Method for degrading antibiotics in water by activating peracetic acid through zero-valent metal
A zero-valent metal, peracetic acid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as secondary pollution, and achieve low by-products, environment-friendly, and low cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Prepare 200 mL of tetracycline solution with an initial concentration of 10 μM in a beaker;
[0028] (2) Add a certain amount of peracetic acid to make the concentration 50 μM;
[0029] (3) Under room temperature conditions, open the magnetic stirring device of reaction vessel and start to stir;
[0030] (4) Add a certain amount of nanometer zero-valent iron to make its concentration 0.06g / L;
[0031] (5) adding glacial acetic acid and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to be 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5 respectively;
[0032] (6) Sampling at specific time intervals, testing the residual concentration of tetracycline in the sample, and drawing a histogram of the degradation efficiency of tetracycline under the conditions of different solution pH values.
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the ordinate represents the removal efficiency of tetracycline, and the degradation efficiency of tetracycline can be realized at a pH value of 3.5-7.5, and the degradation effi...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Prepare 200 mL of tetracycline solution with an initial concentration of 10 μM in a beaker;
[0036] (2) Add a certain amount of peracetic acid to make the concentration 50 μM;
[0037] (3) Under room temperature conditions, open the magnetic stirring device of reaction vessel and start to stir;
[0038] (4) Add a certain amount of nanometer zero-valent iron to make the concentration 0.02-0.1g / L;
[0039] (5) adding glacial acetic acid and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 6;
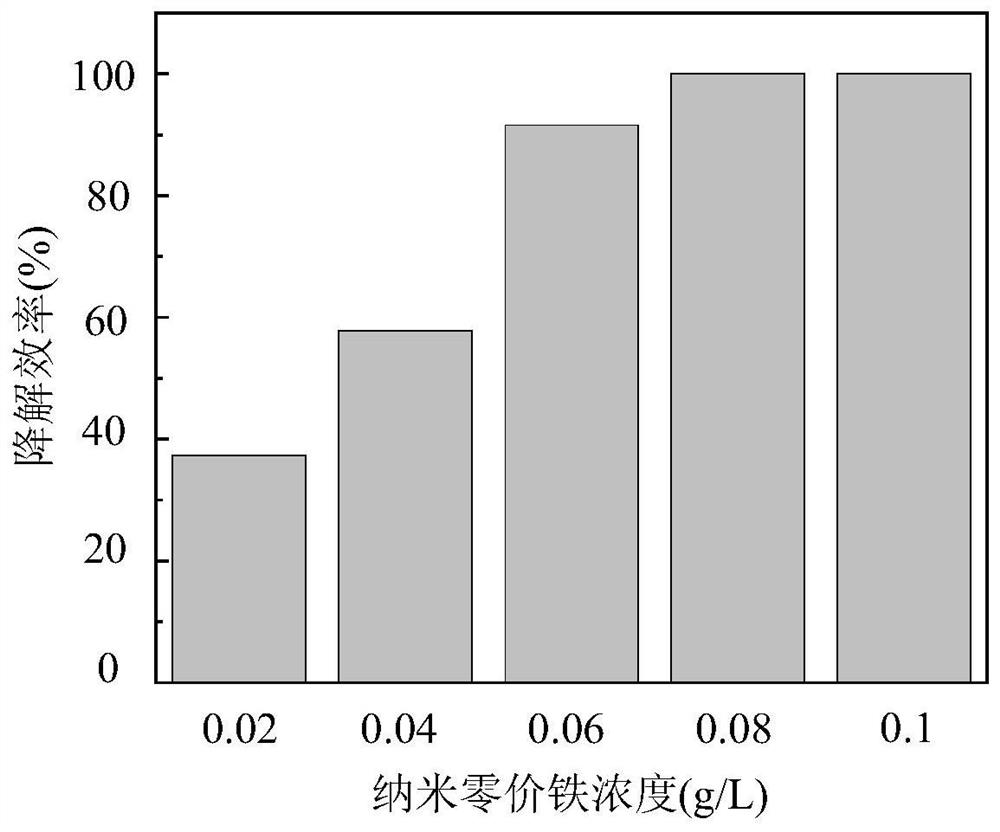
[0040] (6) Sampling at a specific time interval, testing the remaining concentration of tetracycline in the sample, and drawing a histogram of the degradation efficiency of tetracycline under the condition of different nanometer zero-valent iron dosage.
