Multi-network auxiliary positioning method for distributed large-scale multi-antenna system
A multi-antenna system and assisted positioning technology, which is applied in the fields of positioning, machine learning, and wireless communication, can solve the problems of positioning results deviating from accurate values, high data measurement costs, and unfavorable practical applications, and achieve cost reduction, high positioning accuracy, and improved adaptive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
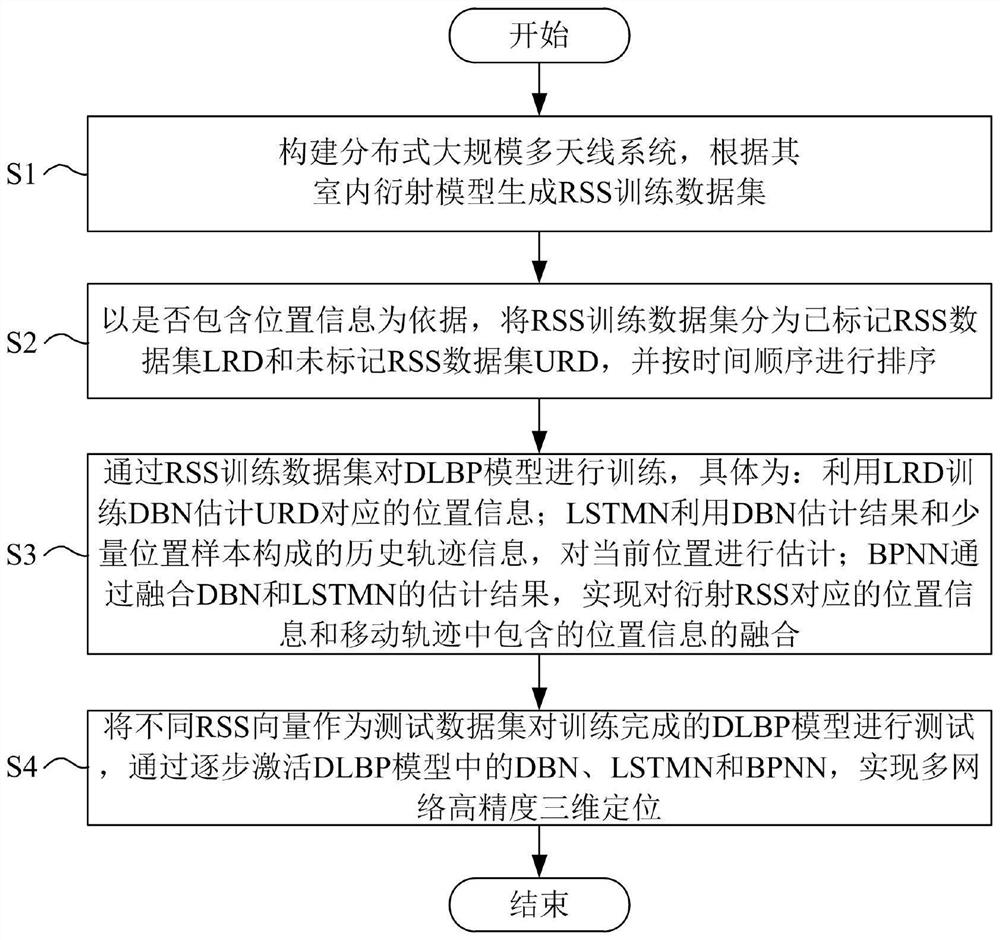
[0036] The present invention relates to the field of wireless communication, positioning, and machine learning, including multi-input Multiple-InputMultiPle-Output, MIMO, based on receive signal strength (RSS), depth confidence neural network (Deep BeliefNetworks) , DBN), Long-Shortterm Memory Networks, LSTMN, Back Propagationneural Networks, BPNN, etc. More specifically, a multi-network aided positioning method for distributed large-scale multi-antenna systems, such as figure 1 As shown, including the following steps:
[0037] S1: Build a distributed large-scale multi-antenna system, generate RSS training data set according to its indoor diffraction model;
[0038] S2: Whether to include location information, divide the RSS training data set into the labeled RSS dataset LRD and unmarked RSS dataset URD, and sort in chronological order;
[0039] S3: Training the DLBP model through the RSS training data set, specifically:
[0040] Utilizing the position information corresponding to...
