Method for creating endogenous herbicide-resistant rice with high resistance and stability
A herbicide-resistant and herbicide-resistant technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve problems such as high cost, low probability, and bad mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Obtaining of the pHUN411-BE3 targeting vector containing the target sequence.
[0038] 1. Select the nucleotide sequence from position 6093 to position 6113 in the rice OsACC gene (LOC4338322), the sequence is CCT CTGTTCATCCTCGCTAACTG, (the underlined part is the reverse complementary sequence of the PAM sequence of NGG structure, wherein, N is A, T, G or C), as the targeting site.
[0039] 2. Synthesize (entrust BGI) forward oligonucleotide chain (OsACC P1) and complementary reverse oligonucleotide chain (OsACC P2) according to the selected target site,
[0040] The specific sequence is:
[0041] OsACC P1: GGCA CAGTTAGCGAGGATGAACAG
[0042] OsACC P2: AAAC CTGTTCATCCTCGCTAACTG
[0043] The part not underlined is the NGG-removed sequence or complementary sequence in the above target site, and the underlined part is the cohesive end used to connect the vector.
[0044] 3. Perform an annealing procedure on OsACC P1 and OACC P2, and anneal the two strands of OsACCP...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of rice
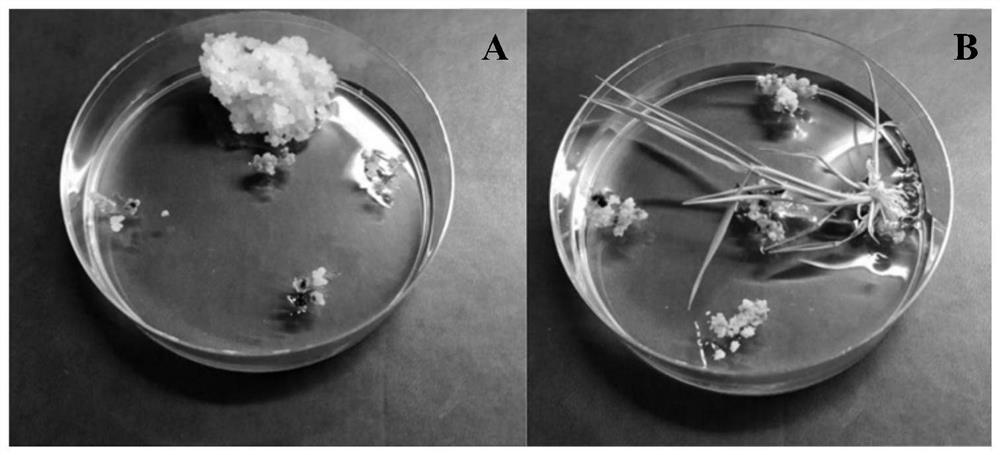
[0049] (1) Callus induction The sterilized rice seeds were soaked overnight in sterile water at 30°C in the dark, and the embryos were peeled off with a scalpel and placed on the induction medium. Place 12 embryos evenly in each dish (disposable plastic petri dish with a specification of 100×25mm, containing 50ml of induction medium), and place them in the dark at 30°C for 2 to 3 weeks to induce callus until light yellow granules grow. healing.
[0050] (2) Pre-cultivation Select the granular callus without lesion from the induction medium, place it on a new induction medium, and culture it in the dark at 30°C for 3-5 days.
[0051] (3) Infection and co-cultivation Transfer the pre-cultured callus to a 50ml sterile tube, add the Agrobacterium bacterium liquid obtained in Example 1 (the OD value of the bacterium liquid is in the range of 0.1~0.2) and soak for 20min, Pour out the bacterial solution, and ...
