DCU cluster-oriented large-scale finite element grid parallel partitioning method and device
A large-scale, finite element technology, applied in special data processing applications, complex mathematical operations, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of long calculation time, reduced efficiency, growth, etc., to shorten processing time, improve efficiency, and improve effect of speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0139] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and advantages to be solved by the present invention clearer, the following will describe in detail with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
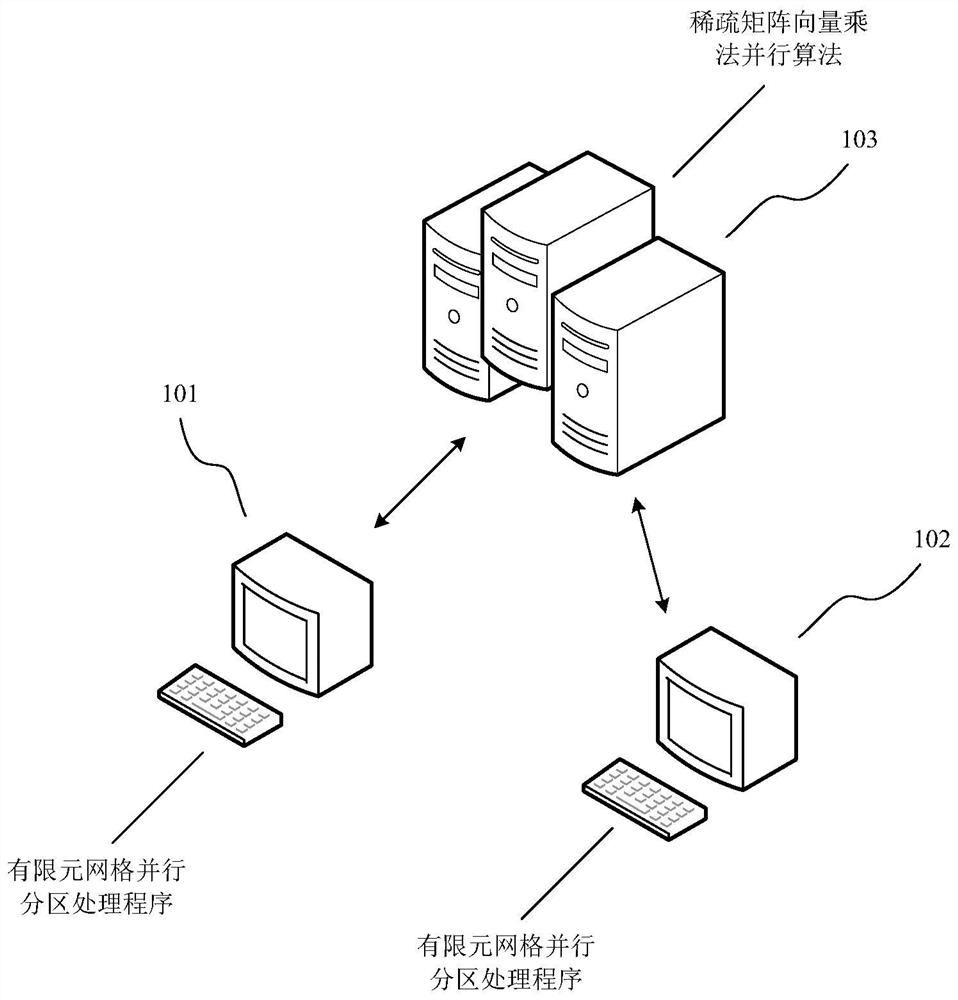
[0140] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for parallel partitioning of large-scale finite element grids oriented to DCU clusters, such as figure 2 As shown, the implementation environment may include at least one terminal 101 and a server 102 for providing services for the terminal 101 . At least one terminal 101 is connected to the server 102 through a wireless or wired network, and the terminal 101 may be a computer device or an intelligent terminal capable of accessing the server 102 . For the process of parallel partitioning of the finite element grid, the terminal 101 can process it alone, or the server 102 can process it alone, or the terminal 101 and the server 102 can jointly process it. One of the feasible methods is exemplif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com