Iron core punching sheet for outer rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor punching technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuits, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low torque density and power density, low cogging torque, low reluctance torque, etc. Achieve the effect of high torque density and power density, large reluctance torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
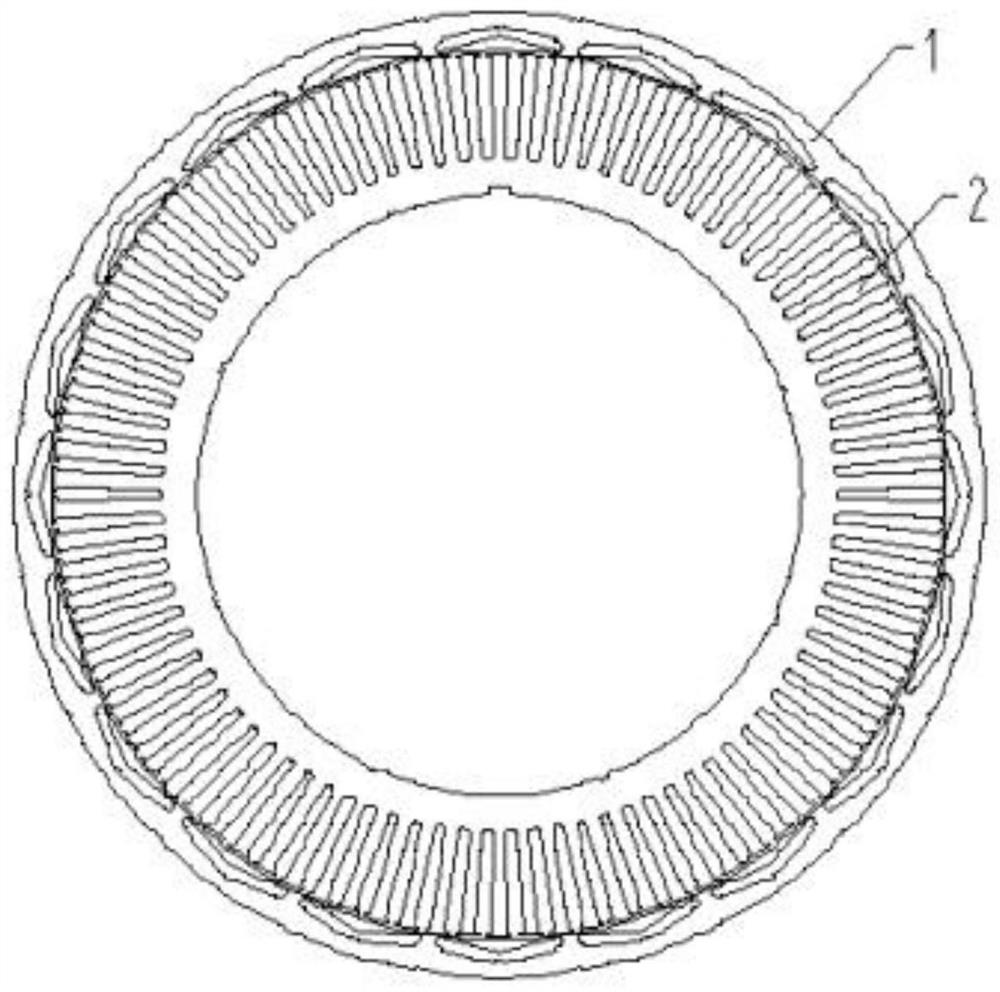
[0037] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, an iron core punch for an outer rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor includes a stator punch 2 and a rotor punch 1 that cooperate with each other, and both the stator punch 2 and the rotor punch 1 are annular, The outer diameter of the rotor punching sheet 1 is larger than that of the stator punching sheet 2, and the body of the rotor punching sheet 1 is uniformly opened with V-shaped grooves 11 along the circumferential direction;
[0038] like Image 6 As shown, the opening of the V-shaped groove 11 is along the inner diameter direction, and is used to place the permanent magnet 3;
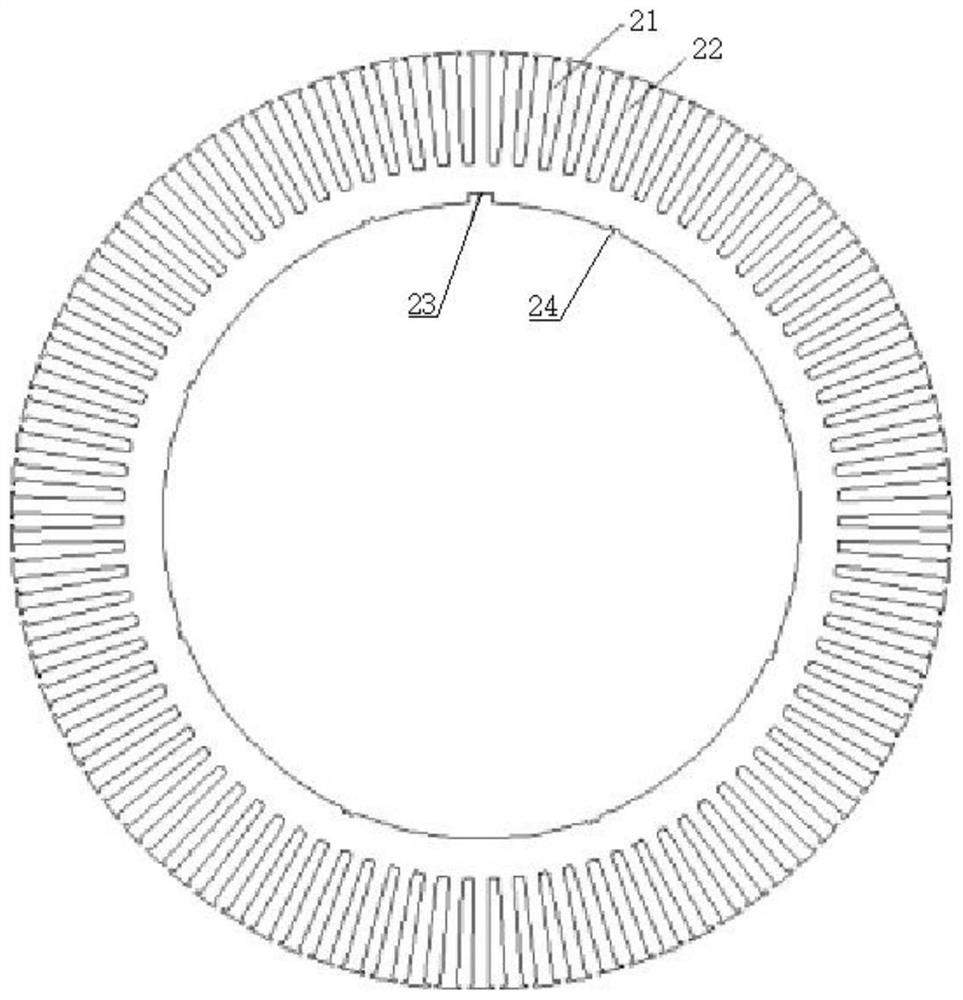
[0039] like image 3 As shown, the stator punching piece 2 is evenly provided with radial opening slots 21 along the outer diameter and circumferential direction; the calculated pole arc coefficient of the rotor punching piece 1 is 0.65-0.7;
[0040] like Figure 4 As shown, auxiliary grooves 12 are distributed on the inner diameter and circumf...
Embodiment 2
