Pd-1 variant having improved binding to pd-l1
A PD-L1 and PD-1 technology, applied in the direction of peptides containing affinity tags, fusion peptides, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of immunogenicity and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
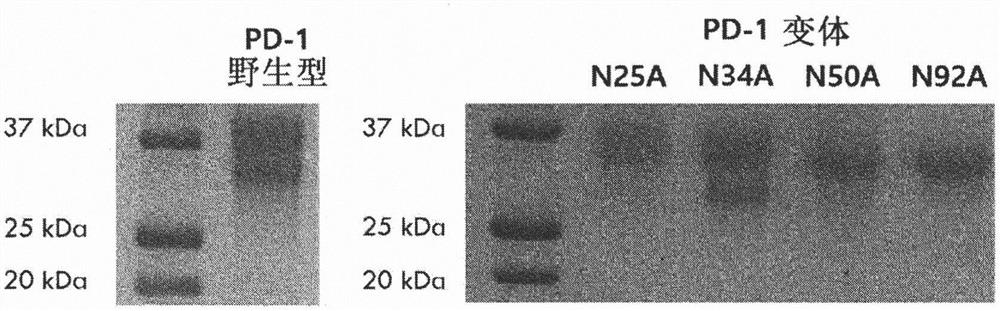
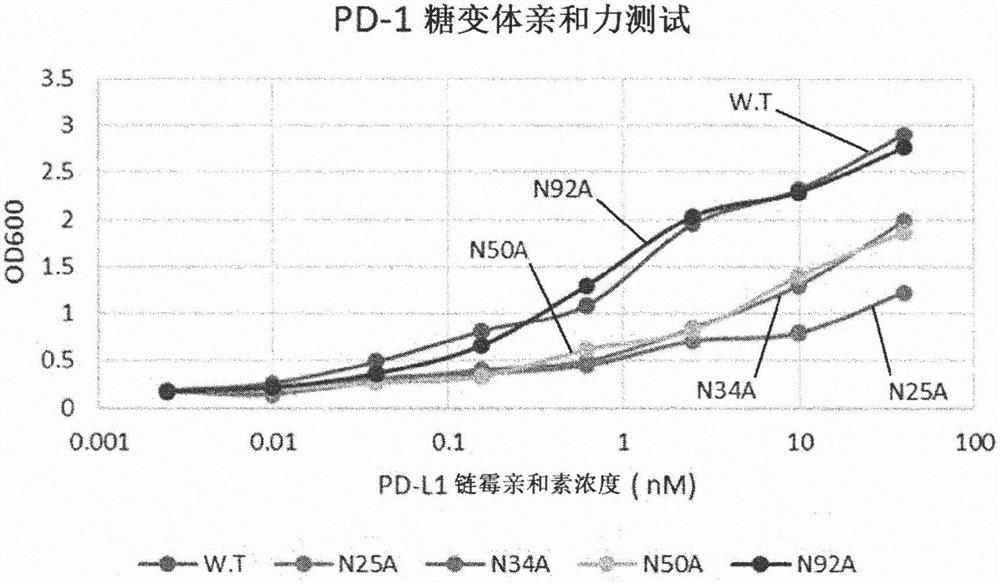
[0100] Example 1: Validation of N-linked glycosylation sites affecting binding to human PD-L1
[0101] To verify that the glycosylation of human PD-1 actually plays an important role in the binding affinity to PD-L1, each of the four glycosylation sites present in PD-1 was tested by deglycosylation Effect of glycosylation on binding affinity. Because PD-1 has four N-glycosylation sites, four genes (N25A, N34A, N50A, N92A) were made by replacing each asparagine at the four sites with alanine. Using the template gene (catalogue number: HG10377-M) and primers for PD-1 (CKJ#1, CKJ#2) and Vent polymerase to amplify by PCR encoding PD-1 outer membrane site (amino sequence L25-Q167) DNA fragments. The amplified DNA fragment was treated with BssHII and XbaI enzymes, and ligated into pMaz vector, which is a vector for expression in animal cells, which was treated with the same enzymes. Transformation into Jude1((F-mcrAΔ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) After 80 lacZΔM15 ΔlacX74 recA1 endA1 araD1...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Example 2: Cloning of Tetrameric Human PD-L1 (PD-L1-Streptavidin) for PD-1 Engineering
[0106] The cDNA of human PD-L1 gene was purchased from Sino Biotech (Cat. No.: HG10084-M), and the gene of PD-L1 outer membrane was amplified by PCR using primers (HW#1, HW#2) and Vent polymerase (Amino sequence F19-R238). Since the dissociation constant between wild-type PD-1 and wild-type PD-L1 is not good enough (equilibrium dissociation constant, KD = about 8.7 μM), tetramerization induction by efficient screening of aglycosylated PD-1 variants affinity effect. Tetramerization was induced by expressing streptavidin at the C-terminus of PD-L1, and a GS linker was inserted between streptavidin and PD-L1 to ensure the flexibility of each protein. After gene amplification using primers (HW#3, HW#4) and Vent polymerase (New England Biolab), assembly PCR was performed using the previously amplified PD-L1 gene and Vent polymerase. The prepared gene was treated with BssHII and XbaI r...
Embodiment 3
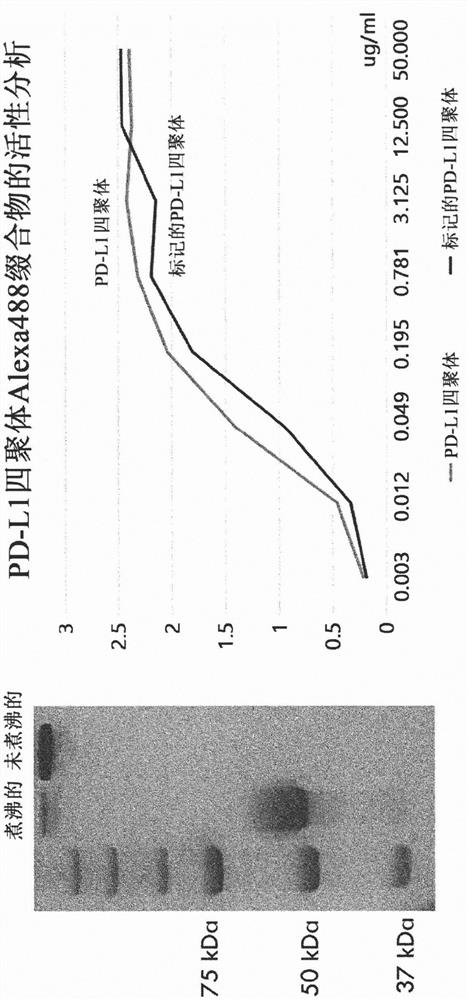
[0107] Example 3: Expression, purification and fluorescent labeling of tetrameric PD-L1-streptavidin in animal cells
[0108] The prepared vector for tetrameric PD-L1 expression was transfected into animal cells (HEK293F). After culturing the cells for 6 days, the cell culture was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was taken and filtered through a 0.22 μm filter. The filtered supernatant was bound to 1 mL of Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen) for 16 hours at 4°C. The bound resin was washed with 10 CV of 10 mM imidazole (Sigma) in PBS and then again with 10 CV of 20 mM imidazole in PBS. Finally, the protein was eluted and recovered with 250 mM imidazole in PBS. The purified PD-L1 tetramers were fluorescently labeled using the Alexa-488 labeling kit. The result of ELISA test is that fluorescently labeled tetrameric PD-L1 shows excellent binding affinity to PD-1 ( image 3 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com