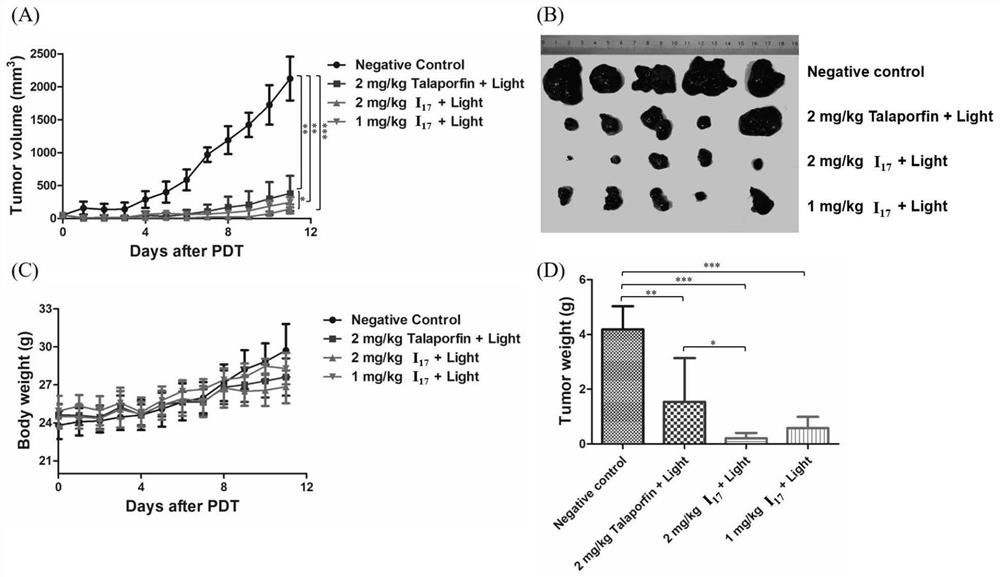
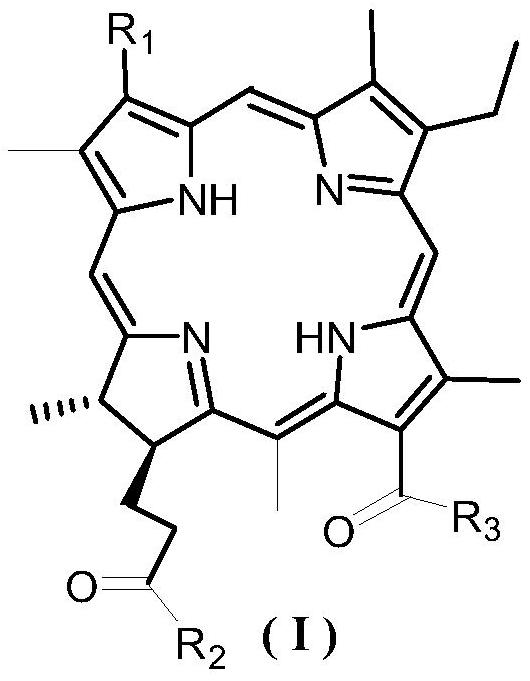
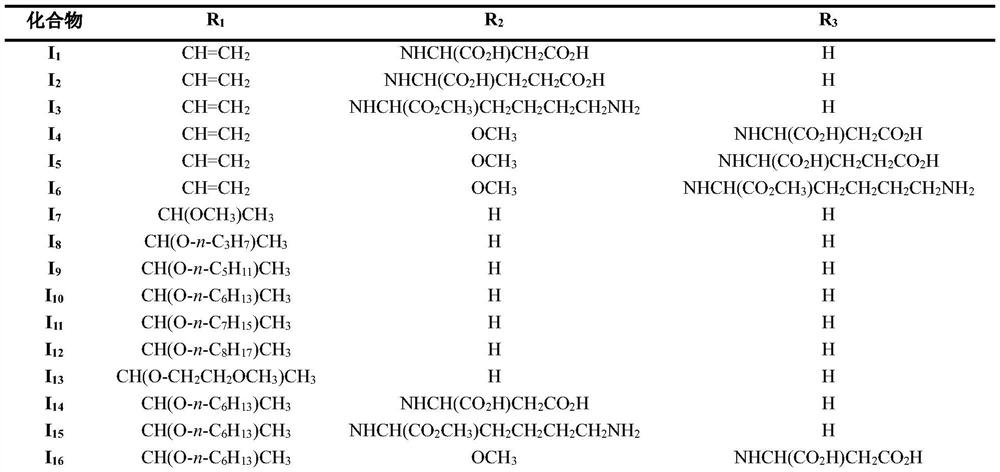
Novel chlorin e4 derivative, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and preparation methods and application of novel chlorin e4 derivative and thepharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
A chlorin and derivative technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as poor stability of chlorin, and achieve the effects of excellent photodynamic killing effect, reducing dark toxicity, and high dark poison/phototoxicity ratio.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Embodiment 1: N-(chlorine e 4 -17 3 -acyl)-L-aspartic acid (I 1 ) preparation
[0071] Compound V (0.1g, 0.181mmol, 1.0equiv) was dissolved in 10mL of dry DMF, HATU (0.076g, 0.199mmol, 1.1equiv), L-aspartic acid di-tert-butyl hydrochloride (0.061g , 0.217mmol, 1.2equiv) and DIPEA (0.068g, 0.543mmol, 3.0equiv), stirred at room temperature for 12h. After the reaction was complete, 100 mL of ethyl acetate was added to dilute the reaction solution, washed three times with saturated NaCl water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. 2 Cl 2 :CH 3 OH:HCO 2 Under the condition of H=40:1:0.1–30:1:0.1, purify with flash preparative column chromatography to obtain black powdery compound N-(chlorin e 4 -17 3 -acyl)-L-aspartic acid di-tert-butyl ester (II-1 1 ). The above II-1 1 Dissolve in 5 mL of dry dichloromethane, add 2 mL of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), and stir at room temperature for 2 h. Add a lot of NaHCO 3 The ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: N-(chlorine e 4 -17 3 -acyl)-L-glutamic acid (I 2 ) preparation