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown, the abscissa represents the concentration of nanometer zero-valent iron, and the ordinate represents the degradation efficiency of tetracycline. The degradation efficiency of tetracycline gradu...
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) Prepare 200 mL of tetracycline solution with an initial concentration of 10 μM in a beaker;
[0044] (2) Add a certain amount of peracetic acid to make the concentration 10-100 μM;
[0045] (3) Under room temperature conditions, open the magnetic stirring device of reaction vessel and start to stir;
[0046] (4) Add a certain amount of nanometer zero-valent iron to make its concentration 0.06g / L;
[0047] (5) adding glacial acetic acid and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to be 6 respectively;
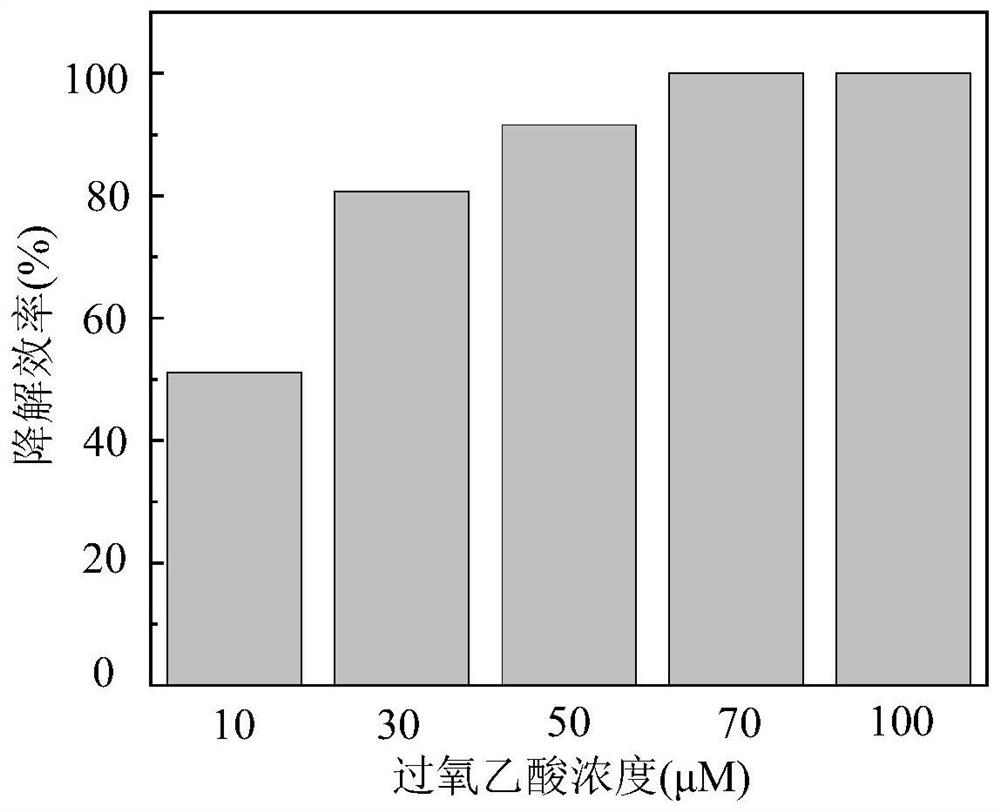
[0048] (6) Sampling in specific time intervals, test the residual concentration of tetracycline in the sample, and draw the histogram of the degradation efficiency of tetracycline under different peracetic acid concentration conditions.
[0049] Such as image 3 As shown, the abscissa represents the concentration of peracetic acid, and the ordinate represents the degradation efficiency of tetracycline. With the increase of peracetic acid concentration, the degrada...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com