Bacterial nucleic acid extraction lysate as well as preparation method and application thereof
A bacterial nucleic acid and lysate technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of unfavorable detection accuracy, increased nucleic acid contamination, and difficulty in obtaining high-purity and high-yield nucleic acid.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] In this example, human feces were used as biological samples for nucleic acid extraction and detection.
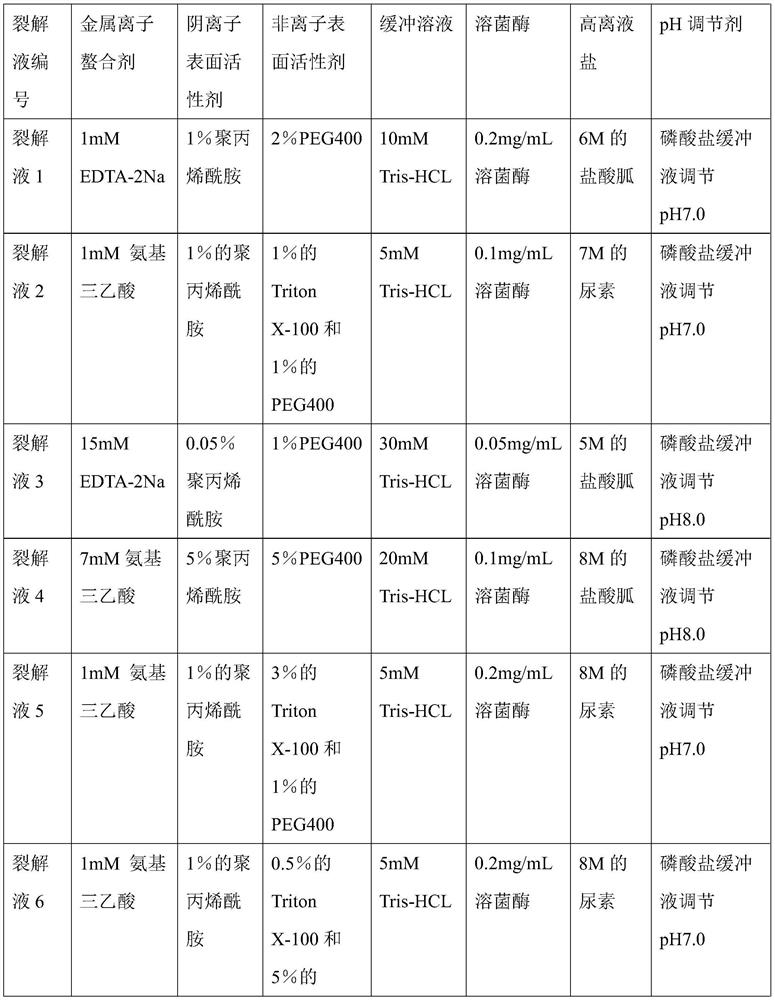
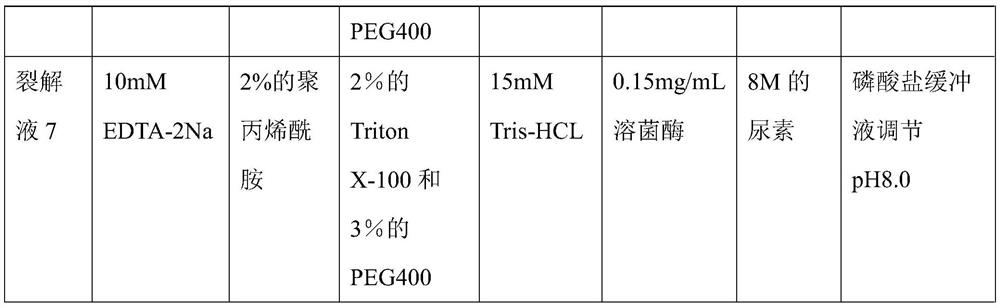
[0021] 1. Preparation of lysate: Prepare 7 parts of lysate according to the ratio of raw material components, as shown in the table below:
[0022] Table 1 lysate 1-7 component list
[0023]
[0024]
[0025] 2. Stool sample processing: For 7 stool samples of patients with diarrhea, draw 1.5mL of stool samples into 2mLEP tubes, centrifuge at room temperature, 2500rpm, 90s, draw 800μL of supernatant and mix well, then quickly dispense 200μL of supernatant to 3 new 2mL EP tubes and place on ice.
