Graphene near-infrared detector with optical micro-cavity structure and manufacturing method thereof
An optical microcavity, graphene technology, applied in the field of infrared detection, can solve the problems of reduced device performance, low light absorption rate, lack of optical gain mechanism, etc., to achieve the effect of improving work stability and reliability, and improving infrared absorption rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
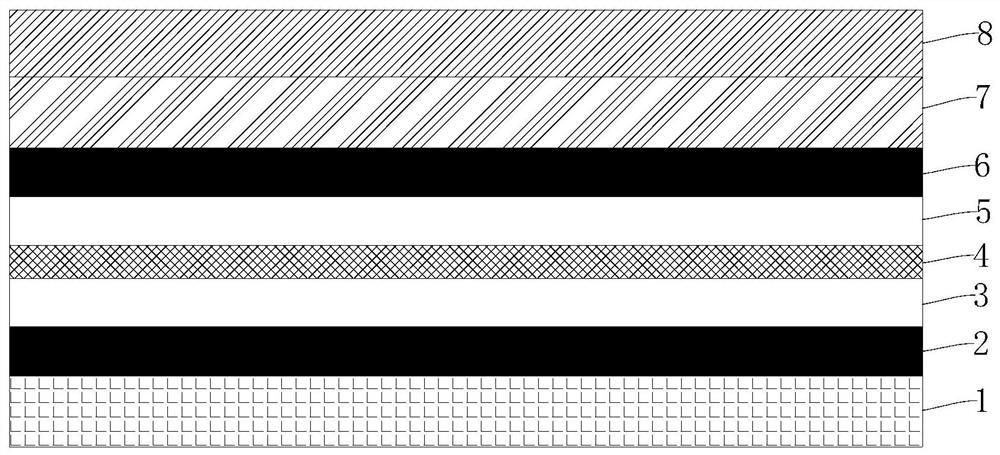
[0038] The present invention also discloses a method for preparing a graphene near-infrared detector with an optical microcavity structure as described above, comprising the steps of:
[0039] 1) sequentially depositing the first reflective layer 2 and the first light-transmitting layer 3 on the substrate 1;
[0040] 2) preparing a graphene layer 4 on the first transparent layer 3;
[0041] 3) preparing the second light-transmitting layer 5 and the second reflective layer 6 sequentially on the graphene layer 4;
[0042] 4) Prepare the electrode layer 7 on the second reflective layer 6 .
[0043] The preparation method of the present invention is simple to operate, and the directly obtained graphene near-infrared detector also has the advantages described above for the detector.
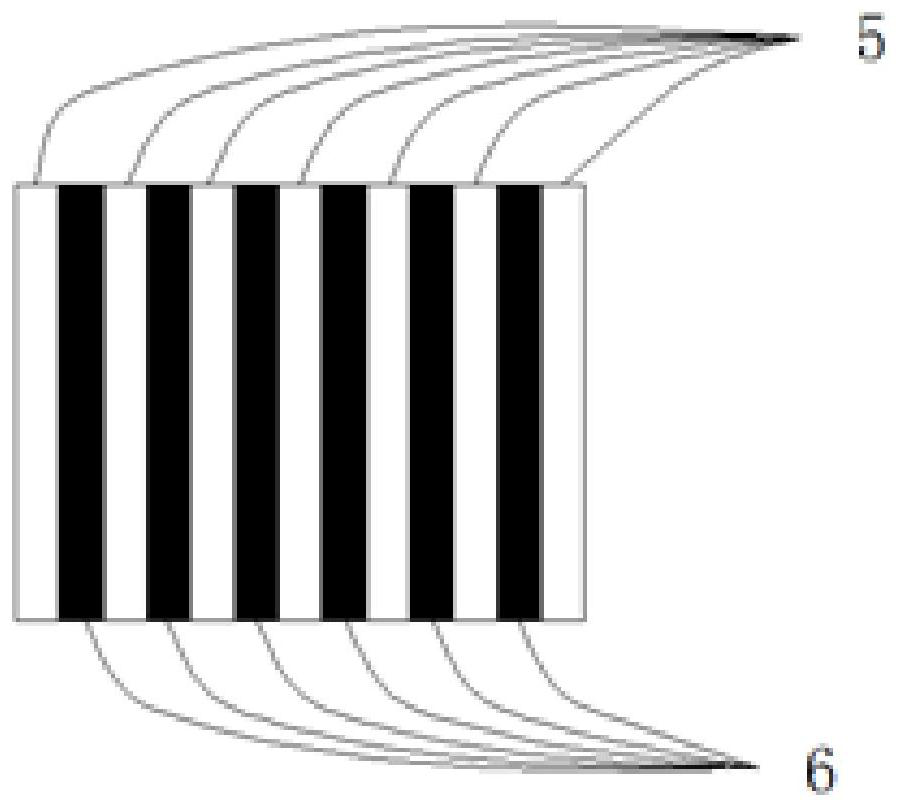
[0044] In this embodiment, in step 3), the specific process of preparing the second reflective layer 6 is:
[0045] 3.1) Making a glue layer array pattern 9 on the surface of the second light-trans...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com