Method for extracting extracellular vesicles from milk
A technology of cells and vesicles, applied in the field of extracting extracellular vesicles, can solve the problems of high cost, low yield and low efficiency of isolated EVs, and achieve the effects of low cost, great clinical transformation prospects, and increased production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
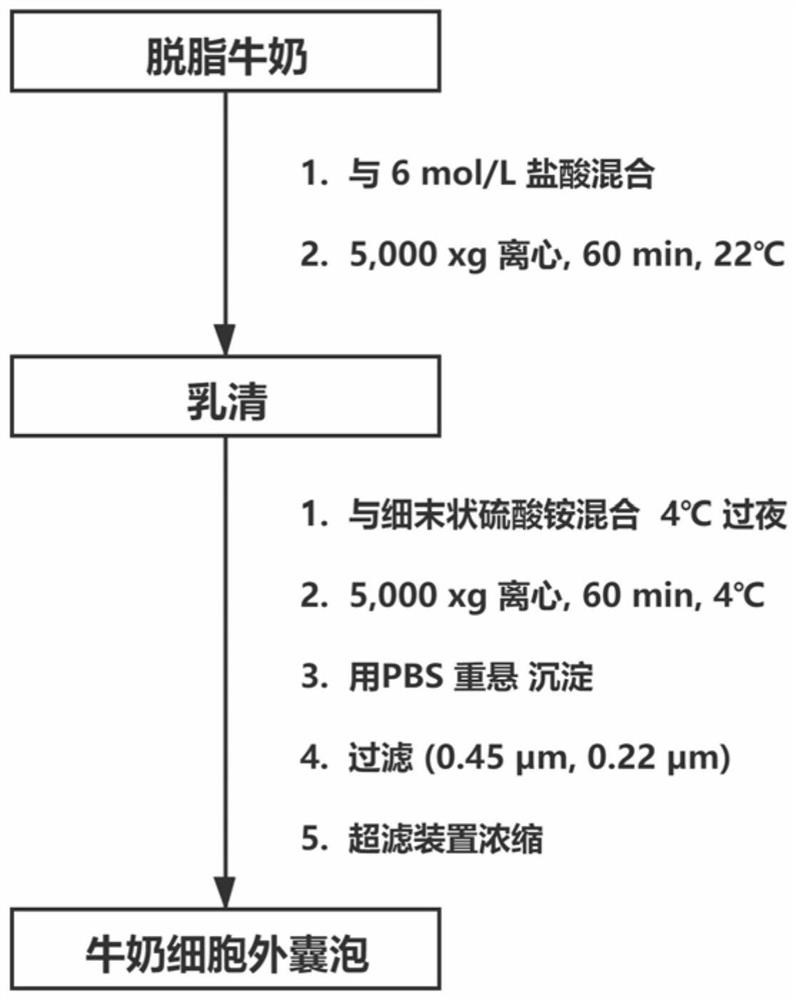
[0043] 1. Milk Collection and Whey Preparation
[0044] 1.1 Pasteurized raw milk produced in the market for refrigerated storage and transportation on the day of purchase—skimmed milk (Beijing Sanyuan Food Co., Ltd.);
[0045] 1.2 Take 50mL skimmed milk in a test tube and preheat at 37°C for 10 minutes;
