Rotor position angle determination method and device based on permanent magnet synchronous motor
A technology of permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor position angle, which is applied in the direction of control of electromechanical transmission, control of generator, motor control, etc., and can solve the problems of reduced accuracy, general lack of adaptability, and inapplicability to various situations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
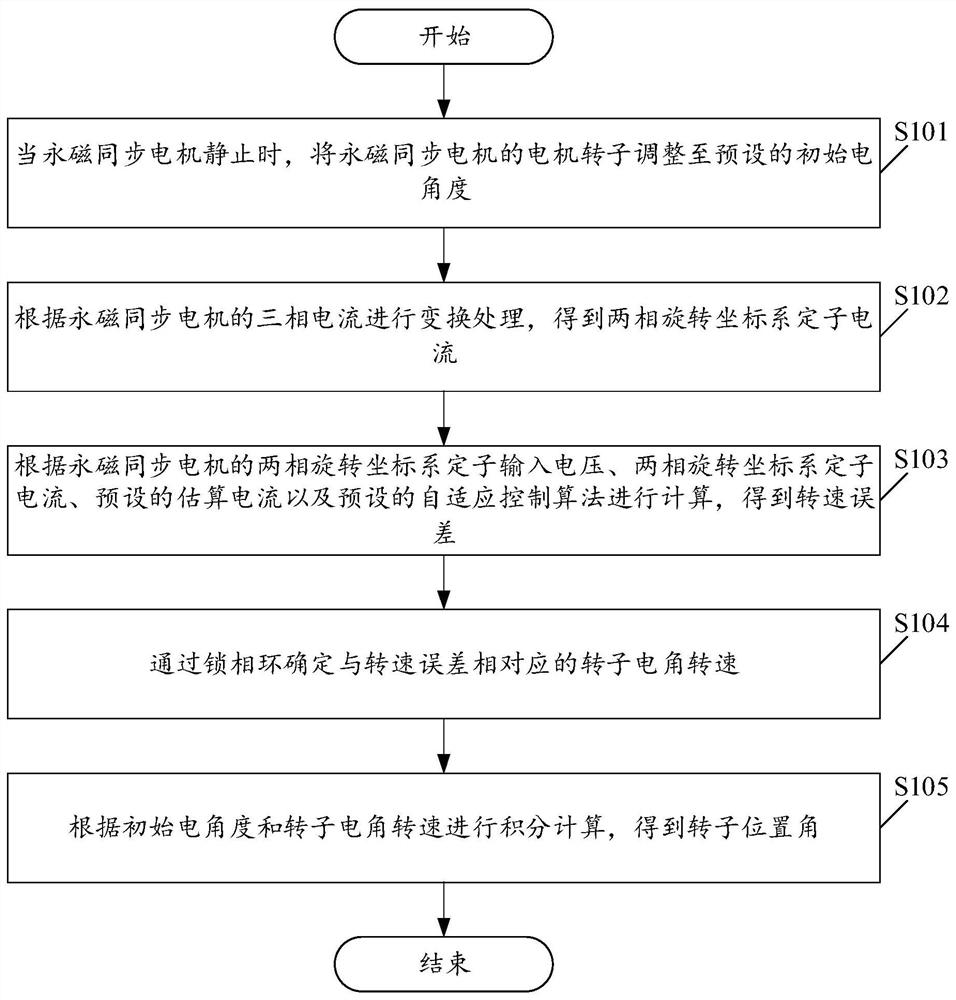
[0055] Please see figure 1 , figure 1 A schematic flowchart of a method for determining a rotor position angle based on a permanent magnet synchronous motor is provided for an embodiment of the present application. Wherein, the method for determining the rotor position angle based on the permanent magnet synchronous motor includes:
[0056] S101. When the permanent magnet synchronous motor is stationary, adjust the motor rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to a preset initial electrical angle.
[0057] In this embodiment, when the permanent magnet synchronous motor is stationary, the method can control the upper bridge arm of the three-phase inverter A phase to open and the lower bridge arm to close, and the upper bridge arms of the B and C phases to close and the lower bridge arm to open. The DC torque at this time will drag the motor rotor to the position of zero electrical angle, so as to realize the precise positioning of the rotor.
[0058] S102. Perform tr...
