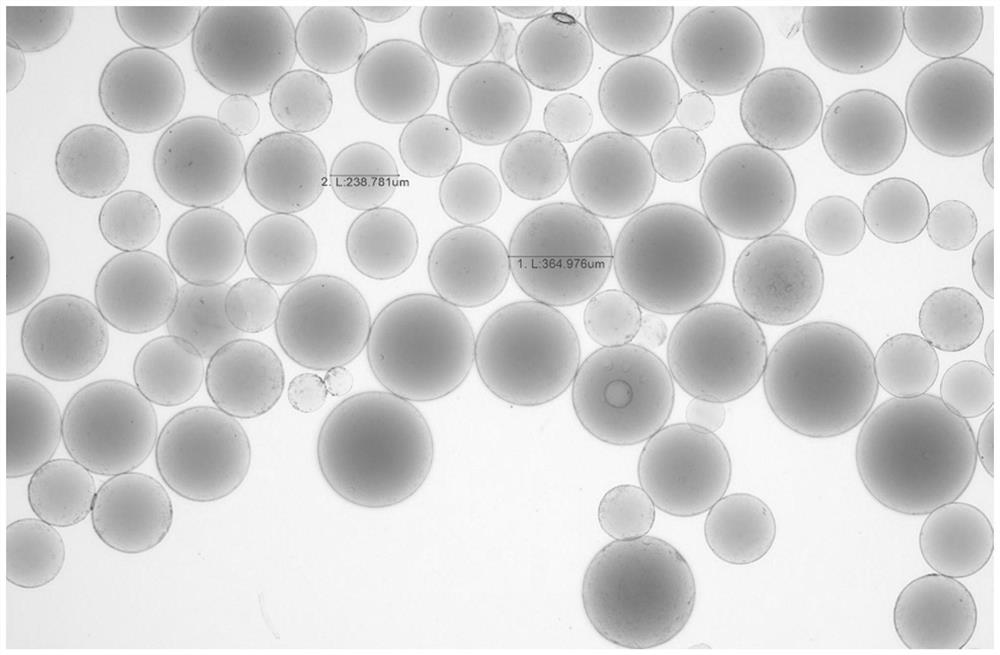
[0058] Preparation Example 1 Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol embolization microspheres:
[0059] S1. Add 10 g of polyvinyl alcohol with a weight average molecular weight of 67,000 into 100 mL of purified water, and dissolve completely at 90° C. Add 5g of N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-2-acrylamide and 42mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and react at 30°C for 8h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 7 with sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 2200 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0060] S2. 15g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate, 3g of 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid sodium salt and 0.75g of potassium persulfate were completely dissolved in 5mL of deionized water. Add 219 mL of butyl acetate and 1.5 g of cellulose acetate butyrate, and finally add 0.75 g of tetramethylethylenediamine under a nitrogen atmosphere, and react at 65° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, fil...
preparation example 3
[0064] Preparation Example 3 Preparation of sodium alginate embolization microspheres:
[0065] S1. Add 10 g of sodium alginate with a weight average molecular weight of 200,000 into 100 mL of purified water, and dissolve completely at 90° C. Add 2g of N-acrylamidoacetaldehyde and 16mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and react at 20°C for 6h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 8 with sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 2000 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0066] S2. Dissolve 10 g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate, 1 g of potassium 3-sulfopropyl methacrylate and 0.2 g of ammonium persulfate in 10 mL of deionized water. Then add 63.2mL cyclohexane and 0.5g Tween 20, finally add 0.2g N,N-dimethylaniline under nitrogen atmosphere, and react at 60°C for 4h. After the reaction, filter and wash with ethyl acetate, acetone and deionized water to obtain calcium alginate ...
preparation example 5
[0070] Preparation Example 5 Preparation of Sodium Hyaluronate Microspheres:
[0071] S1. Take 20g of hyaluronic acid sodium salt with a weight average molecular weight of 140,000, add it to 50g of water, heat to 80°C, stir for 2h, add 0.4g of N-(2,2-dimethoxyethyl)-2-acrylamide With 8mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, react at 35°C for 3h. After the reaction, the pH of the reaction system was adjusted to 7.3 with sodium hydroxide solution. Finally, the solution was concentrated to a viscosity equal to 2000 cps to obtain a microsphere intermediate.
[0072] S2. Dissolve 20 g of the above-mentioned microsphere intermediate, 1.5 g of sodium acrylate and 0.2 g of sodium persulfate in 10 mL of deionized water. Add 180 mL of butyl acetate and 1.68 g of Span 20, and finally add 0.32 mL of triethylamine under an inert gas atmosphere, and react at 65° C. for 6 h. After the reaction, filter and wash with ethyl acetate, acetone and deionized water to obtain hyaluronic acid microsp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com