[0043] This embodiment is an iron core punching sheet for an outer rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor. The main components are composed of a stator iron core and a rotor iron core. They are both punched and punched from silicon steel sheets and then laminated, such as figure 1 and Image 6 As shown, it is used for a permanent magnet synchronous motor in which the permanent magnet 3 is placed inside the rotor core of the motor;
[0044] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, including the stator punch 2 and the rotor punch 1 that cooperate with each other, the two parts are used together in pairs and cannot be used alone;
[0045] like figure 2 and image 3 As shown in the figure, both the stator punch 2 and the rotor punch 1 are annular, the outer diameter of the rotor punch 1 is larger than that of the stator punch 2, and the body of the rotor punch 1 is uniform in the circumferential direction A V-shaped groove 11 is opened, the opening of the V-shaped groove 11 is ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The difference between this embodiment and the above-mentioned Embodiment 2 is that the calculated pole arc coefficient of the rotor punch 1 is 0.7, the depth H from the bottom of the auxiliary groove 12 to the inner diameter circumference of the rotor punch 1 is 0.4 mm, and α =5.2°, the outer diameter of the rotor punch 1 is 480 mm, the annular width of the rotor punch 1 is 20 mm, and the gap between the inner diameter of the rotor punch 1 and the outer diameter of the stator punch 2 is 1.5 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com