Forming system and method for film blowing processing of functional polymer material
A technology for functional polymers and polymer materials, applied in the field of molding systems for blown film processing functional polymer materials, can solve problems such as poor blown film processing performance, and achieve the effect of wide application range and simple process technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
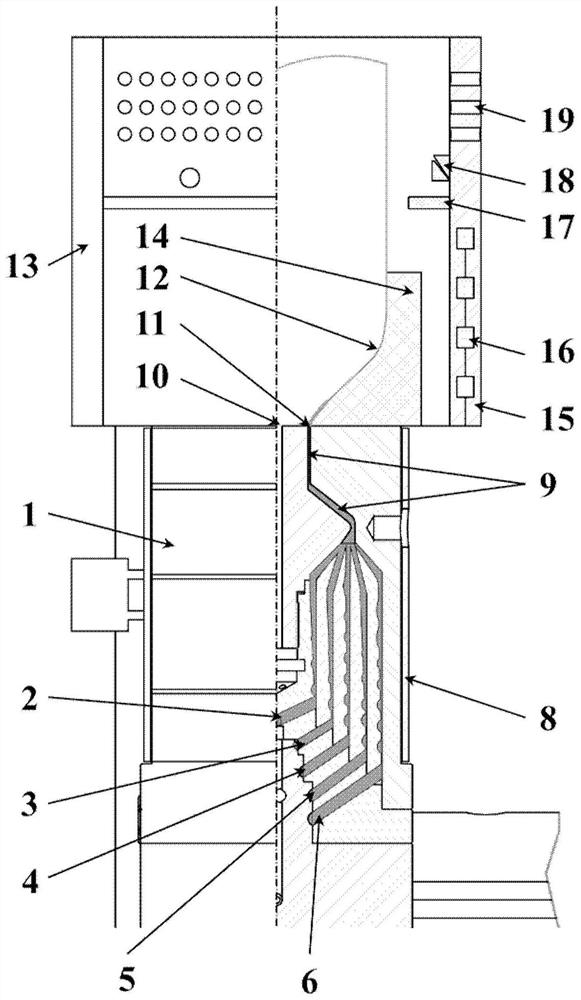
[0072] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a molding device for blown film processing of functional polymer materials, including a five-layer co-extrusion die head 1 and a temperature control molding device 13; the target functional polymer material and the protective layer material are respectively After being melted and plasticized by the extruder, it enters the co-extrusion die 1, the target functional polymer material enters the flow channel 4, and the protective layer material enters the flow channels 2, 3, 5 and 6 respectively. After entering the runners 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, first pass through a layer of filter structure in each runner to filter the solid particles that are not fully melted, and finally converge to the co-extrusion runner 9, the co-extrusion runner The ratio of the length of the die to the diameter of the die is 0.2 to 50. Adjusting the ratio can adjust the thickness distribution of the functional polymer material ...
experiment example 2
[0074] Utilize a kind of molding device and method for blown film processing functional polymer material provided in the above specific example 1, prepare biodegradable polymer poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate ) film, the melting point of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) is 150°C, the crystallization temperature is 126°C, and the protective layer material is polyethylene and modified polyadipate / terephthalic acid Butylene formate has melting points of 112°C and 125°C respectively. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) has low melt viscosity, narrow processing temperature window, and poor thermal stability, so it cannot be directly blown into film. Such as figure 1 As shown, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) material enters runner 4, polyethylene enters runners 3 and 5, and modified poly(butylene adipate / terephthalate) Enter runners 2 and 6, die head temperature is 160°C, film inflation molding stage temperature is 131-135°C, inflation...
experiment example 3
[0076] Using the same method in Example 2, the difference from Example 2 is that the temperature of the film inflation molding stage is 140-145 ° C, the inflation ratio is 3.5, and the temperature of the film cooling and solidification stage is 80-85 ° C, The total thickness of the finally obtained five-layer co-extruded film was 140 μm, and the protective layer material was directly peeled off to obtain a single-layer poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) film with a thickness of about 24 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com