Embodiment 3
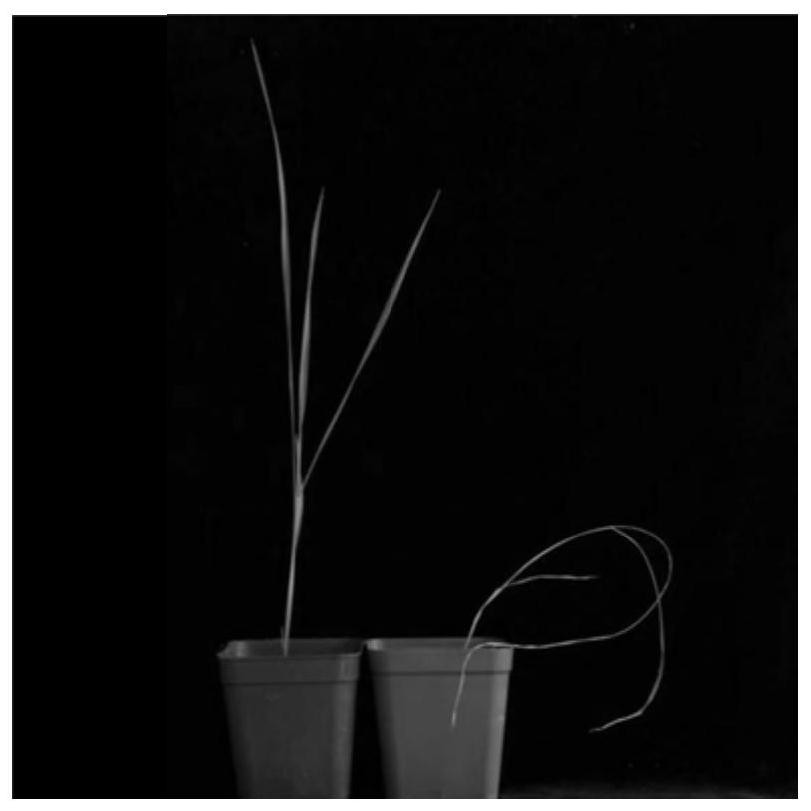
[0056] Example 3: Detection of ACCase base mutation sites in herbicide-resistant rice
[0057] Extract the leaf DNA of positive plants in the resistant rooting medium of 50 mg / l hygromycin and 9 μmol of metilofop as the selection agent, and design the following pair of primers for editing the ACCase gene target position, ACC FP: gctgtggagactcagaccatga
[0058] ACC RP: gtttatcttgctatcaaccaca
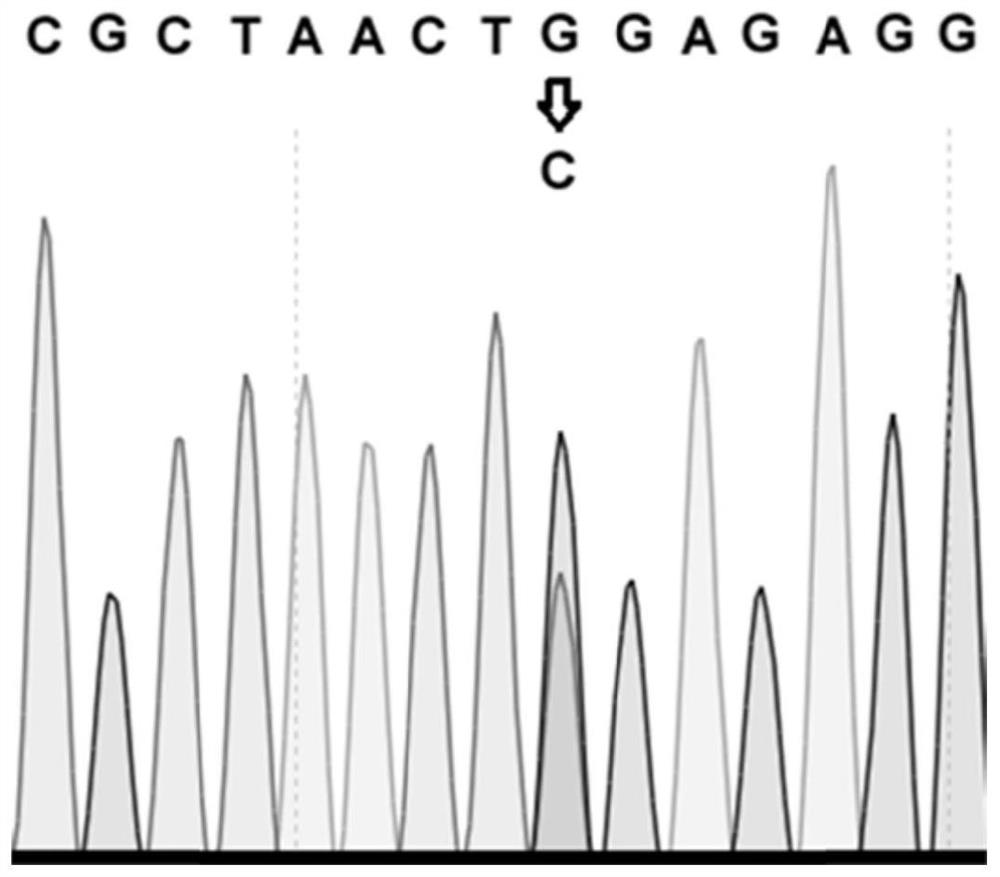
[0059] Amplify the upstream and downstream sequences of the target site. The amplified products were subjected to Sanger sequencing. Compared with the wild-type ACCase gene sequence, it was found that the 6113 nucleotide G on the rice ACCase gene with herbicide resistance was replaced by a nucleotide C ( figure 2 ). The pHUN411-BE3 system mediated C:G mutation to T:A site-specific substitution. The inventors of the present application found that the nucleotide G on the ACCase mutant gene was replaced by C, which is a non-target produced by the pHUN411-BE3 system. to mutation. This p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com