Embedded memory management method and device based on global byte array
A byte array, memory management technology, applied in the field of embedded technology and the Internet of Things, can solve the problem of high complexity and redundancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Compared with the existing static allocation method based on global variables, it is difficult to use complex data structures in software design, such as linked lists and hash tables, and the complexity and redundancy of software design and implementation are high, and the readability is relatively low. In order to solve the problem of poor quality, this embodiment provides an embedded memory management device based on global byte arrays, which implements efficient and reliable memory management on the basis of global byte arrays, and supports complex data structures in embedded software design usage of.
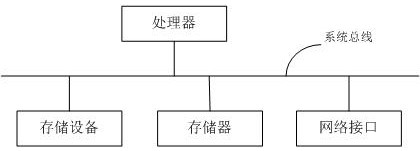
[0042] The device of this embodiment includes a memory pool and a memory manager;
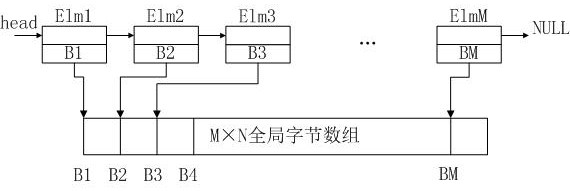
[0043] The memory pool is created by defining a global byte array in the embedded system, and the memory pool is divided into multiple fixed-size memory blocks;
[0044] The memory manager includes a memory pool usage status and a one-way linked list. The memory pool usage status is u...
Embodiment 2
[0072] This embodiment performs memory dynamic application management based on the management method provided in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, specifically as Figure 5 As shown, the memory dynamic application management process in this embodiment specifically includes:
[0073] Step S11, judging whether there are free memory blocks according to the number of free memory blocks in the memory pool usage state, if the free number is greater than zero, there is available memory space, and step S12 is executed, if the free number is equal to zero, there is no available memory space, and a null value is returned directly.
[0074] Step S12, temporarily storing the first address of the first node of the one-way linked list, and pointing the head of the one-way linked list to the next node.
[0075] Step S13, updating the usage status of the memory pool: subtracting one from the idle number of the usage status of the memory pool, and adding one to the used number;
[0076] Step ...
Embodiment 3
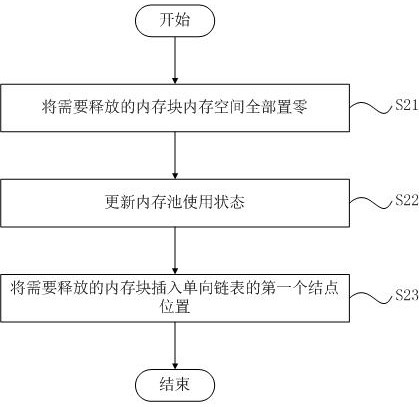
[0079] This embodiment performs memory dynamic release management based on the management method provided in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, specifically as Figure 7 As shown, the memory dynamic release management process in this embodiment specifically includes:
[0080] Step S21, all the memory space of the memory block that needs to be released is set to zero, so that it can be directly used next time;
[0081] Step S22, adding one to the idle number of the memory pool usage state, and decrementing the used number by one;
[0082] Step S23, insert the memory block to be released into the first node position of the one-way linked list.
[0083] Specific as Figure 8 The schematic diagram of the state after one dynamic release of memory is shown (among them, the block filled with squares represents the used memory block). In this embodiment, it is assumed that the first memory block is released for the first time, and the corresponding one-way linked list The subscript ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com