[0026] 3. Nucleic acid extraction: Centrifuge the above-mentioned 2mL EP tube containing 200 μL supernatant at 12000 rpm for 2 minutes to discard the supernatant, add 100 μL of the lysate of the present invention to the collected precipitate, mix well, and place in a metal bath at 37 °C Heated at medium temperature for 20 minutes, and vortexed 3-4 times during the he...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Use saliva as a biological sample for nucleic acid extraction and detection.
[0032] 1. Sample processing and nucleic acid extraction: Take 7 samples of saliva without pretreatment. After mixing them upside down, add 7 parts of the lysate prepared in Example 1, mix well, and heat in a metal bath at 37°C for 20 minutes. , and vortex 3-4 times during the heating process. After the heating is completed, vortex again to mix and boil in a metal bath at 100°C for 10 minutes; after cooling slightly, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 2 minutes, and the supernatant obtained can be used for nucleic acid amplification. Increased DNA solution.
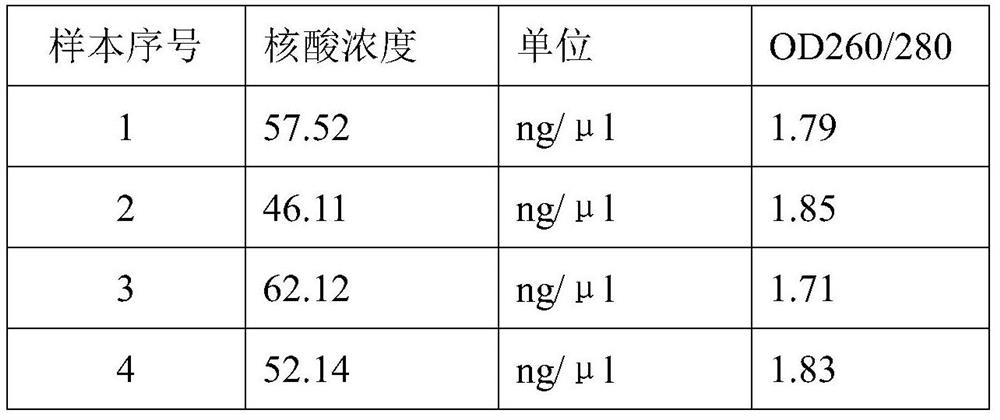
[0033] 2. Nucleic acid detection: 7 parts of the extracted saliva samples in Example 1 were respectively tested for nucleic acid concentration, and the test results are shown in Table 3 below; it shows that the lysate of the present invention is used to extract nucleic acid with high efficiency and high purity.
[0034] Table 3 Detection of Nuc...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Nasal swabs were used as biological samples for nucleic acid extraction and detection.
[0038] 1. Sample processing and nucleic acid extraction: Take 7 nasal swab samples without pretreatment. After mixing them upside down, add 7 lysates prepared in Example 1, mix well, and place them in a metal bath at 37°C Heat for 20 minutes, and vortex 3-4 times during the heating process. After the heating is completed, vortex and mix again, then place in a 100°C metal bath and boil for 10 minutes; after a little cooling, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2 minutes, and the supernatant obtained can be used DNA solution for nucleic acid amplification.
[0039] 2. Nucleic acid detection: 7 parts of the extracted nasal cavity swab samples in Example 1 were respectively tested for nucleic acid concentration, and the test results are shown in Table 4 below; it shows that the efficiency and purity of nucleic acid extraction using the lysate of the present invention are high.
[0040] Table 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com