Embodiment 2
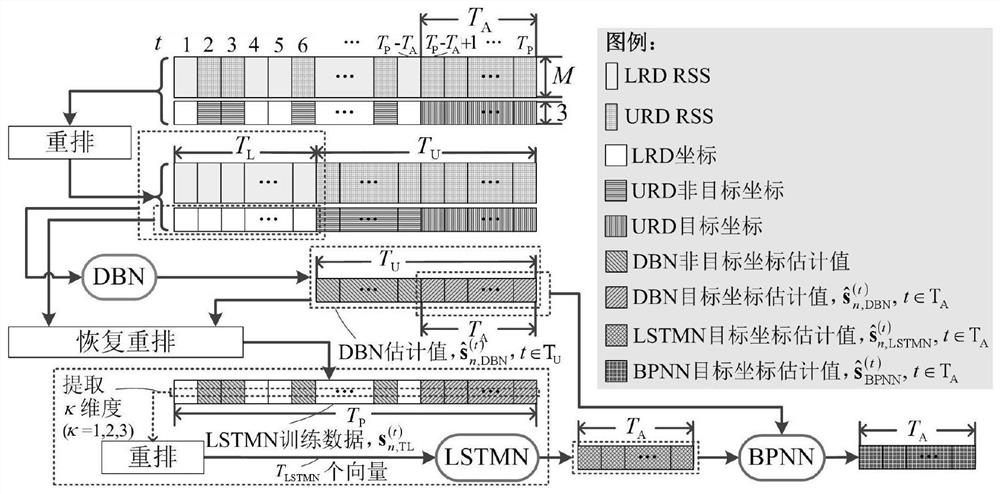
[0049] (1) RSS training data generation process based on diffraction model
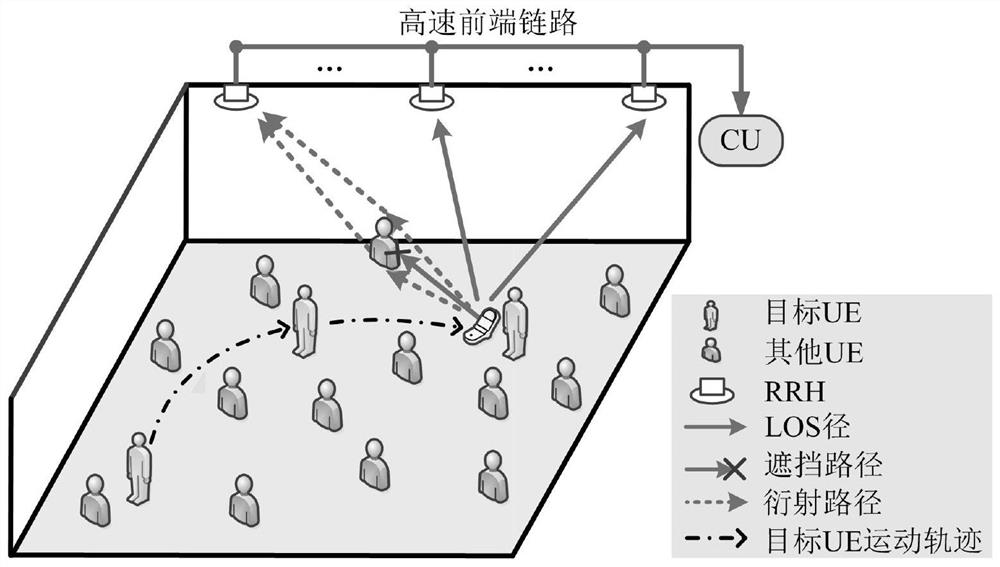
[0050] On the basis of Example 1, indoor positioning scenes such as image 3 As shown, in order to facilitate the presentation, in the step S1 of the present aspect, the same term "UE" is used to represent the device and the person using the device. There are M rRH and N UEs in the DM-MIMO system, each RRH or UE has 1 antenna. The UE moves in the random route and transmits the pilot signal to all RRH. The system proposed in this scenario is reasonably arranged by reasonably arranged the pilot, such as time division multiplexing, such as time division multiplexing, so that the pilots are kept orthogonal to eliminate multi-user interference. Do not losing generally, assume that in the time domain, each UE sends T P Time domain pilot training, the time interval between the two consecutive pilots of the same UE is T 0 . It is worth noting that image 3 As shown, since the dynamic topology of the UE, one UE tran...
Embodiment 3
[0178] More specifically, in order to further verify the beneficial effects of this program, such as Figure 8 As shown in the RRH number m = 20 as an example, two different antenna distributions are given, and the present solution demonstrates the performance of the DLBP method in different antenna distribution. Unless otherwise stated, the main simulation parameters are listed in Table 1, where M and P L The value may vary depending on the applicable simulation scenario. At the same time, traditional DBN-based positioning, DBNP, and BPNN-based Positioning, BPNNP) methods are used as comparative methods.
[0179] Table 1 Simulation Parameter Table
[0180]
[0181]
[0182] Figure 9 The positioning performance of different RRHs is shown, where the proportion of the LRD in all training data is set to P. L = 0.6. It can be observed that the DLBP method proposed in this program implements the lowest RMSE in all methods. Further, when M is increased, the positioning system perform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com