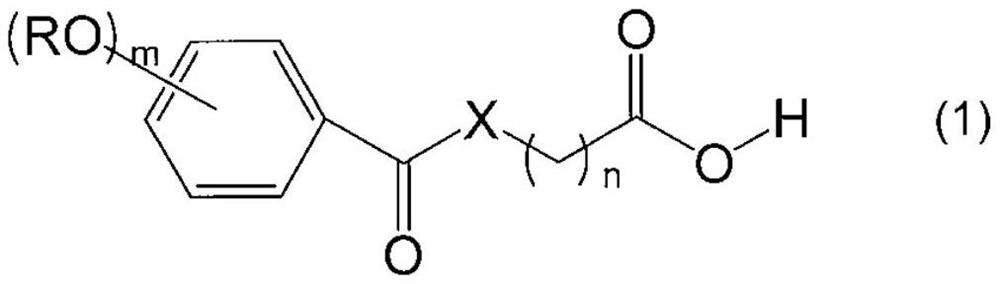
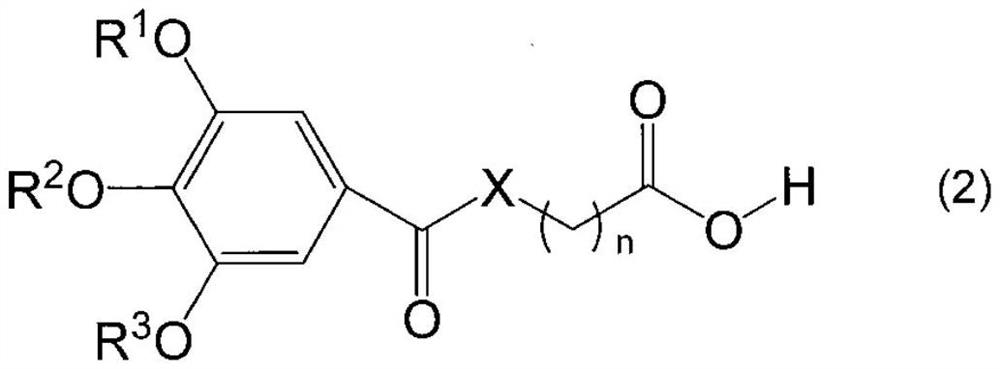
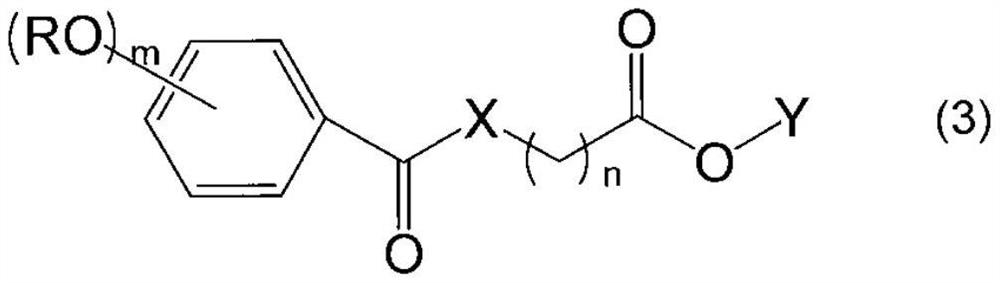
Alkoxyphenyl derivative, nucleoside protector, nucleotide protector, method for producing oligonucleotide, and method for removing substituent
A technology of derivatives and protecting groups, which is applied in the field of selective alkoxyphenyl derivatization of protected bodies or nucleotide protected bodies, and can solve problems such as difficulties in intermediate structure analysis, synthesis difficulties, and problems with versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
[0437] (1) Synthesis of 2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl 3,4,5-tris(octadecyloxy)benzoate
[0438]
[0439] Add triethylamine (0.39g, 3.87mmol), tert-butyl 2-bromoacetate After ester (0.76g, 3.87mmol), it was stirred at 60°C for 2 hours. After cooling the reaction liquid to room temperature, the precipitated solid by dropwise addition of methanol (54 mL) was filtered. After the solid was washed with methanol, it was dried under reduced pressure at 50°C to obtain the title compound (1.95 g, 97%) as a white solid.
[0440] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.88(t, 9H, J=6.8Hz), 1.16-1.41(m, 84H), 1.41-1.57(m, 6H), 1.49(s, 9H), 1.66-1.88(m, 6H), 3.95-4.11(m, 6H), 4.70(s, 2H), 7.31(s, 2H).
[0441] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ14.02, 22.48, 22.66, 22.83, 26.08, 26.11, 27.88, 28.08, 29.35, 29.40, 29.56, 29.64, 29.65, 29.70, 29.97, 30.22, 30.36, 31.76, 35, 31, 32.10, 691 82.32, 108.69, 108.90, 123.82, 123.93, 143.11, 143.38, 152.93, 165.83, 166.90.
[0442] TOF / MS (ESI): C 67 h 12...
Embodiment 1-2
[0444] (2) Synthesis of 2-((3,4,5-tris(octadecyloxy)benzoyl)oxy)acetic acid
[0445]
[0446]To a solution of 2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl 3,4,5-tris(octadecyloxy)benzoate (5.21 g, 5.0 mmol) in chloroform (20 mL) was added trifluoro After acetic acid (11.40 g, 100.0 mmol), stirred at 50° C. for 17 hours. After cooling the reaction solution to room temperature, the precipitated solid by dropwise addition of acetonitrile (50 mL) was filtered. The solid was washed with an acetonitrile-chloroform mixed solvent, and then dried under reduced pressure at 50°C to obtain the title compound (4.89 g, 99%) as a white solid.
[0447] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.88(t, 9H, J=7.0Hz), 1.16-1.54(m, 90H), 1.69-1.88(m, 6H), 3.95-4.11(m, 6H), 4.87(s, 2H), 7.30(s, 2H).
[0448] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ14.08, 22.68, 26.06, 26.10, 29.36, 29.41, 29.57, 29.65, 29.66, 29.72, 30.35, 31.93, 60.49, 69.30, 73.57, 108.53, 123.31, 143.17, 152.96, 165.7
[0449] TOF / MS (ESI): C 63 h 116 o 7 ...
Embodiment 1-3
[0452] (1) Synthesis of 2-benzyloxy-2-oxoethyl 3,4,5-tris(octadecyloxy)benzoate
[0453]
[0454] Add triethylamine (0.20 g, 1.94 mmol), benzyl 2-bromoacetate to a suspension of 3,4,5-tris(octadecyloxy)benzoic acid (0.90 g, 0.97 mmol) in chloroform (5 mL) (0.45g, 1.94mmol), stirred at 50°C for 14 hours. After the reaction liquid was cooled to room temperature, the precipitated solid by dropwise addition of methanol (18 mL) was filtered. After the solid was washed with methanol, it was dried under reduced pressure at 50°C to obtain the title compound (1.02 g, 97%) as a white solid.
[0455] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.88(t, 9H, J=6.8Hz), 1.16-1.41(m, 84H), 1.41-1.54(m, 6H), 1.66-1.91(m, 6H), 3.95-4.08(m, 6H ), 4.86(s, 2H), 5.23(s, 2H), 7.24-7.41(m, 7H).
[0456] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ14.08, 22.71, 26.13, 26.16, 29.40, 29.43, 29.46, 29.62, 29.69, 29.71, 29.76, 30.00, 30.43, 31.98, 61.24, 67.07, 69.40, 73.59, 108.76, 1128.69, 0 135.35, 143.28, 152.96, 153.01, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com