High-ductility self-recovery cement-based material and preparation method thereof
A cement-based material and self-restoring technology, which is applied in the field of high-ductility self-restoring cement-based materials and its preparation, can solve problems such as limiting the use of shape memory alloys, difficulty in implementation, and new structural hazards, so as to improve service life and reduce structural damage. Damage, the effect of improving electrical conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
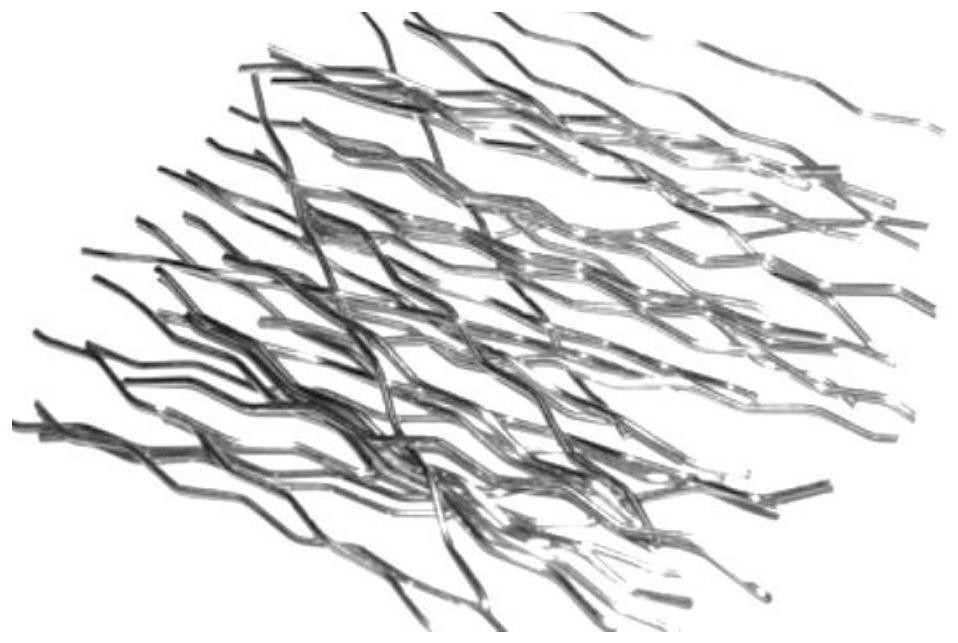
[0024] A high ductility self-healing cement-based material, including cement mortar, carbon black, and SMA fiber. The cement mortar includes the following components according to the mix ratio: 200 parts of Portland I type cement, 25 parts of glass powder, and 400 parts of refined quartz sand , 900 parts of Class I fly ash, 330 parts of water, 4 parts of polycarboxylate high-performance water reducing agent; the unit is Kg / m 3 . Wherein, the dosage of SMA fiber is 0.5% of the volume of cement mortar, and 5 parts of conductive carbon black. The ratio of SMA fiber to carbon black is 32:5. SMA fiber shapes such as figure 1 shown.
[0025] The method for preparing the above-mentioned high-ductility self-healing cement-based material specifically includes the following steps:
[0026] (1) Accurately weigh the quality of each raw material according to the mix ratio;
[0027] (2) Start the mixer, first wet the inner surface of the mixer, then add cement, quartz sand, fly ash and...
Embodiment 2
[0032] On the basis of Example 1, different from Example 1, 250 parts of Portland Type I cement, 20 parts of glass powder, 420 parts of refined quartz sand, 900 parts of Class I fly ash, 350 parts of laboratory tap water, 6 parts of polycarboxylate high-performance water reducing agent, 10 parts of conductive carbon black, the volume content of SMA fiber is 1%, and the ratio of SMA fiber to carbon black is 64:10.
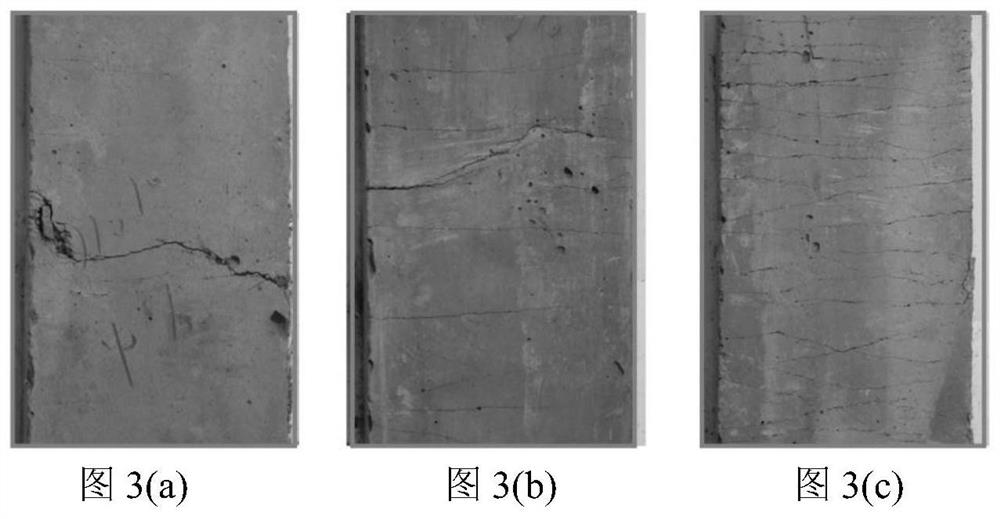
[0033] The test under the same conditions as in Example 1 showed that the 28d tensile strength was 4.8 MPa, and the ultimate tensile strain was 0.23%. In its ultimate tensile strain stage, the stress is removed after cracking, and after standing for a period of time, most of the tiny cracks are closed, and the closing rate reaches more than 50%, and the width of the main cracks in the final stretching area is significantly reduced, as image 3 (b) shown. By comparing the change of resistivity after cracking and recovery, it is found that the resistivity after recov...
Embodiment 3
[0035] On the basis of Example 1, different from Example 1, 200 parts of Portland Type I cement, 950 parts of Class I fly ash, 350 parts of laboratory tap water, 10 parts of conductive carbon black, the volume of SMA fiber mixed The amount is 1.5%, and the ratio of SMA fiber to carbon black is 96:10.
[0036] The test was carried out under the same conditions as in Example 1, the 28d tensile strength was 5.0 MPa, and the ultimate tensile strain was 0.37%. In its ultimate tensile strain stage, the stress is removed after cracking, and after standing for a period of time, most of its tiny cracks are closed, and the closing rate reaches more than 80%. The width of the main cracks in the final stretching area is obviously reduced and almost completely closed, showing an obvious cracking mode with many cracks, such as image 3(c) shown. By comparing the change of resistivity after cracking and recovery, it is found that the resistivity after recovery is 75% lower than that after ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com