Choroidal neovascularization targeting nanoparticle coated with macrophage membrane and preparation method of choroidal neovascularization targeting nanoparticle
A technology targeting nanoparticles and neovascularization, which is applied in the field of choroidal neovascularization targeting nanoparticles and its preparation, can solve the problems that there is no intravenous nano-preparation for the treatment of retinal diseases, poor drug compliance of patients, etc., and achieve high drug loading efficiency , strong drug-loading ability, and efficient treatment of diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
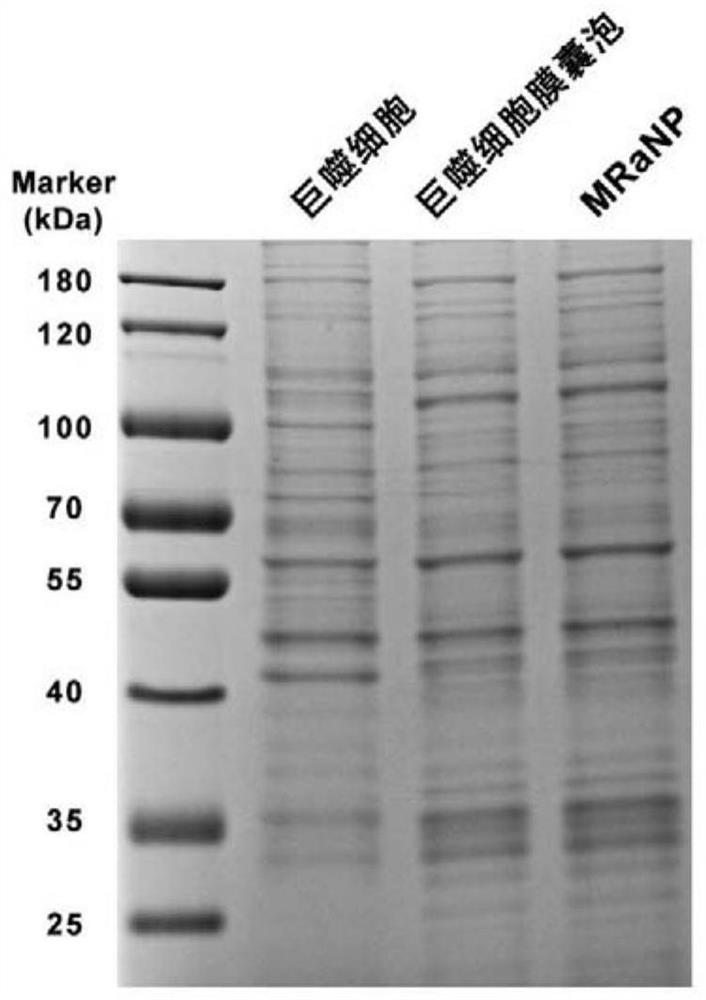
[0046] (1) Extraction of macrophages: 25 g of C57 male mice were intraperitoneally injected with 1 mL of 4% thioglycolate broth. After 3 days, the mice were sacrificed, the whole body was immersed in 75% ethanol for disinfection, and 5 mL of medium was injected twice to extract peritoneal macrophages. Cells were extracted at 37°C. 5%CO 2 Cultivate to 80%-90% under certain conditions;
[0047] (2) Collect the obtained cells into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge 3 times at 500g×5min, freeze and thaw repeatedly 3 times with liquid nitrogen to lyse the cells, and then repeatedly grind 20 times with a Dawns homogenizer to further break the cells;
[0048] Collect the cell lysate in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3200g×5min at 4°C to remove large cell debris;
[0049] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 20000g×25min at 4°C to remove organelles;
[0050] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 100000g×60min, 4°C, discard the supernatant, and the resulting white precipitate is the...
Embodiment 2
[0059] (1) Extraction of macrophages: SD rats were injected intraperitoneally with 1 mL of 4% thioglycollate broth, sacrificed 3 days later, immersed in 75% ethanol for disinfection, and injected 5 mL of medium twice to extract peritoneal macrophages Cells were extracted at 37°C. 5%CO 2 Cultivate to 80%-90% under certain conditions;
[0060] (2) Collect the obtained cells into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge 3 times at 500g×5min, freeze and thaw repeatedly 3 times with liquid nitrogen to lyse the cells, and then repeatedly grind 20 times with a Dawns homogenizer to further break the cells;
[0061] Collect the cell lysate in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3200g×5min at 4°C to remove large cell debris;
[0062] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 20000g×25min at 4°C to remove organelles;
[0063] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 100000g×60min, 4°C, discard the supernatant, and the resulting white precipitate is the cell membrane; resuspend the cell membrane pellet i...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Preparation of membrane-coated nanoparticle preparations of rapamycin-loaded macrophages labeled with cell membrane orange-red fluorescent probe DiI.
[0070] (1) Obtain macrophages directly from the mouse mononuclear macrophage leukemia cell line Raw264.7 cells, at 37°C, 5% CO 2Cultivate to 80%-90% under certain conditions;
[0071] (2) Scrape the macrophages obtained in (1), collect them in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge 3 times at 500g×5min, freeze and thaw them 3 times with liquid nitrogen to lyse the cells, and grind them repeatedly with a Dawns homogenizer 20 times to further break the cells; collect the cell lysate in a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3200g×5min, 4°C to remove large cell debris;
[0072] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 20000g×25min at 4°C to remove organelles;
[0073] Collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 100000g×60min, 4°C, discard the supernatant, and the resulting white precipitate is the cell membrane; resuspend the cell membrane pel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com