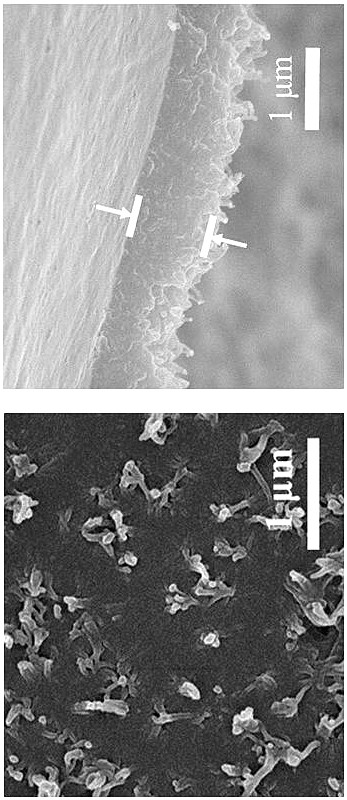
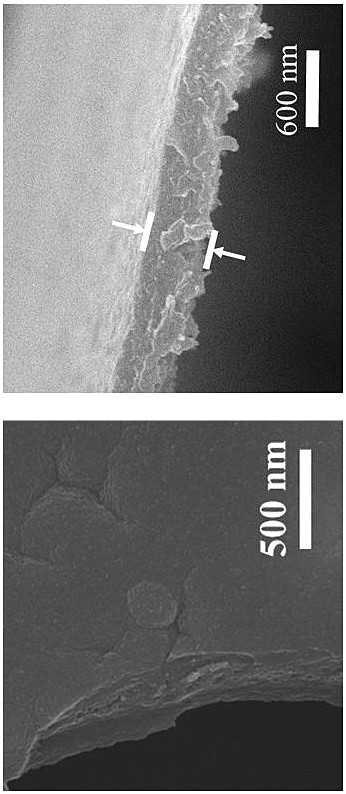
Method for preparing high-crystallinity covalent organic framework film by using ionic liquid-water interface
A covalent organic framework, ionic liquid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve the problems of interface disturbance, environmental pollution, volatile, etc. The effect of improving film quality and crystallinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034]Dissolve 16.8 mg of aldehyde monomer mesityl in 20 mL of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide ionic liquid to obtain solution A, the concentration of mesityraldehyde in solution A is 5 mM; 18.4 mg of the amine monomer benzidine and 38 mg of the acid catalyst p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) were dissolved in 20 mL of deionized water to obtain solution B, and the concentration of benzidine in solution B was 5 mM. Afterwards, 2 mL of solution A was transferred to a 15 mL reactor, and 4 mL of deionized water was added on the surface of solution A, the layers were separated, and then 2.6 mL of solution B was slowly added to the surface of the deionized water layer within 2 min. In the upper part, the reactor was reacted at room temperature for 3 days, and the double-diffusion control mechanism of the acidic catalyst and the hydrogen bond between the amine monomer and the high viscosity of the ionic liquid simultaneously limited the diffusion rate of the two m...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Dissolve 16.8 mg of aldehyde monomer mesityl in 20 mL of 1-octyl-3-methylimidazole bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide ionic liquid to obtain solution A, the concentration of mesityraldehyde in solution A is 5 mM; 18.4 mg of the amine monomer benzidine and 38 mg of the acid catalyst p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) were dissolved in 20 mL of deionized water to obtain solution B, and the concentration of benzidine in solution B was 5 mM. Afterwards, 2 mL of solution A was transferred to a 15 mL reactor, and 4 mL of deionized water was added on the surface of solution A, the layers were separated, and then 2.6 mL of solution B was slowly added to the surface of the deionized water layer within 2 min. In the upper part, the reactor was reacted at room temperature for 4 days, and the synthesis of copolyester was synthesized by utilizing the hydrogen bond interaction between the acidic catalyst and the amine monomer and the high viscosity of the ionic liquid itself to limit the diffu...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Dissolve 16.8 mg of aldehyde monomer mesityl in 20 mL of 1-decyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonimide ionic liquid to obtain solution A, the concentration of mesityraldehyde in solution A is 5 mM; 18.4 mg of the amine monomer benzidine and 38 mg of the acid catalyst p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) were dissolved in 20 mL of deionized water to obtain solution B, and the concentration of benzidine in solution B was 5 mM. Afterwards, 2 mL of solution A was transferred to a 15 mL reactor, and 4 mL of deionized water was added on the surface of solution A, the layers were separated, and then 2.6 mL of solution B was slowly added to the surface of the deionized water layer within 2 min. In the upper part, the reactor was reacted at room temperature for 5 days, and the double-diffusion control mechanism of the hydrogen bond between the acidic catalyst and the amine monomer and the high viscosity of the ionic liquid itself simultaneously limited the diffusion rate of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com