Nanoparticle targeting breast cancer cell and lymph node metastasis focus, preparation method and application
A technology for lymph node metastasis and breast cancer cells, which is applied in the field of preparation and dual-targeting of nanoparticles of breast cancer cells and their lymph node metastases, can solve the problems of low reliability of identification of breast cancer lymph node metastasis, and achieves good labeling effect and improved The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The embodiment of the present invention provides a preparation method of nanoparticles for double-targeting breast cancer cells and their lymph node metastases:
[0058] A1, first weigh 14mg HA and dissolve it in 5ml deionized solution, add 6mg carbodiimide (EDAC), and react at 37°C for 2h; then add 0.5mg DMPE phospholipid to the HA solution, and continue to react at 37°C for 24h. After purification, the HA-DMPE polymer is obtained, and finally the HA-DMPE polymer is verified by hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum (1H NMR).
[0059] A2, weigh DMPC (3μmol), C.O (0.1μmol), DiR-BOA (0.2μmol), DSPE-PEG200 (0.0114μmol) and HA-DMPE (0.04μmol) respectively in glass test tubes, add 500μl chloroform solution to fully Mix and seal the tube with parafilm.
[0060] A3, vacuum drying
[0061] The mixture in step A2 was passed through a steady stream of nitrogen to dry the chloroform in the test tube, and then the test tube was dried in a vacuum desiccator for 1 h.
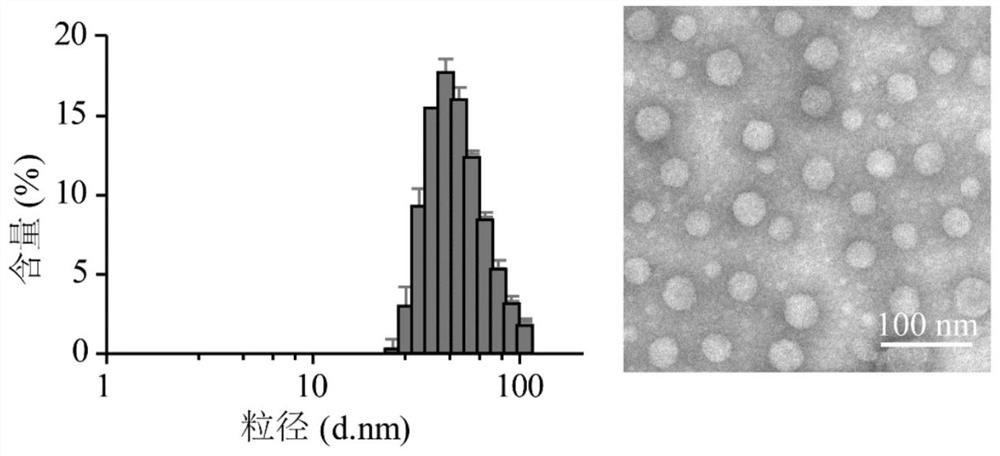
[006...
Embodiment 2
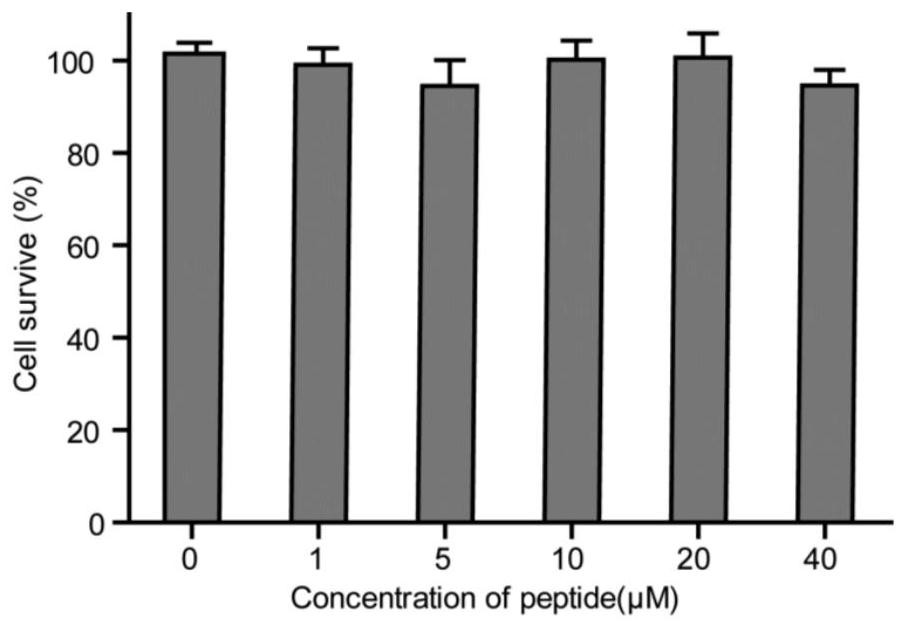
[0070] For the toxic effect of the dual-targeted nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 on 4T1 breast cancer cells, see figure 2 . figure 2 It is shown that in the range of 1-40 μM R4F polypeptide concentration of nanoparticles, the interaction between nanoparticles and 4T1 breast cancer cells for 24 hours has basically no great impact on the survival of breast cancer cells. These results indicate that hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles have good biocompatibility for in vivo applications.
Embodiment 3
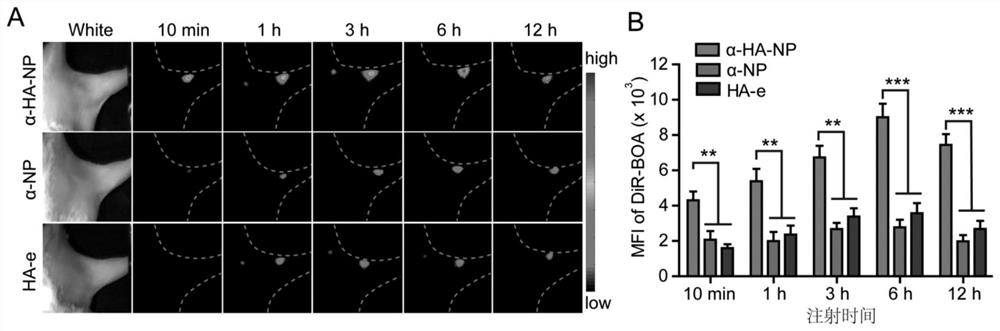
[0072] The effect of α-HA-NP prepared in Example 1 targeting lymph nodes is shown in image 3 . After the nanoparticles were subcutaneously injected from mouse footpads, the aggregation effect of nanoparticles in lymph nodes was observed at different time points using a whole-body fluorescence imaging system. The imaging results showed that the dual-targeted nanoparticle α-HA-NP can quickly (less than 10min) accumulate in the lymph nodes of the knee bend, and the fluorescence signal intensity in the lymph nodes is much stronger than that of the single-targeted nanoparticle α-NP in the control group and HA-e. At 6h, the fluorescence signal intensity in the lymph nodes of α-HA-NP group was 3.0 and 2.3 times that of α-NP and HA-e, respectively, and at 12h, it was 3.2 times and 2.5 times, respectively. This result shows that the dual-targeted nanoparticles can target lymph nodes quickly and efficiently, laying the foundation for in vivo labeling of lymph nodes with tumor metasta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com