Vernier permanent magnet motor with transversely staggered stator modulation teeth
A lateral dislocation, permanent magnet motor technology, applied in the direction of motor, magnetic circuit, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of low space utilization, high power density, high torque, etc., to reduce copper consumption and high torque density , the effect of improving torque density and power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
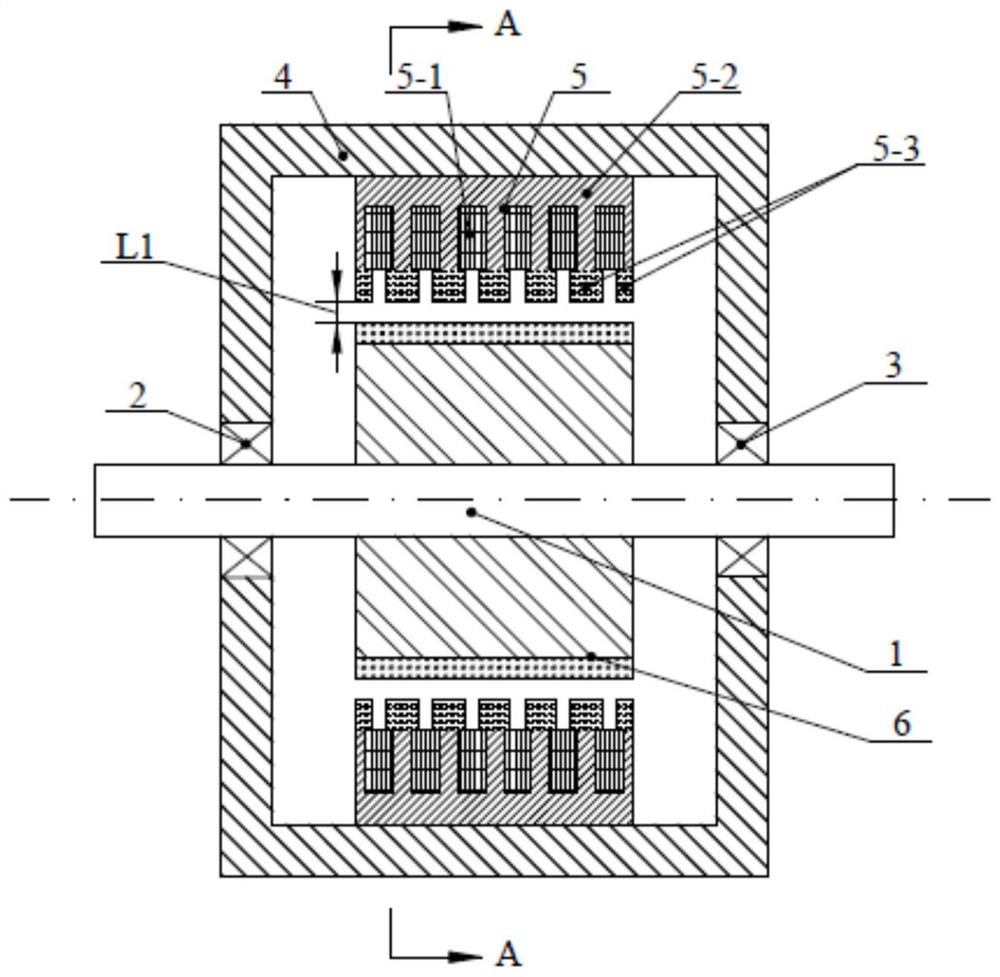
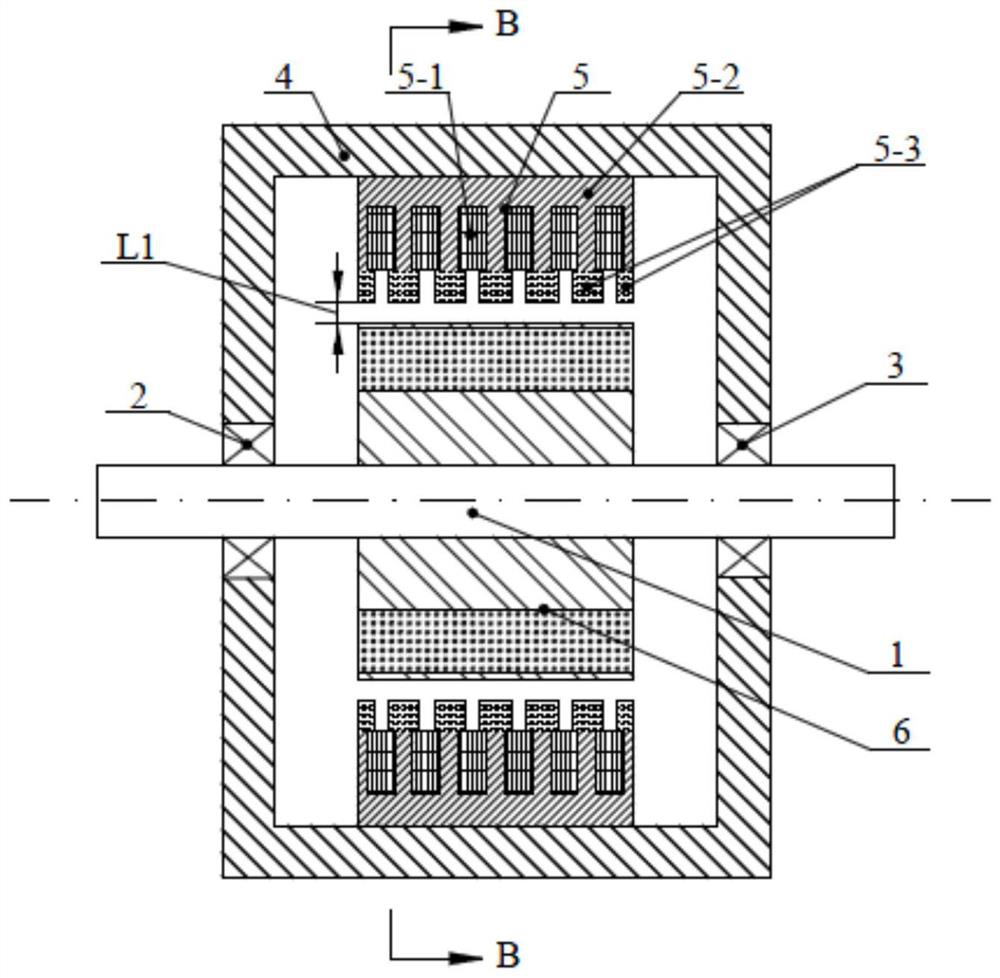
[0043] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 13 and Figure 14 Describe this embodiment mode, a kind of vernier permanent magnet motor of stator modulating tooth lateral dislocation described in this embodiment mode, it comprises casing 4, stator 5, permanent magnet rotor 6, permanent magnet rotor output shaft 1; Stator 5 is fixed on casing On the inner circle surface of 4, the permanent magnet rotor 6 is fixed on the output shaft 1 of the permanent magnet rotor, and is rotationally connected with the side end cover of the casing 4 through bearings 2 and 3.