[0073] According to the method of Example 1, compound V (0.1g, 0.181mmol, 1.0equiv) was mixed with 1.1 equivalents of HATU, 1.2 equivalents of L-di-tert-butyl glutamate hydrochloride and 3 times equivalents in dry DMF. Equivalent DIPEA makes N-(chlorine e 4 -17 3 -Acyl)-L-glutamic acid di-tert-butyl ester (II-1 2 ), then compound II-1 2 Dissolve in 5 mL of dry dichloromethane, add 2 mL of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), stir at room temperature for 2 h, and obtain black powder compound I 2 0.093 g, yield 73.6%. HPLC purity: 99.3%. 1 H-NMR (600MHz, Acetone-d 6 ,ppm)δ10.19(s,1H),9.93(s,1H),9.39(s,1H),8.20(dd,J=17.8,11.4Hz,1H),6.37(d,J=17.9Hz,1H ),6.20(d,J=11.4Hz,1H),4.71–4.65(m,2H),4.21(t,J=6.6Hz,2H),3.91(s,3H),3.89(s,3H),3.61 (s, 3H), 3.50 (s, 3H), 3.34 (s, 3H), 2.28–2.19 (m, 4H), 1.83 (d, J=7.3Hz, 4H), 1.31 (s, 3H). MS (ESI + )m / z:682.57(M+H) + (100%).
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3: N α -(chlorin e 4 -17 3 -acyl)-L-lysine methyl ester (I 3 ) preparation
[0075] According to the method of Example 1, compound V (0.1g, 0.181mmol, 1.0equiv) was mixed with 1.1 equivalents of HATU and 1.2 equivalents of N in dry DMF. ε N α -(chlorin e 4 -17 3 -acyl)-N ε -tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-lysine methyl ester (II-1 3 ), then compound II-1 3 Dissolve in 5 mL of dry dichloromethane, add 2 mL of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), stir at room temperature for 2 h, and obtain black powder compound I 3 0.088g, yield 69.3%. 1 H-NMR (600MHz, Acetone-d 6 ,ppm)δ9.79(s,1H),9.78(s,1H),9.10(s,1H),8.33(dd,J=11.7Hz,10.4Hz,1H),6.47(d,J=11.7Hz, 1H), 6.19(d, J=10.2Hz, 1H), 4.64(s, 2H), 4.08(s, 3H), 3.96(s, 3H), 3.71(t, 3H), 3.59(s, 3H), 3.37 (s, 3H), 1.99 (m, 4H), 1.82 (d, 4H), 1.74 (d, 4H), 1.10 (s, 3H). MS (ESI + )m / z:695.55(M+H) + (100%).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com