Method for short-process extraction of rubidium chloride from rubidium-containing high-salt brine
A rubidium chloride, short-process technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, rubidium/cesium/francium compounds, polluted waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers treatment, etc. Small size, serious potassium co-extraction phenomenon, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of subsequent treatment, reducing the amount of production, and reducing the number of stages of extraction and washing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
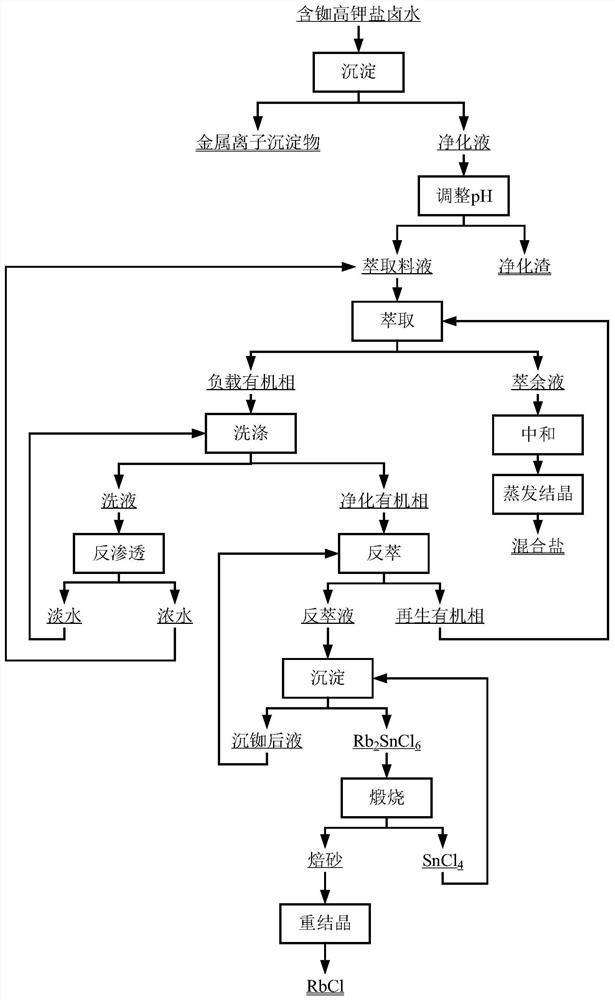
[0046] use figure 1 The process flow shown is to extract rubidium from a certain solid waste leach solution (ie high potassium salt brine containing rubidium), and its main metal components are shown in Table 1.
[0047] Table 1 Main metal components of solid waste leachate
[0048] Element Rb Cs K Na Cu Zn Content (g / L) 3.77 0.41 140.71 47.23 4.78 2.10
[0049] S1: Add NaOH to the solid waste leaching solution, adjust the pH value of the solution to 10, let it stand for 2 hours, precipitate metal ion precipitates, filter and remove the metal ion precipitates, and obtain a purified solution;
[0050] S2: adding NaOH to the purification solution obtained in step S1, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 13.5, and filtering after standing for 2 hours to obtain the extraction material liquid and the purification residue;
[0051] S3: performing extraction-washing-reverse osmosis-back-extraction treatment on the extraction liquid obtained ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] use figure 1 The process flow shown is to extract rubidium in the leaching solution of a certain rubidium-containing ore sinter (ie high-potassium salt brine containing rubidium), and its main metal components are shown in Table 4.
[0064] Table 4 Main metal components of rubidium-containing ore sinter leachate
[0065] Element Rb Cs K Na Cu Zn Pb Content (g / L) 1.74 0.005 88.21 13.26 1.34 8.72 1.11
[0066] S1: adding NaOH to the leaching solution of rubidium-containing ore sinter, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 10, standing for 2 hours, depositing metal ion precipitates, filtering and removing the metal ion precipitates, and obtaining a purified solution;
[0067] S2: adding NaOH to the purification solution obtained in step S1, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 13.5, and filtering after standing for 2 hours to obtain the extraction material liquid and the purification residue;
[0068] S3: performing extract...
Embodiment 3
[0080] use figure 1 The process flow shown is to extract rubidium in a simulated rubidium-containing salt lake water (ie, rubidium-containing high-potassium salt brine), and its main metal components are shown in Table 7.
[0081] Table 7 The main metal components of simulated rubidium-containing salt lake water
[0082] Element Rb Cs K Na Li Mg Content (g / L) 0.21 0.002 27.72 96.95 6.85 28.38
[0083] S1: adding NaOH to the leaching solution of rubidium-containing ore sinter, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 10, standing for 2 hours, depositing metal ion precipitates, filtering and removing the metal ion precipitates, and obtaining a purified solution;
[0084] S2: adding NaOH to the purification solution obtained in step S1, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 13.5, and filtering after standing for 2 hours to obtain the extraction material liquid and the purification residue;
[0085] S3: performing extraction-washing-rever...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com