[0044] The slots of the stator 5 are arranged in the form of semi-closed slots along the axial direction with equal tooth widths, the tooth widths of the two ends are 1 / 2 of the middle tooth width, and the slots of the semi-closed slots of the stator core 5-2 face the permanent magnet rotor 6. The ring winding 5-1 is embedded in the semi-closed slot; the ring winding...
specific Embodiment approach 2
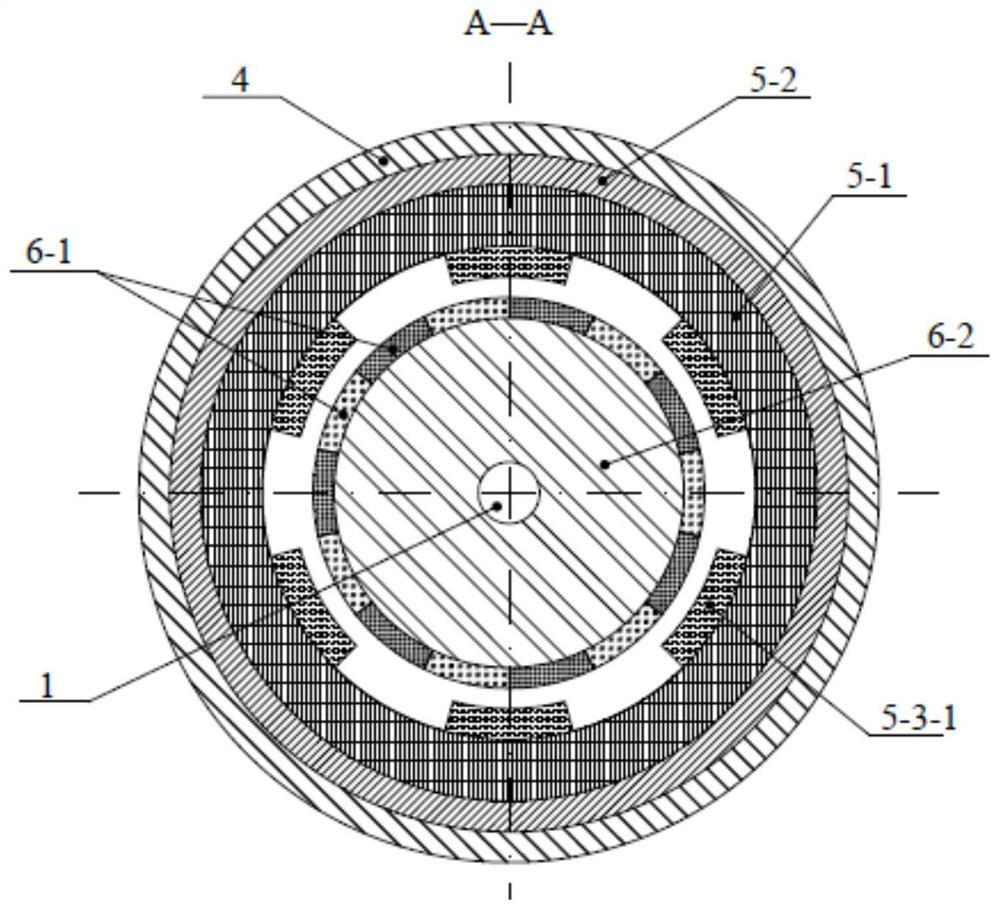
[0087] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that n×2p PM A permanent magnet 6-1 is embedded in the permanent magnet rotor core 6-2, the cross section of the permanent magnet 6-1 is rectangular, n×2p PM The permanent magnets 6-1 are radially distributed inside the permanent magnet rotor core 6-2 with the permanent magnet rotor output shaft 1 as the center, and the magnetization direction of the permanent magnets 6-1 is tangential parallel magnetization.
[0088] In this embodiment, the permanent magnet rotor belongs to the magnetic accumulation structure. Under the parallel action of the adjacent permanent magnets of the permanent magnet rotor, it has a prominent effect on increasing the air gap magnetic density, thereby increasing the no-load back electromotive force and electromagnetic torque of the motor.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0089] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination Figure 5 and Figure 6 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that n×2p PM A permanent magnet 6-1 is embedded in the permanent magnet rotor core 6-2, the cross section of the permanent magnet 6-1 is rectangular, the magnetization direction of the permanent magnet 6-1 is parallel magnetization, and the magnetic force line passing through the midpoint is a Towards.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com