Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on FeS2/C/MQDs/GCE modified electrode and preparation method thereof
A technology for modifying electrodes and molecular imprinting, applied in scientific instruments, material analysis through electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex and expensive detection methods, and achieve the effect of wide practical application prospects and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] FeS 2 Preparation of / C / MQDs / GCE Modified Electrode
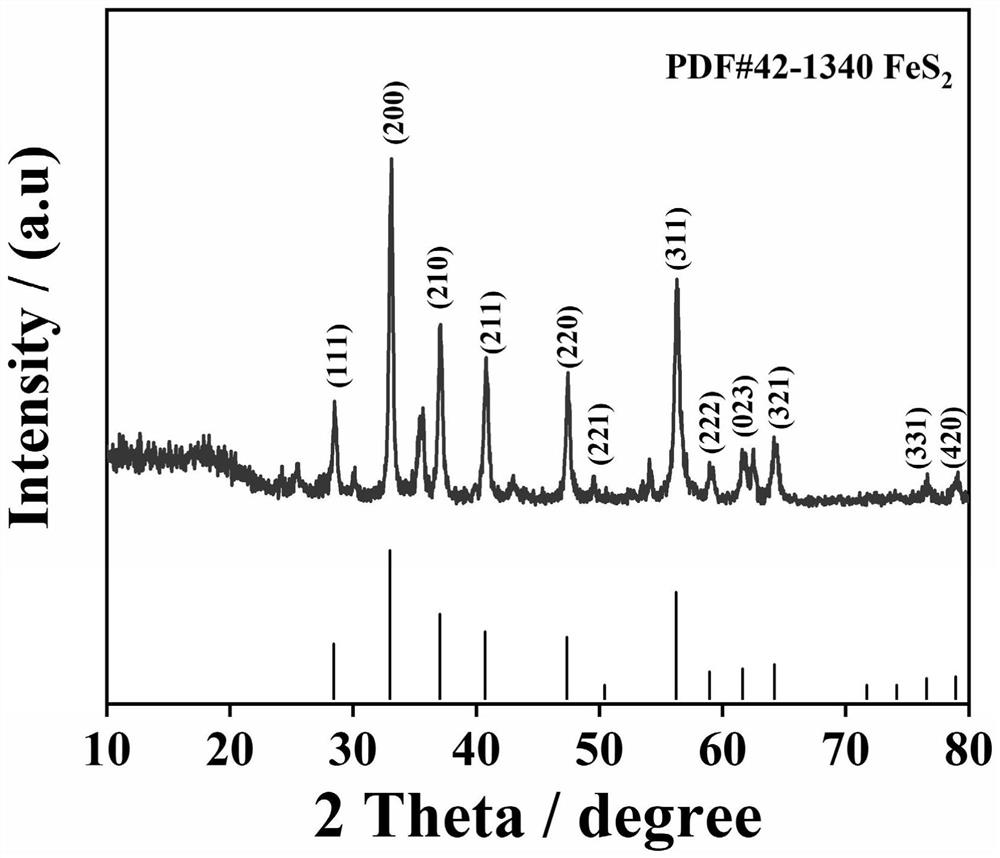
[0042] FeS 2 / C and MQDs were synthesized according to the reported literature. Thereafter, 2mg of MQDs and 2mg of FeS 2 / C were dispersed in 1 mL of 0.2% chitosan-acetic acid solution (CS). 1.5 μL of MQDs solution was dropped onto the GCE and dried at 60 °C. Then add 7.5 μL of FeS 2 / C solution was dropped onto the obtained MQDs / GCE and dried at 60 °C to obtain FeS 2 / C / MQDs / GCE modified electrodes.
