Application of inhibitor of histone methyltransferase DOT1L in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating peritoneal fibrosis after peritoneal dialysis
A methyltransferase, peritoneal dialysis technology, applied in the direction of drug combinations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antipyretics, etc., can solve problems such as poor effect, achieve significant technological progress, reduce inflammatory cell infiltration, reduce Effects of peritoneal pathological changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Embodiment 1 Materials and methods
[0017] 1) Reagent consumables
[0018] DOT1L, H3K79me2, Snail, and Slug antibodies were purchased from Abcam. Vimentin antibody was purchased from cell signalingTechnology company. Collagen I (A2), E-cadherin and GAPDH antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Company. F4 / 80 antibody was purchased from Sewell Company. EPZ5676 was purchased from APExBIO company. α-SMA antibody and other reagents were purchased from Sigma.
[0019] 2) Mouse peritoneal fibrosis model and experimental grouping
[0020] The mouse peritoneal fibrosis model was established by intraperitoneal injection of 4.25% high glucose peritoneal dialysis fluid. All animal experiments complied with the Chinese regulations on the management and use of laboratory animals.
[0021] 28-day mass percent concentration of 4.25% high-glucose peritoneal dialysis fluid induced mouse peritoneal fibrosis model
[0022] a. sham group (n=6): intraperitoneal injection of the s...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 EPZ5676 inhibits the occurrence of peritoneal fibrosis in mice induced by high-glucose peritoneal dialysis fluid
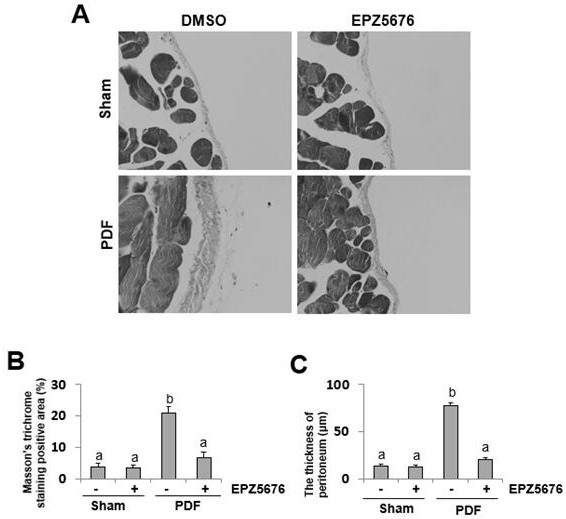
[0042] In the animal model, the present invention successfully establishes the animal model of peritoneal fibrosis after 28 days by giving mice an intraperitoneal injection of 3ml of high-glucose peritoneal dialysis solution with a mass percentage concentration of 4.25%. Masson staining shows that the subperitoneal area of the mice in the dialysis group is significantly thickened. The mice in the treatment group were given intraperitoneal injection of EPZ5676 after daily injection of high-glucose peritoneal dialysis solution. It was found that EPZ5676 treatment could significantly reduce the peritoneal thickness and the positive area of Masson staining ( figure 1 A-1C). The above results indicate that DOT1L may play an important regulatory role in the development of peritoneal fibrosis, and the DOT1L inhibitor EPZ5676 can alleviate the occur...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 EPZ5676 inhibits mouse peritoneal epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition induced by high-glucose peritoneal dialysis fluid
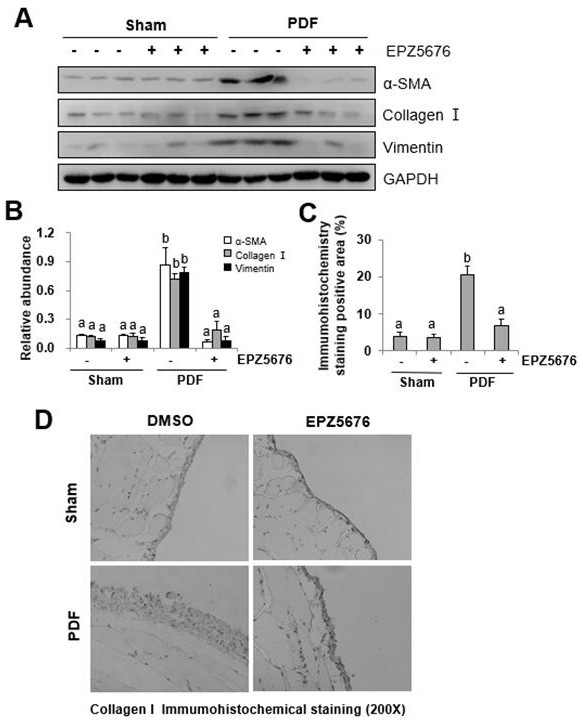
[0044] In the animal model of the present invention, the expression of ECM protein and EMT-related markers α-SMA, Collagen I and Vimentin in the peritoneal tissue is further detected by immunoblotting technology. The results showed that α-SMA, Collagen Ⅰ and Vimentin were highly expressed in the peritoneal tissue of mice injected intraperitoneally with high glucose dialysate for 28 days, and EPZ5676 could significantly down-regulate the expression levels of these proteins ( figure 2 A and 2B). Similarly, immunohistochemical staining showed that the expression of Collagen Ⅰ increased in the dialysis model group and decreased in the treatment group ( figure 2 C and 2D). These results indicated that EPZ5676 could inhibit high glucose peritoneal fluid-induced EMT and ECM deposition in mouse peri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com