Early prediction system for predicting severity of acute pancreatitis patient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Establishing an Early Prediction System for Predicting the Probability of Acute Pancreatitis Patients Developing into Severe Acute Pancreatitis
[0053] The early prediction system of the present invention is a visual nomogram for predicting the probability of acute pancreatitis patients developing severe acute pancreatitis, and the construction method includes the following steps.
[0054] 1. Patient information
[0055] (1.1) Inclusion and exclusion criteria
[0056] Inclusion criteria: (1) clearly diagnosed AP, (2) aged from 18 to 80 years old, (3) from the onset of abdominal pain to hospital admission within 48 hours.
[0057] Exclusion criteria: chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic tumor, trauma or pregnancy as the etiology of AP, patients with serious systemic complications.
[0058] (1.2) Data source
[0059] Including the training queue, internal validation and external validation queues, as follows:
[0060] (1) Training cohort: A retrospective data s...
Embodiment 2
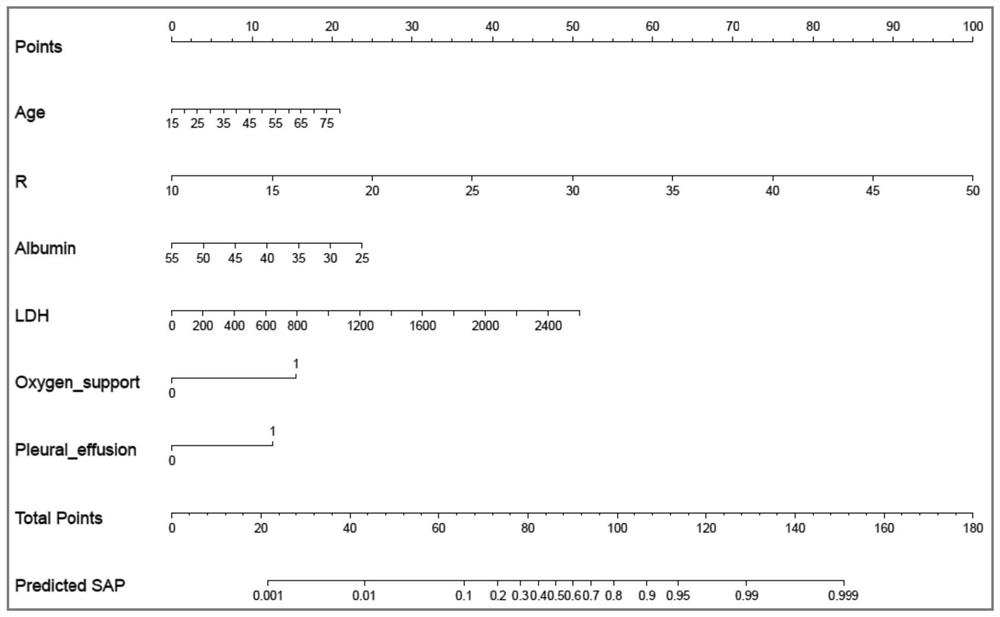
[0084] Embodiment 2 Nomogram Visualization Webpage Calculator
[0085] Based on the calculation formula of the nomogram obtained in Example 3, make a webpage calculator for predicting the occurrence of POF in AP patients when calculating admission, and input 6 independent prognostic factors (age, respiratory rate, albumin, lactate dehydrogenation) of the patient to be predicted. After enzyme LDH, oxygen support and pleural effusion), the corresponding predicted probability value can be automatically output.
[0086] Figure 4 For example: a 47-year-old patient had a respiratory rate (R) of 20 breaths / minute, albumin (Albumin) 43IU / L, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 257IU / L, and oxygen on admission. With supportive treatment but no pleural effusion, the probability of developing severe AP is 9.7%.