[0043] Based on FeS 2 Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors Using / C / MQDs / GCE Modified Electrodes
[0044] The modified electrode (FeS 2 / C / MQDs / GCE) were immersed in 0.01M phosphate buffer (PBS, pH 3.5) containing 1mM DIP, 1mM QS and 3mMβ-CD as functional monomers, and then the modified electrode was immersed in it, and the three-electrode system CV electrode Polymerized to FeS 2 / C / MQDs / MIP / GCE. The electropolymerization potential range is -0.1-0.9V, the number of polymerization cyc...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 2.4 Characterization of nanomaterials
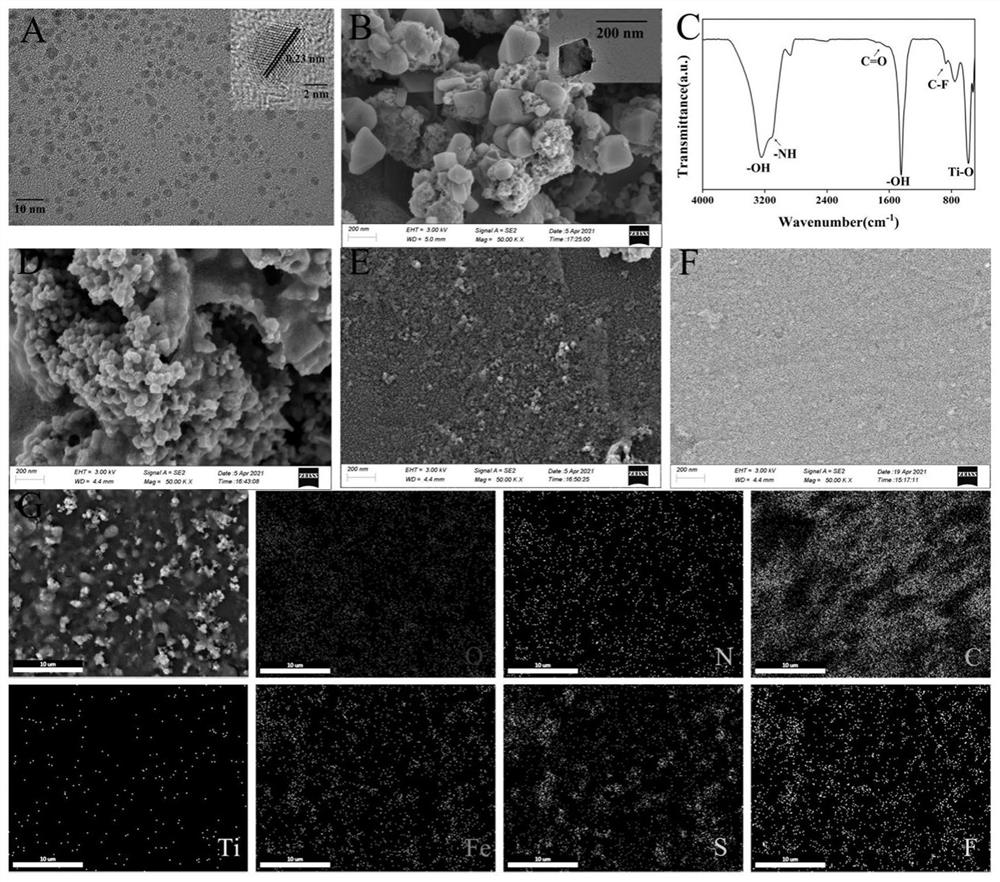
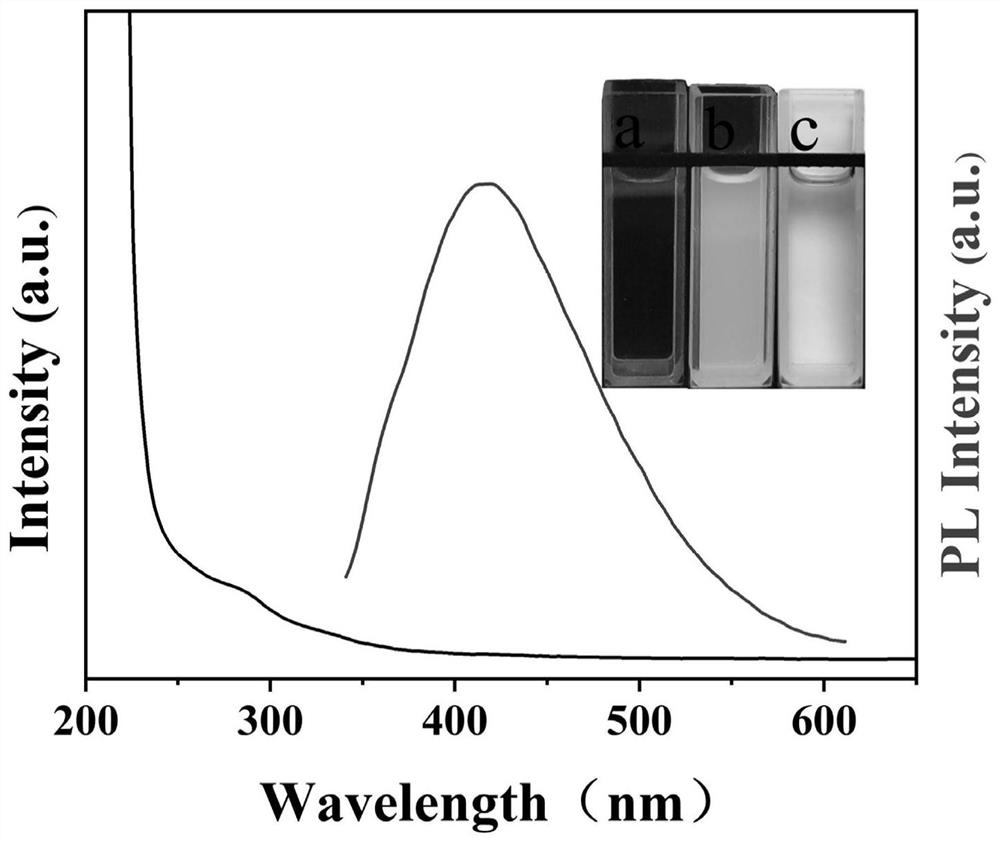
[0047] During the preparation of the modified electrodes, SEM and TEM were used to characterize the morphology of the composite nanomaterials. From figure 1 The TEM in A shows that the MQDs are uniformly dispersed with an average size of about 3 nm. HRTEM image ( figure 1 Inset in A) shows the lattice properties of MQD particles. The lattice spacing is 0.23 nm, which corresponds to the 008 crystal plane of the MQDs. Meanwhile, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to characterize the types of functional groups on the surface of MQDs. Such as figure 1 As shown in B, functional groups such as -OH, -NH, -C=O, -C-F and Ti-O were observed, respectively. MQD at 3105cm -1 The vibration at is attributed to the -NH group, which indicates that the surface of the MQD is passivated by the -NH group. It is precisely because of the existence of these functional groups that it is more conducive to the subsequent combina...
Embodiment 3
[0055] In order to improve the measurement performance of imprinted nanocomposites, a series of experimental factors such as the molar ratio of template to monomer, number of polymerization cycles, pH value, elution and incubation time, and scanning rate were investigated respectively. By fabricating FeS under single factor parameters 2 / C / MQDs / MIP / GCE, the electrochemical response of DIP and QS was measured by DPV in PBS (pH 3.5) buffer containing a mixture of 40 μM DIP and QS. The results of the optimization part are shown below.
[0056] The number and intensity of molecularly imprinted cavities formed by CV electropolymerization are related to the ratio of template molecules to functional monomers. Such as Figure 6 As shown in A, between 1:1:0.5-1:1:7, when the ratio of template to functional monomer is 1:1:3, the peak current response is the strongest. Therefore, the optimal molar ratio of the template molecules DIP and QS to the functional monomer is 1:1:3. In addit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com