Method for detecting tumor exosome-induced cell canceration process based on atomic force microscopy
An atomic force microscopy, inducing cell technology, applied in scanning probe microscopy, measuring devices, scanning probe technology, etc., can solve the problems of ignoring changes in the physical properties of exosome cells, unable to detect multi-dimensional information of cells, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
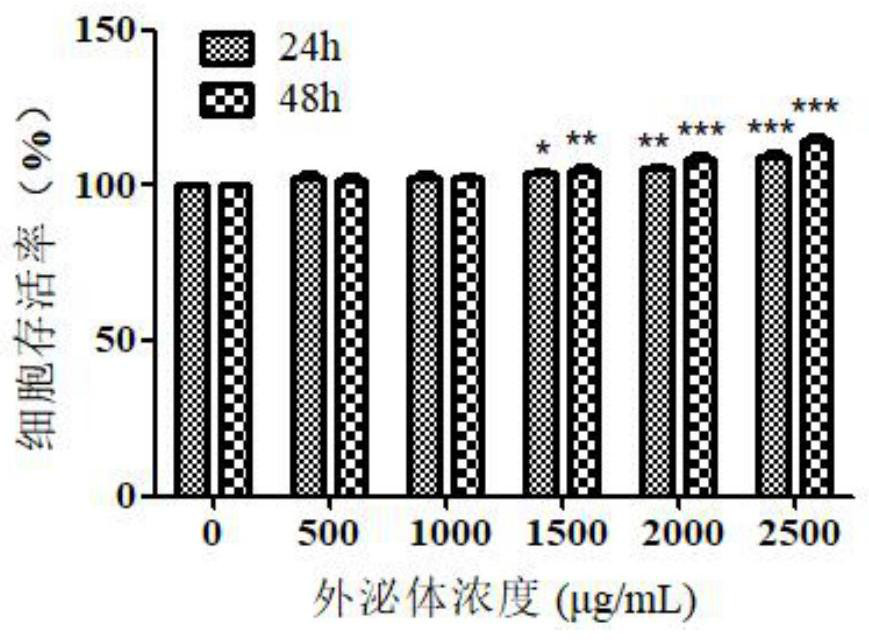
[0024] HL-7702 cells in 8×10 3 / well density into 96-well culture plates. After the cells grew to 80%, the control group was cultured with 1640 medium containing 10% FBS and 1% double antibody (penicillin / streptomycin), and the experimental group was cultured with different concentrations of HCC-LM3-exos (500, 1000, 1500, 2000 and 2500 μg / mL) culture medium. After culturing for 24h and 48h, the absorbance value of each well solution at a wavelength of 490nm was measured by the MTT method. Experimental results such as figure 1 As shown, HCC-LM3-exos at a concentration of 1500 μg / mL can significantly promote the proliferation of HL-7702 cells, and the proliferation effect is more significant with the increase of time and concentration.
Embodiment 2
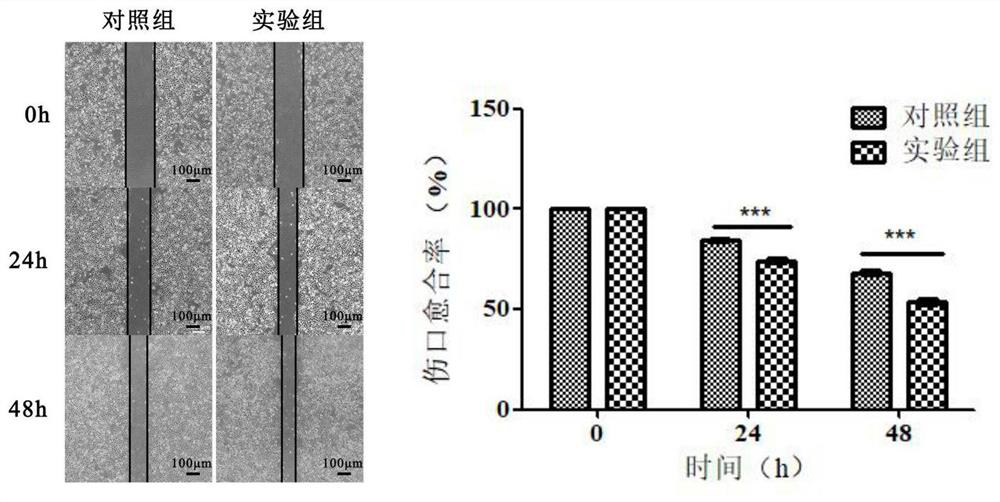
[0026] HL-7702 cells were seeded in 6-well plates. When the cell fusion rate reaches about 90% of the bottom area of the culture dish, use a 200 μL yellow sterile pipette tip to draw a vertical line in the center of each well, wash with PBS twice, and remove floating cells. The experimental group was added with medium containing 1500 μg / mL HCC-LM3-exos, and the control group was cultured with normal medium. The scratched position of the cell was photographed at 0h, 24h and 48h respectively. Such as figure 2 As shown, the results showed that the wound healing rate of the cells in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the migration effect was more significant with the increase of time.