Embodiment 2
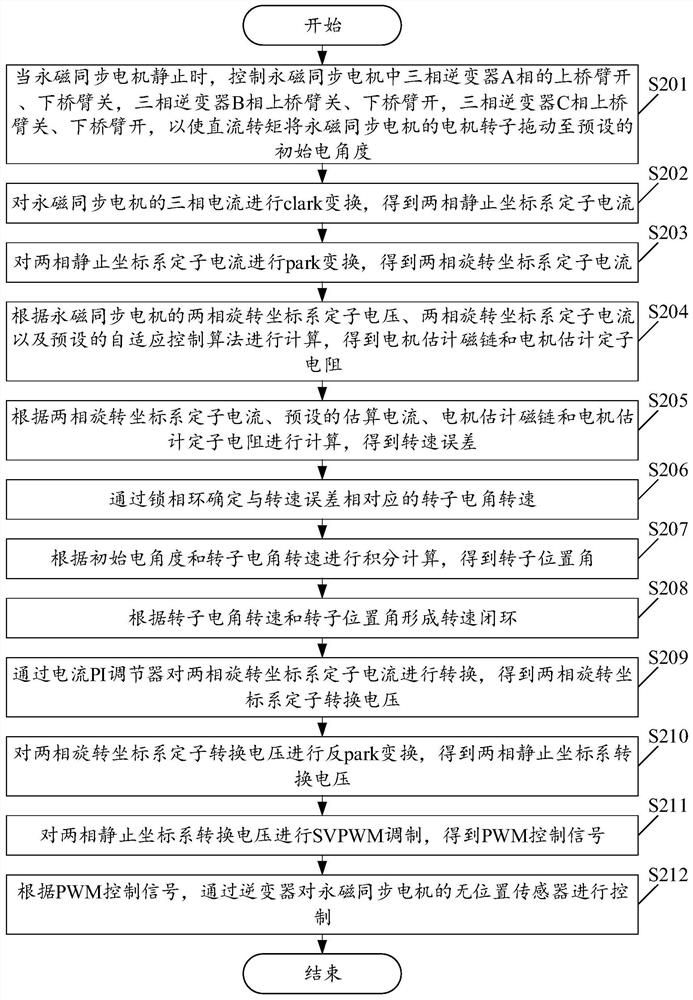
[0072] Please see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic flowchart of a method for determining a rotor position angle based on a permanent magnet synchronous motor provided in an embodiment of the present application. like figure 2 As shown, wherein, the method for determining the rotor position angle based on the permanent magnet synchronous motor includes:
[0073] S201. When the permanent magnet synchronous motor is at rest, control the upper bridge arm of the three-phase inverter A phase to open and the lower bridge arm to close, and the three-phase inverter B phase upper bridge arm to close and the lower bridge arm to open , the upper bridge arm of phase C of the three-phase inverter is closed, and the lower bridge arm is opened, so that the DC torque will drag the motor rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to a preset initial electrical angle.
[0074] S202 , performing clark transformation on the three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous mo...
Embodiment 3
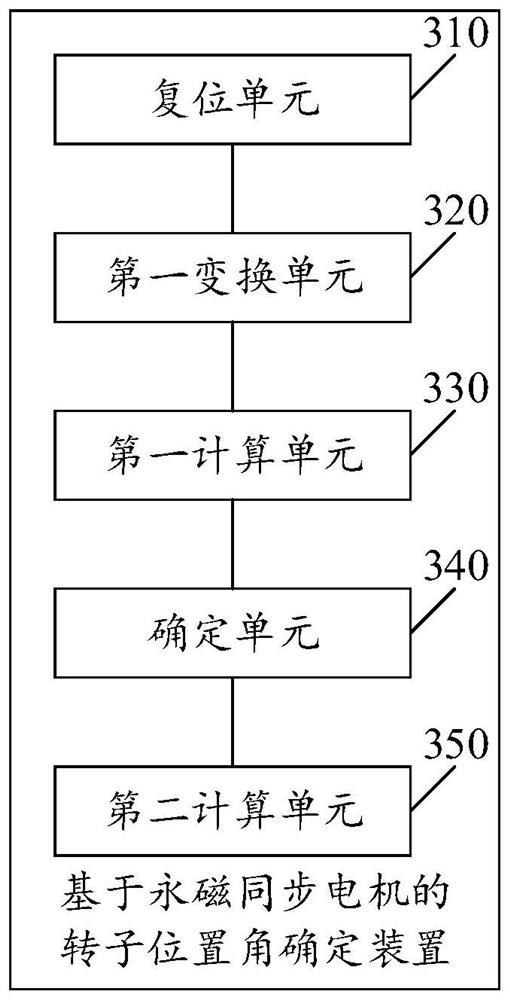
[0110] Please see image 3 , image 3 A schematic structural diagram of a device for determining a rotor position angle based on a permanent magnet synchronous motor provided in an embodiment of the present application. like image 3 As shown, the rotor position angle determination device based on permanent magnet synchronous motor includes:
[0111] The reset unit 310 is used to adjust the motor rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to a preset initial electrical angle when the permanent magnet synchronous motor is stationary;
[0112] The first conversion unit 320 is configured to perform conversion processing according to the three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor to obtain the stator current of the two-phase rotating coordinate system;
[0113] The first calculation unit 330 is used to perform calculations based on the stator input voltage of the two-phase rotating coordinate system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the stator c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com