[0046]1.3 Acidified milk: add a little 6mol / L hydrochloric acid, the volume ratio of milk / hydrochloric acid is about 100:1, adjust the pH to 4.6, and let stand for 5 minutes;
[0047] 1.4 Centrifuge at 5000xg for 1 hour at 22°C to remove casein and obtain a relatively transparent supernatant—whey;
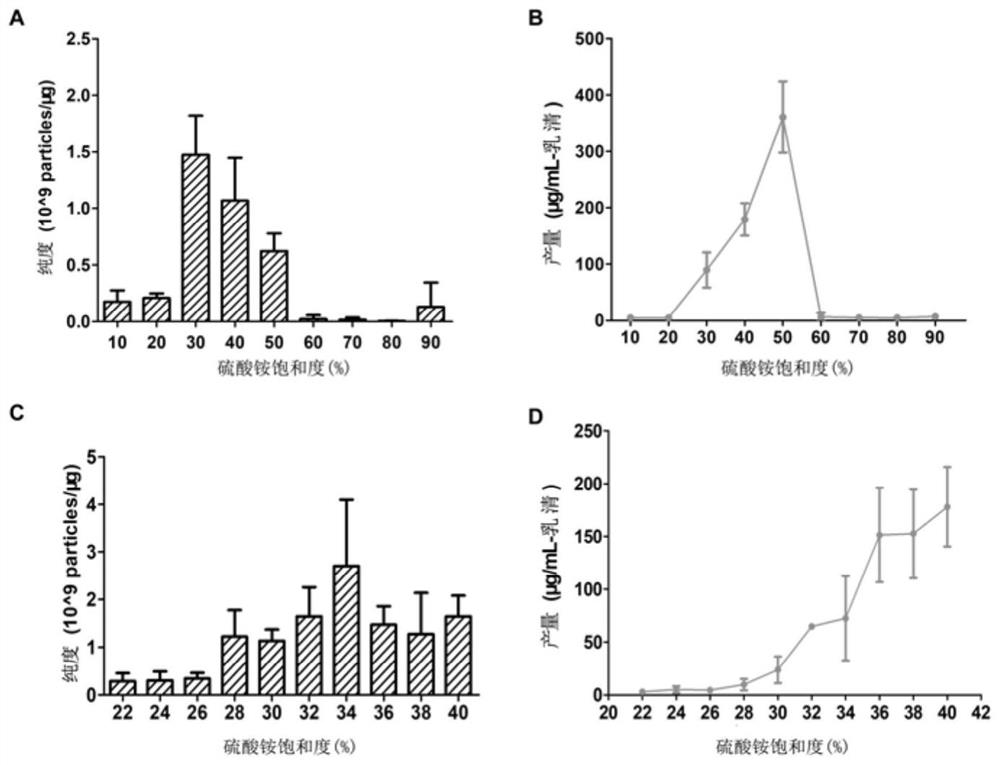
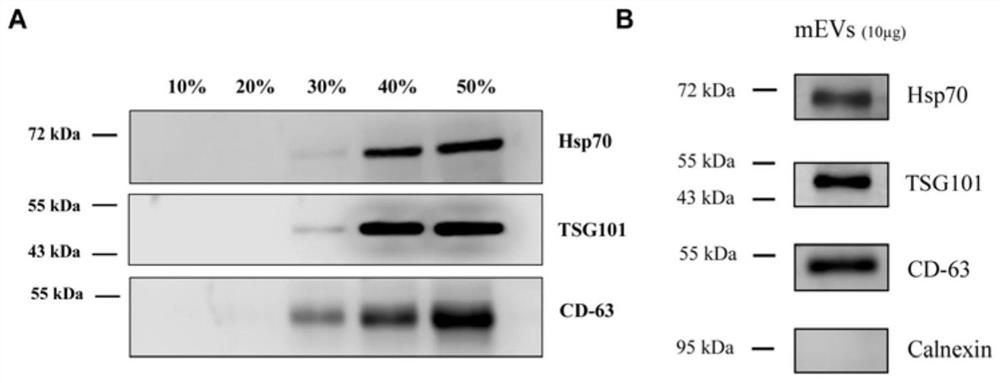
[0048] 1.5 Add powdered ammonium sulfate solids to the supernatant obtained in the previous step and mix thoroughly, and prepare solutions with different saturations of ammonium sulfate. This experiment adopts the following table (the solution of the remaining saturation of ammonium sulfate is calculated using the following website: https: / / www.encorbio.com / protocols / AM-SO4....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com