Application of molecular marker based on TYRP1 gene in giant salamander body color breeding
A technology of molecular markers and genes, which is applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of less research on molecular genetics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
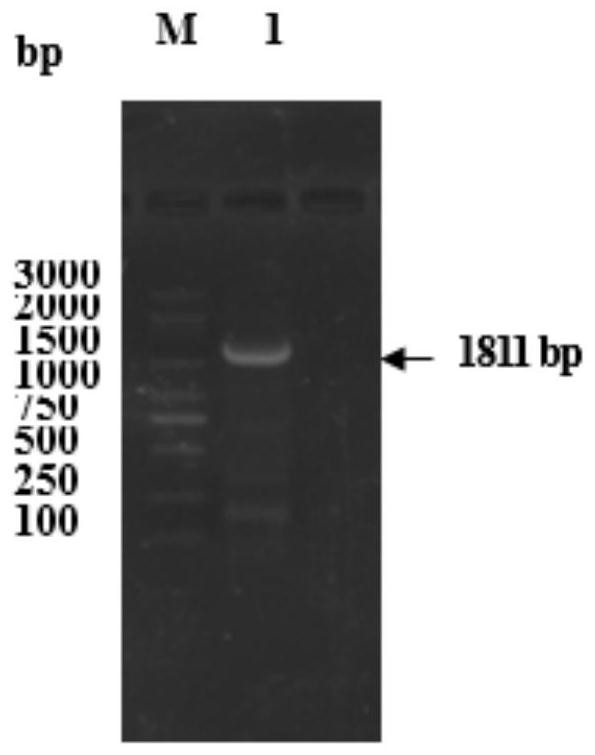
[0075] TYRP1 gene cloning and sequencing
[0076] 1> RNA extraction
[0077] The RNeasy Mini kit was used to extract total RNA from giant salamander skin tissue, and all precautions for RNA manipulation were strictly followed throughout the process. Unless otherwise specified, all steps were performed at room temperature.
[0078] 2> cDNA first strand synthesis
[0079] Total RNA was reverse transcribed using the RevertAid cDNA Synthesize Kit. Unless otherwise specified, the following steps are performed on ice.
[0080] (1) In an RNase-Free 0.5 μL centrifuge tube, add 2 μg (2-4 μL) of total RNA, 1 μL of oligoDT(18) primer, and add DEPC-treated water to 12 μL.
[0081] (2) Incubate at 65°C for 5 minutes, cool on ice, and centrifuge briefly.
[0082] (3) Add the following components: 2 μL of 5× buffer, 1 μL of RNase inhibitor, 1 μL of 10 mM dNTP mix, and 1 μL of reverse transcriptase.
[0083] Instantaneous centrifugation, PCR reaction, the reaction program: 42 ° C, 60 mi...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Real-time quantitative fluorescent PCR analysis of TYRP1 gene expression in different tissues of giant salamander
[0148] 1>Total RNA extraction and reverse transcription
[0149] The Tizol one-step method was used to extract the total RNA from giant salamander muscle, skin, heart, liver, spleen, lung, stomach, pancreas, kidney, gonad (ovary / testis), and intestinal tissue, and reverse transcribed it into cDNA. The specific experimental steps were implemented in the same way. example 1.
[0150] 2>Primer design and synthesis
[0151] Using the CDS region sequence of the Chinese giant salamander TYRP1 gene sequenced, real-time fluorescent quantitative primers were designed using the online software PrimerQuest (http: / / sg.idtdna.com / Primerquest / Home / IndexPrimer). The relevant information is shown in Table 1. Primers were synthesized by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Company.
[0152] 3>Reaction system and conditions
[0153] The reaction system is: add 1 μL cDNA to e...
Embodiment 3
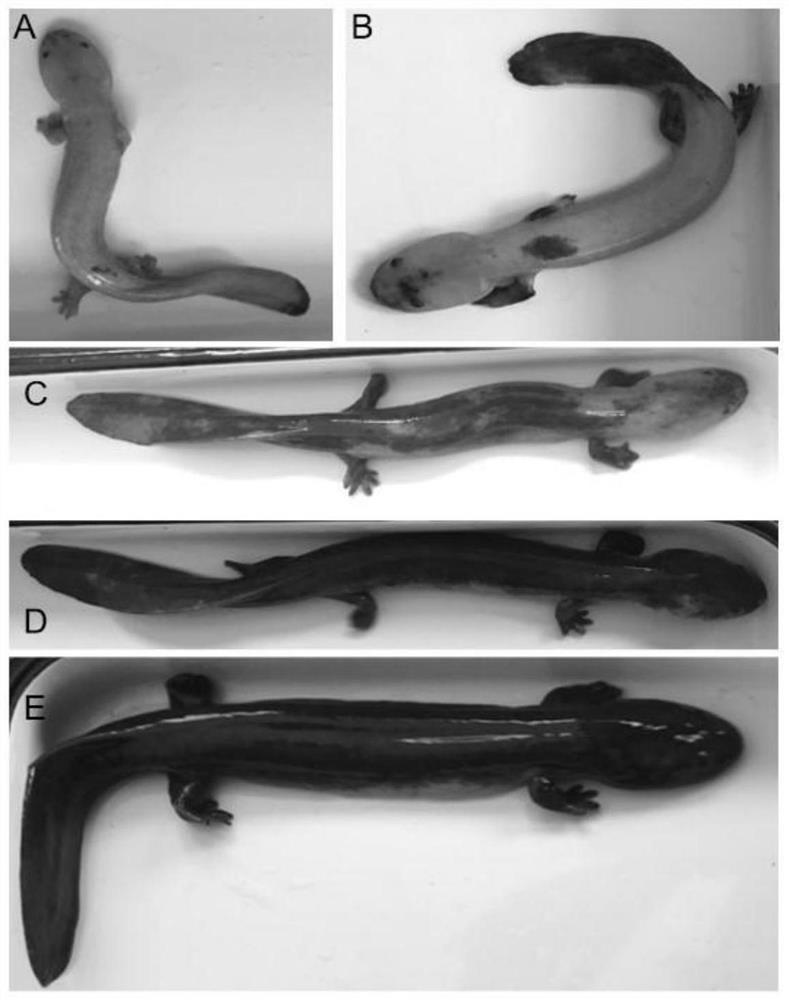
[0157] Real-time quantitative fluorescent PCR analysis of the expression of TYRP1 gene in the tail skin tissue of giant salamander with different body colors
[0158] 1>Total RNA extraction and reverse transcription
[0159] Tizol one-step method was used to extract total RNA from the tail skin tissues of giant salamanders with body colors YL, Y(B), B(Y), B(SY) and GY, and reverse transcribed it into cDNA. The specific experimental steps were the same as in Example 1.
[0160] 2>Primer design and synthesis
[0161] With embodiment 1.
[0162] 3>Reaction system and conditions
[0163] With embodiment 1.
[0164] 4> Test data analysis
[0165] With embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com