Laser scanning microscopic measurement device and method thereof
A technology of microscopic measurement and laser scanning, which is applied in the direction of microscope, optics, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of easily causing diffraction and detecting small pinholes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
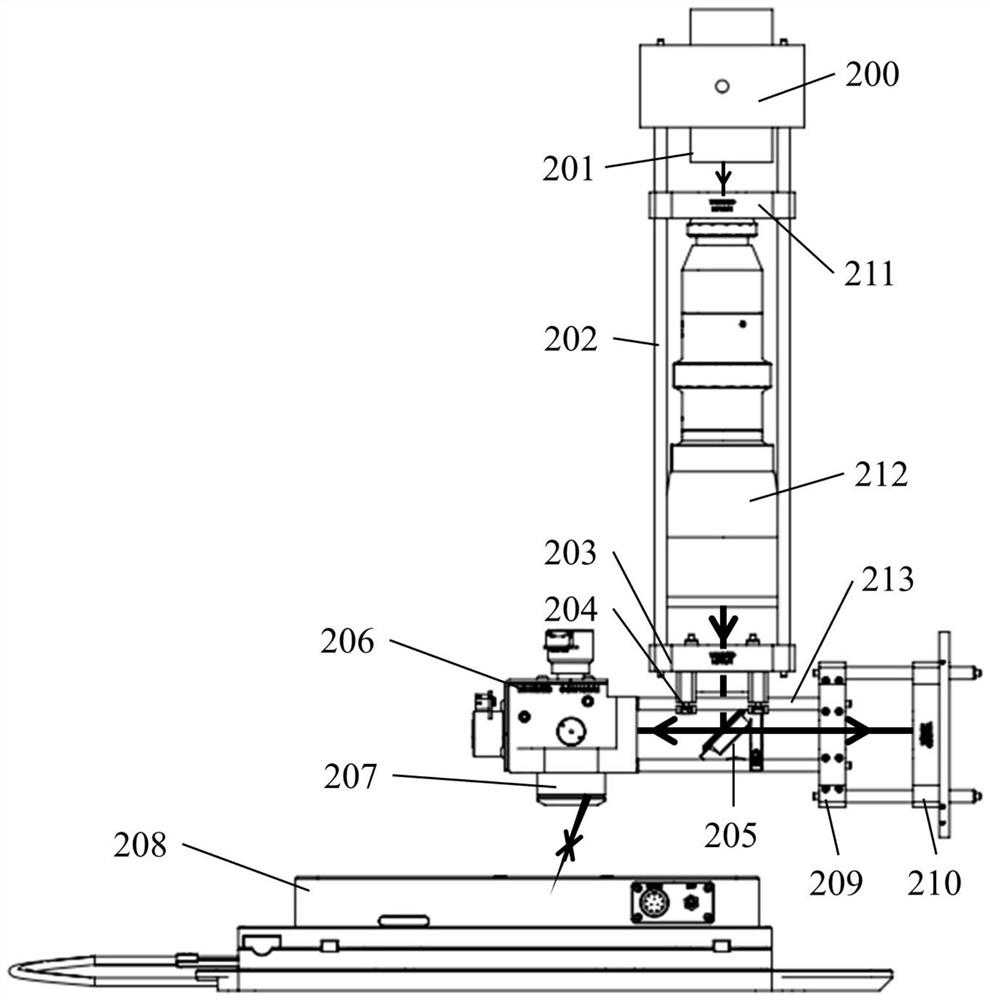
[0057]A 405nm laser 201 with a maximum power of 200mW (Changchun New Industry Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., model MDL-XS-405) emits laser light with a diameter of 1.2mm, and passes through a beam expander 212 with a variable magnification of 2 to 5 times (Solebo, model BE -02-05-A) After the spot size is enlarged, it is reflected into the galvanometer 206 by the half mirror 205, and the galvanometer 206 controls the two-dimensional deflection of the laser, and the galvanometer with sensor measurement is used to allow the galvanometer mirror to work in a closed loop And can output the coordinates of the galvanometer. After scanning the objective lens 207, it focuses on the sample on the three-dimensional translation stage 208. The three-dimensional translation stage is composed of a two-dimensional translation stage and a piezoelectric ceramic Z-axis unit. The two-dimensional movement of the axis and the Y axis, the piezoelectric ceramic Z-axis unit (Solebo, model MZS50...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Measurement of peak and valley values of scratches by laser scanning microscopy.
[0066] Piezoelectric ceramics move Z-axis displacement 20μm, step size 0.25μm. At each Z-axis coordinate, a scanning objective lens with a focal length of 4 mm is used to scan the surface of the glass sample, with a single scanning format of 282.6 μm×210 μm, and the scanning angles in the X-Y directions are 4.0° and 3.0°, respectively. Measuring the surface topography photos of scratches as image 3 As shown, the maximum height value Rp of each point in this area is 2.65 μm, the minimum height value Rv of each point in this area is -2.72 μm, and the peak-to-valley value of scratches is equal to Rp–Rv=5.4 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Under different virtual pinhole sizes, according to P S (z) The relationship between the normalized power calculated by the formula and the axial position is as follows Figure 4 shown. The virtual pinhole size corresponding to curve a and curve b is the magnification of the scanning objective lens multiplied by the beam waist size and the beam waist size respectively. The half-height width of curve a is larger than curve b, so the smaller the virtual pinhole size, the better the longitudinal Z-axis accuracy. high. However, the smaller the size, the lower the intensity, which requires a high magnification and sufficient sensitivity of the detection module. To improve the longitudinal precision, in addition to reducing the size of the virtual pinhole, it can also be achieved by reducing the focal length of the scanning objective lens.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com