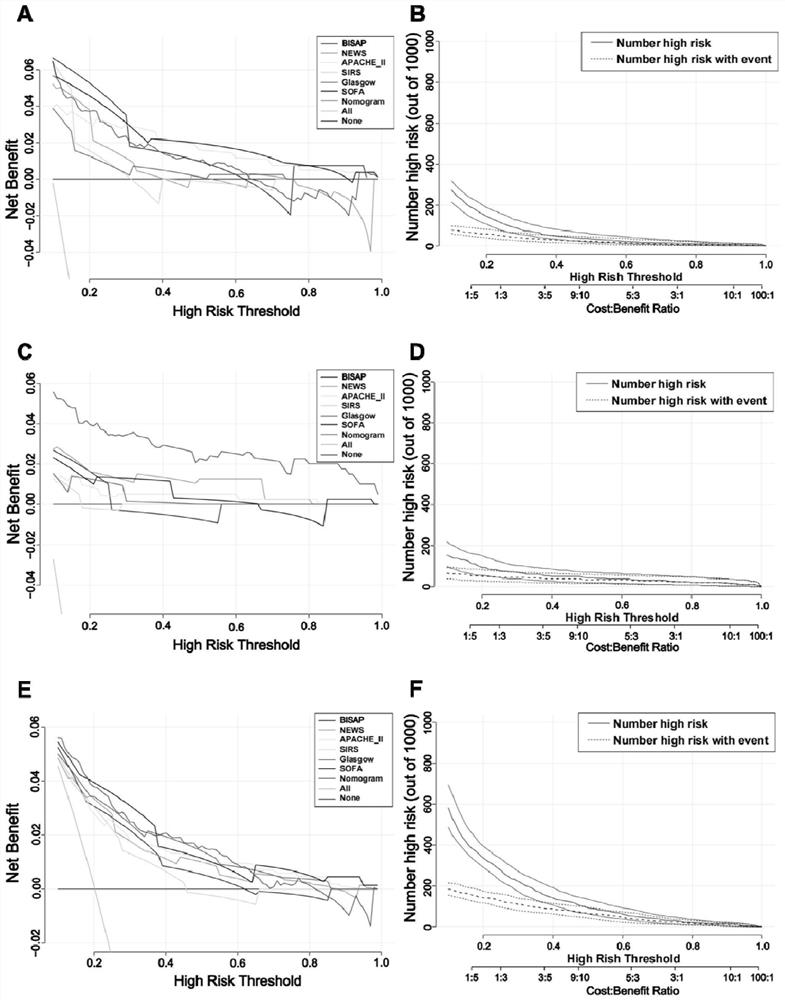
[0087] The prediction effect of the prediction system of the present invention is demonstrated through the following experimental examples.
experiment example 1
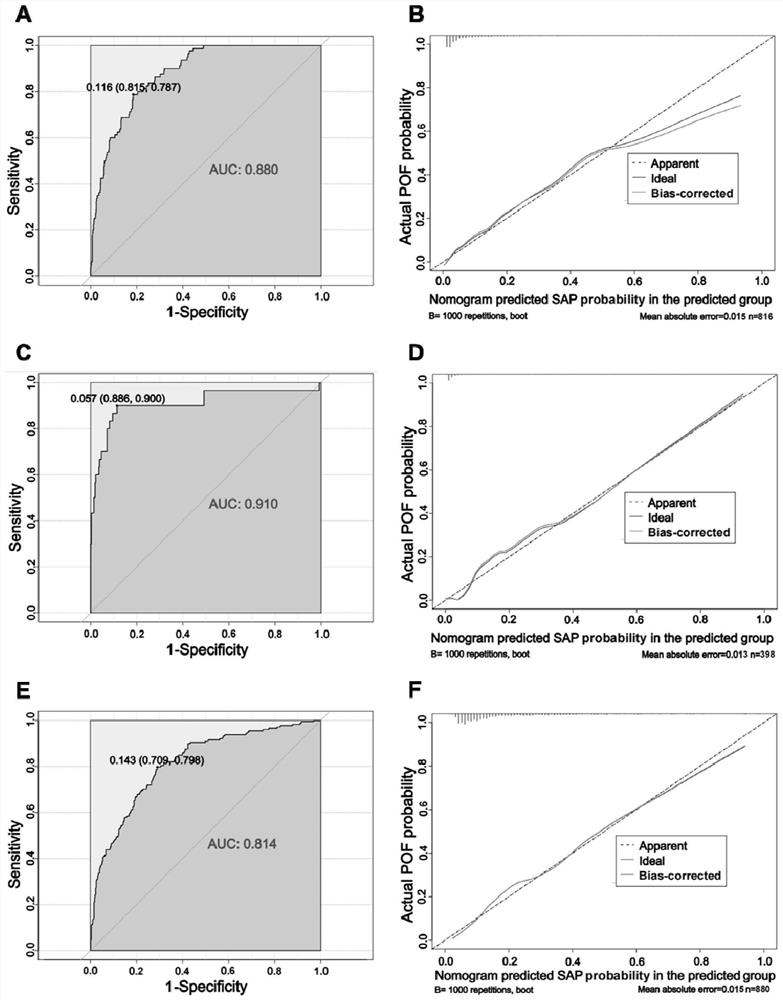
[0088] Experimental Example 1 Discrimination and Calibration Verification
[0089] 1. Experimental method
[0090] (1) Validation model discrimination: evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), also called the C index. The larger the AUC, the better the discrimination ability of the prediction model.
[0091] (2) Verify the calibration of the model: draw a calibration curve, and the closeness of the data points to the solid red line in the figure reflects the calibration of the model.
[0092] 2. Experimental results
[0093] In the training cohort, the C index of the nomogram was 0.88 ( figure 2 A), the calibration curve for predicting severe AP ( figure 2 B) Shows good agreement with actual occurrence of POF. In the internal validation cohort, compared with the training cohort, the C-index of the nomogram for predicting severe AP reached 0.91 ( figure 2 C) and has better consistency ( figure 2 D). The C-index in the external v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com