Embodiment 3
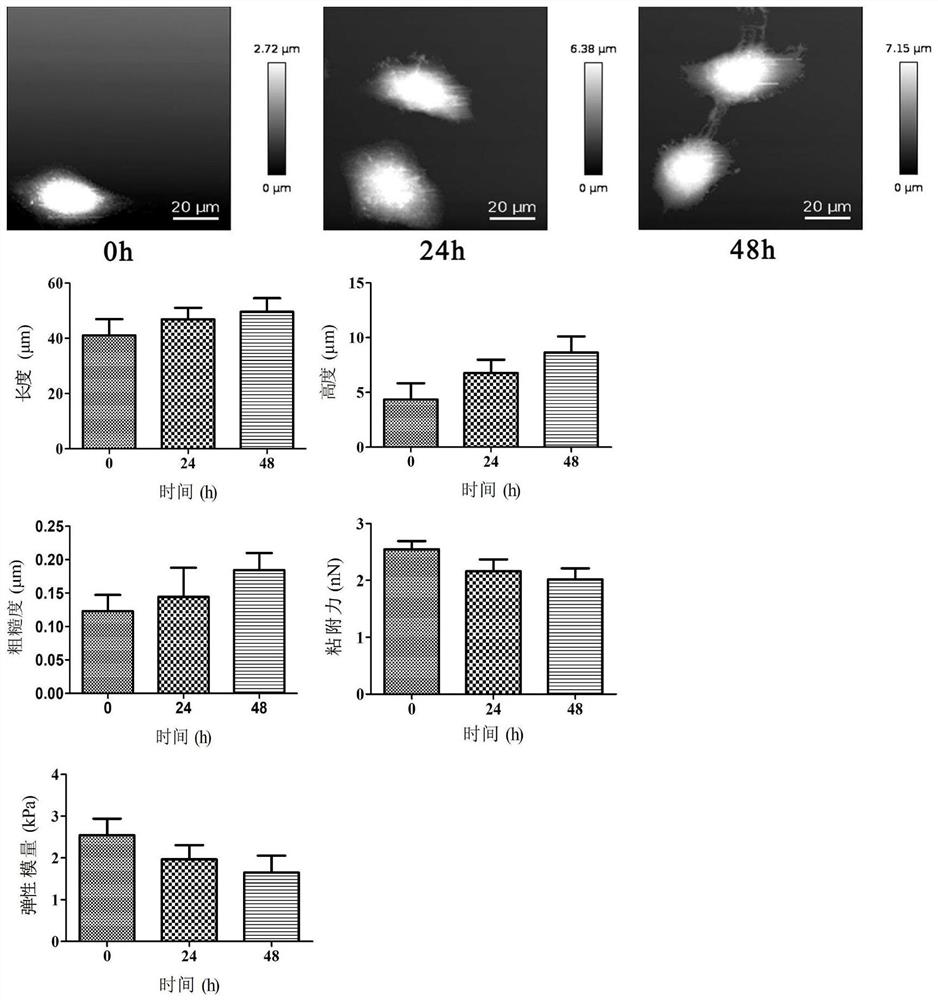
[0028] The morphology, elastic modulus, adhesion, and surface roughness of cells were measured using an atomic force nanomanipulation system. First, HL-7702 cells were seeded on coverslips at an appropriate density at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 cultured under concentration conditions. The control group was cultured with normal medium, and the experimental group was added with HCC-LM3-exos at a concentration of 1500 μg / mL. After culturing for 24h and 48h, the cells were detected. The model of the atomic force probe used in the experiment is SHOCONG-10, and the spring constant used in the experiment is 0.1N / m. Experimental results such as image 3 As shown, the edges of the cells in the control group were clear, but after being treated with HCC-LM3-exos for different times, the edges of the cells were blurred and showed a state of outward diffusion. As the treatment time of HCC-LM3-exos increased, the cell length, height, and surface roughness increased, while the adhesion force and ela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com