Method for extracting and separating flavonoid components in lindera aggregata leaves
A technology of black medicine leaves and ketones, which is applied in the field of separation and purification, can solve the problems of large solvent consumption, no extraction, separation and purification of chemical components, and reduced efficiency of the extraction, separation and purification process, and achieves good separation effect, less impurities, and purity. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Embodiment 1: the selection of adsorbent kind
[0076] In parallel, 30 mg of 4 parts of black herb leaf powder were weighed and added to 4 groups of agate mortars, and 30 mg of different adsorbents (Florida Sillica (Ningbo Hongpu Instrument Technology Co., Ltd.), molecular sieve SBA-15 (Nanjing Jicang Nanotechnology Co., Ltd.) Ltd.), Al 2 o 3 (Shanghai Anpu Experimental Technology Co., Ltd.), Sillica gel (Shanghai Anpu Experimental Technology Co., Ltd.), respectively added to 4 groups of mortars and grinded for 3 minutes with the powder of black leaves. Pass the ground solid mixture through the matrix solid-phase column (with a gasket), add 2mL of 70% ethanol for pressure elution, collect the eluate, concentrate, and finally add 1mL of methanol to dissolve, at a speed of 13000rpm Centrifuge for 5 minutes with a centrifuge, collect and centrifuge to obtain the supernatant, take the supernatant and put it into a sample bottle, and perform detection and analysis with a h...
Embodiment 2
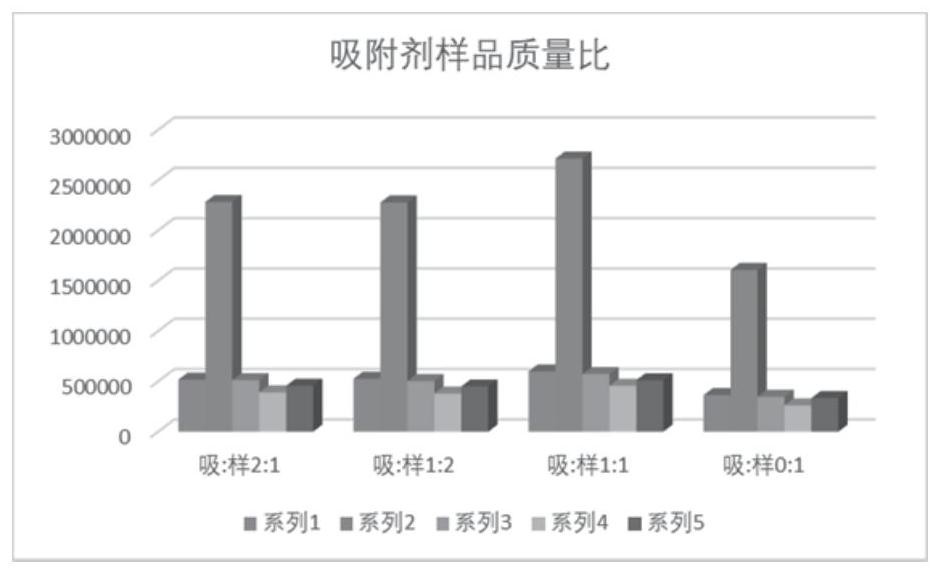
[0078] Embodiment 2: the selection of the mass ratio of sample and adsorbent
[0079] Weigh 30 mg of 4 parts of Aegina leaf powder in parallel, add them to 4 groups of agate mortars, and weigh silica gel with different masses (0 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg), add them into 4 groups of mortars and grind them 3min. Pass the ground solid mixture through the matrix solid-phase column (with a gasket), add 2mL of 70% ethanol for pressure elution, collect the eluate, concentrate, and finally add 1mL of methanol to dissolve, at a speed of 13000rpm Centrifuge for 5 minutes with a centrifuge, collect and centrifuge to obtain the supernatant, take the supernatant and put it into a sample bottle, and perform detection and analysis with a high-performance liquid chromatograph.
[0080] The extraction effects of different mass ratios of sample to adsorbent are as follows: Figure 2b As shown, the results show that the extraction efficiency of the target analyte increases gradually when the mas...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3: Elution solvent type selection
[0082] Weigh in parallel 6 parts of 30 mg of black herb leaf powder and 6 parts of 30 mg of silica gel, add them into two groups of agate mortars, and grind them for 3 minutes respectively. The ground solid mixture is passed through the matrix solid-phase small column (pad), add 2mL of ethanol, 70% ethanol, methanol, 50% methanol, 70% methanol, 90% methanol, preferably 70% ethanol eluent, add The eluate was collected and concentrated, and finally 1 mL of 70% methanol was added to dissolve it, centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min, collected and centrifuged to obtain the supernatant, and the supernatant was put into a sample bottle and used High-performance liquid chromatography for detection and analysis.
[0083] The extraction effects of different elution solvent types are as follows: Figure 2c Shown, result shows, 70% ethanol is higher than methanol, 50% methanol, 70% methanol, 90% methanol, ethanol, preferably 70% etha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com