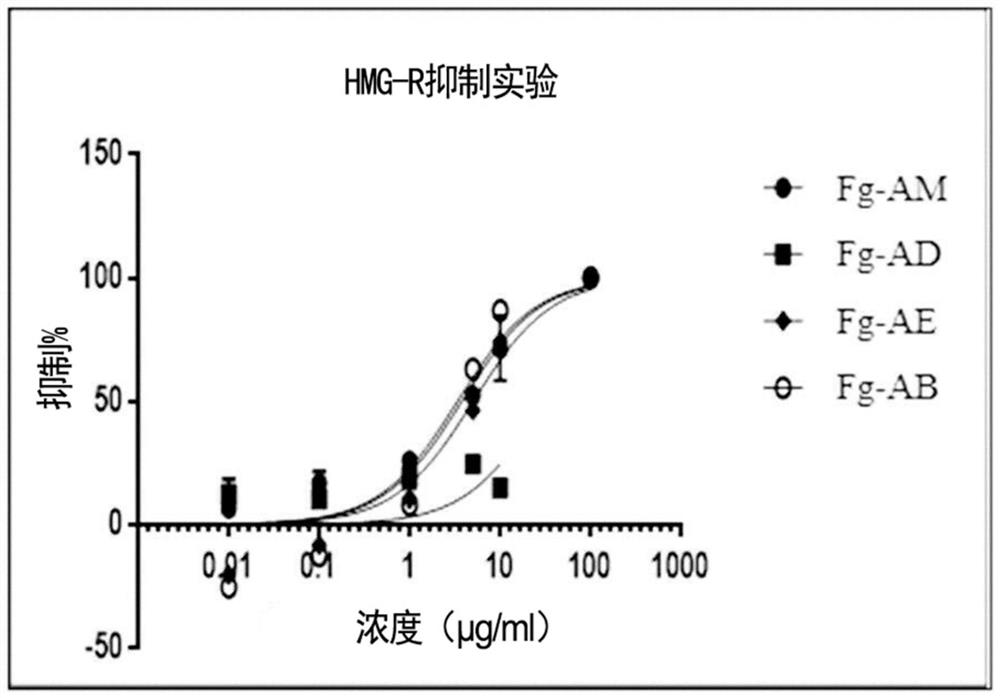
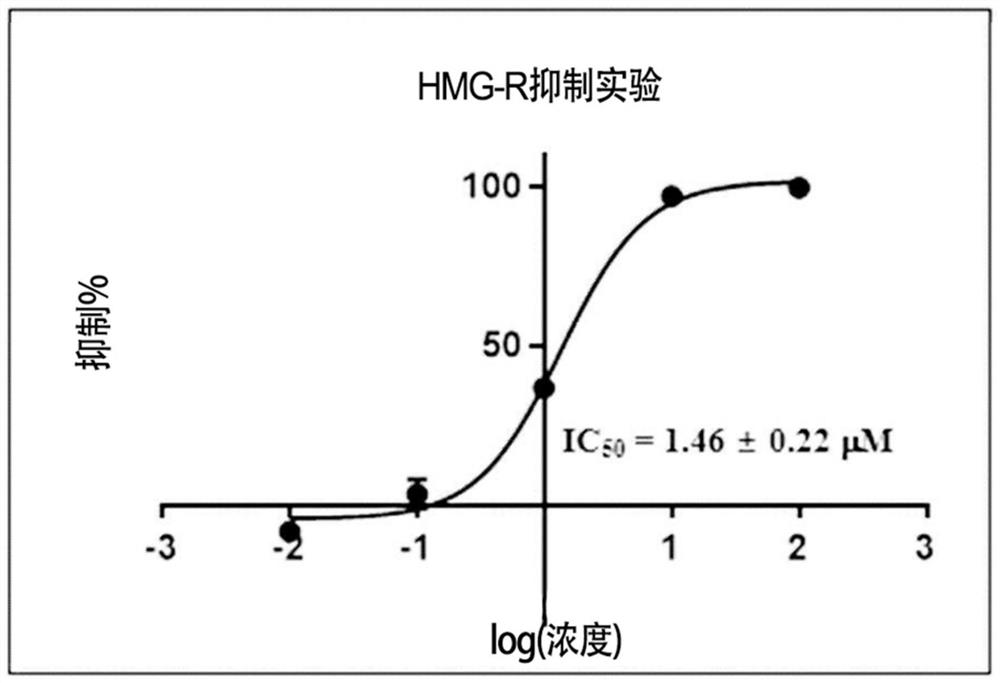
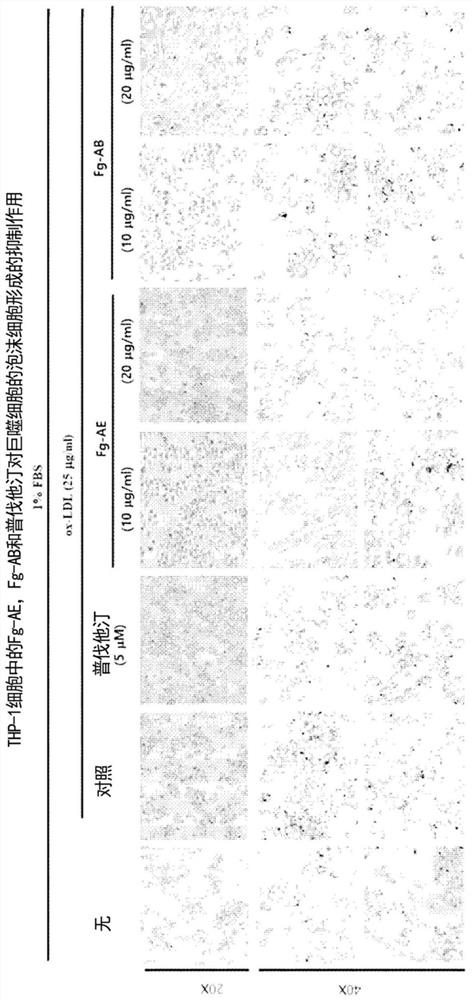
Food compositions and pharmaceutical compositions containing Filipendula glaberrima extract
A technology of Mosquito grass and extract, which is applied in the fields of food compositions and pharmaceutical compositions containing Mosquito chinensis extract, and can solve problems such as side effects and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0077] Each step of the method for preparing the Mosquito japonica extract and its extraction parts according to the present invention will be described in detail below.
[0078]Add 0.1-5 L, preferably 0.5-1.0 L of extraction solvent per kg of Mosquito japonica, and let it stand at room temperature for 4 to 5 days. This extraction may be performed 1 to 5 times, or may be performed a plurality of times if necessary. In addition, the temperature at the time of extraction is preferably 10°C-100°C, more preferably room temperature, but not limited thereto. The extraction time is preferably 1 to 7 days, more preferably 3 to 7 days, but not limited thereto. The obtained extract was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain a solvent extract. The vacuum concentration is preferably performed using a vacuum rotary evaporator, but is not limited thereto. In addition, drying may be performed using one selected from reduced pressure drying, vacuum drying, boili...
Embodiment 1
[0138] The extract of embodiment 1 maple leaf mosquito grass leaf or the preparation of extraction part
[0139] 6 L of methanol was added to the collected leaves (dry weight 840 g) of Mosquito japonica, and extraction was performed at room temperature for one week. After repeating this process three times, the resulting product was filtered and concentrated to dryness at 40° C. with a rotary concentrator to obtain 194.6 g of methanol extract. The methanol extract was suspended in 2,000 mL of water, and then extracted with dichloromethane (2,000 ml×3). The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (2,000 mL×3) to obtain ethyl acetate extraction fractions. Then, the aqueous layer was extracted again with butanol (2,000 mL×3) to obtain butanol-extracted sites.
Embodiment 2
[0140] The extract of embodiment 2 maple leaf Mosquito grass stem or the preparation of extraction part
[0141]2 L of methanol was added to the collected stems (dry weight 300 g) of Mosquito japonica, and extraction was performed at room temperature for one week. After repeating this process three times, the resulting product was filtered and concentrated to dryness with a rotary concentrator at 40°C to obtain 42.13 g of methanol extract. The methanol extract was suspended in 400 mL of water, then extracted with dichloromethane (400 mL×3). The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (400 mL×3) to obtain ethyl acetate extraction fractions. Then, the aqueous layer was extracted again with butanol (400 mL×3) to obtain butanol-extracted fractions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com