Method for removing iopamidol in water by UV/NH2Cl combined process
A combined process and water removal technology, which is applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of limited treatment effect, unstable removal rate, and low removal rate, and achieve the effects of complete degradation, improved feasibility and operability, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] UV / NH 2 Cl combined process removes the method for iopamidol in water, and concrete steps are as follows:
[0049] Use ultrapure water to prepare the initial concentration of iopamidol to be 10 μM, use acid and alkali solution to adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0, add NH to the iopamidol solution 2 Cl, the dosage is 200μM, and the ultraviolet radiation is carried out at the same time, and the ultraviolet intensity is controlled to be 2.43mW / cm 2 , control the reaction temperature to 25°C.
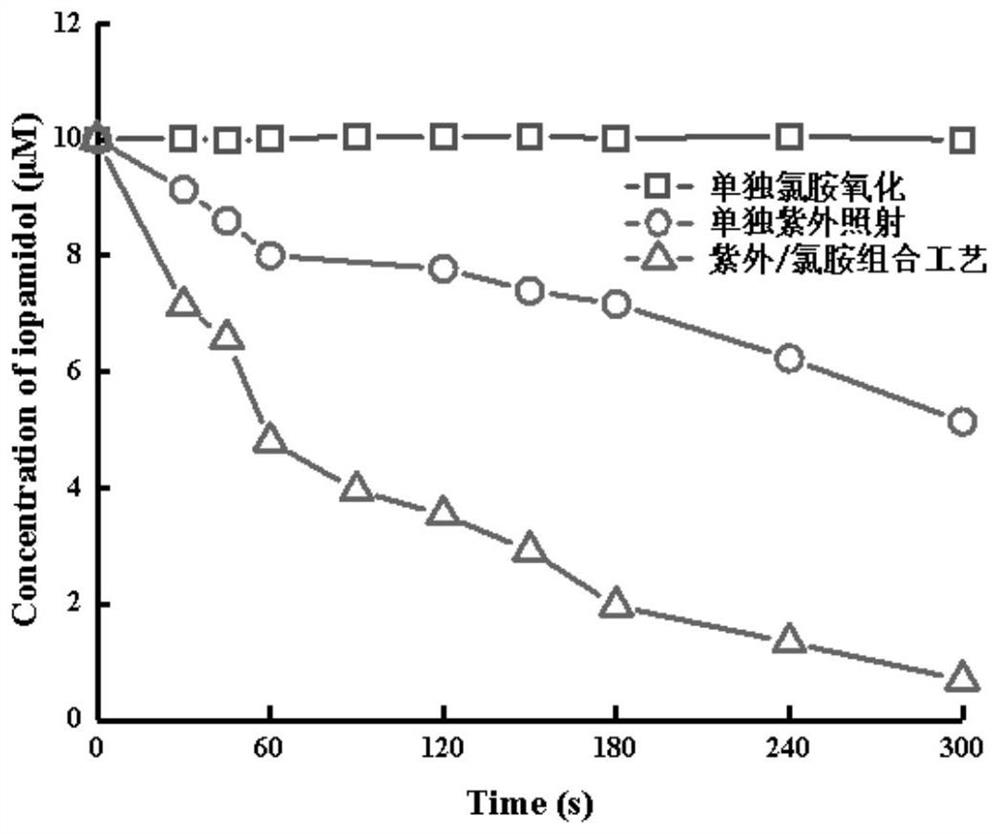
[0050] NH alone 2 Cl process (comparative example 1), separate UV process (comparative example 2) and UV / NH 2 In the Cl combined technique (embodiment 1), the iopamidol concentration curve with time is as figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that the removal effects of iopamidol under different processes are different. UV / NH 2 The simultaneous action of Cl can greatly increase the removal rate of iopamidol. NH alone 2 The Cl process has almost no removal effect ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] UV / NH 2 Cl combined process removes the method for iopamidol in water, and concrete steps are as follows:
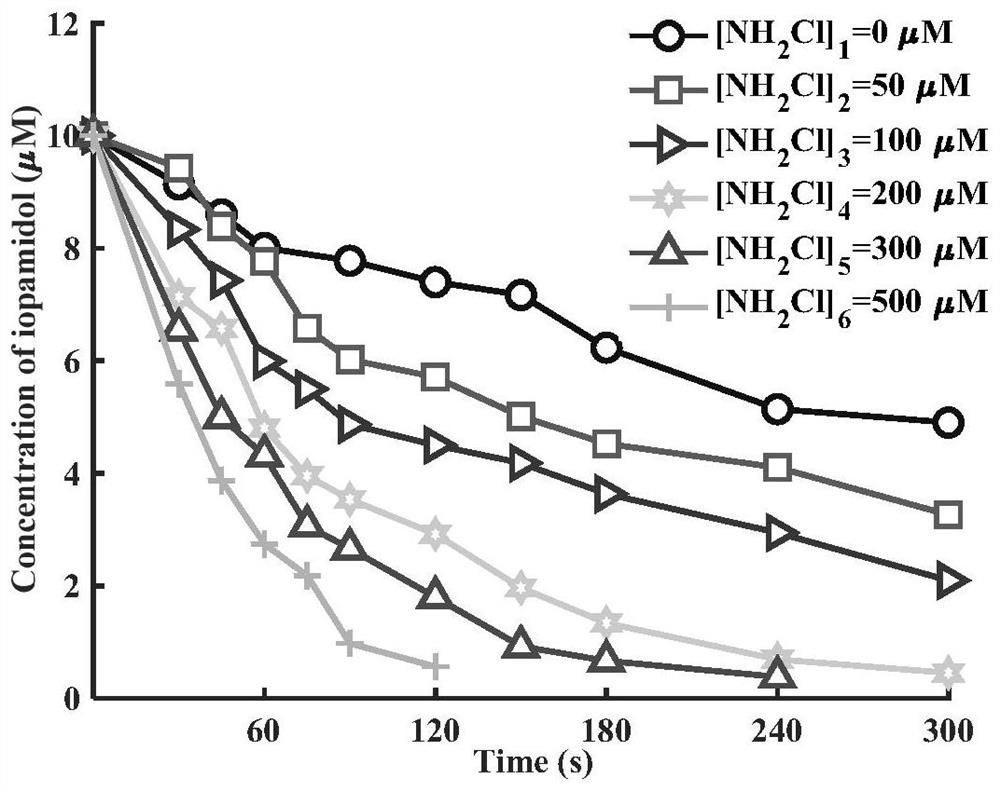
[0053] Use ultrapure water to configure the initial concentration of iopamidol to be 10 μM, use acid and alkali solution to adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0, add NH to the iopamidol solution 2 Cl, control NH 2 The dosing concentration of Cl was 0, 50, 100, 200, 300 and 500 μM, and at the same time, UV irradiation was carried out immediately and the UV intensity was controlled at 2.43mW / cm 2 , the reaction temperature is controlled at 25°C during the reaction, and the degradation of iopamidol after 300s of reaction is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0054] From figure 2 It can be seen that the removal efficiency of iopamidol increases with that of NH 2 increased with the increase of Cl dosage. Under the same UV intensity, with NH 2 The concentration of Cl gradually increased from 0 to 500 μM, and the removal rate of iopamidol also increased ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] UV / NH 2 Cl combined process removes the method for iopamidol in water, and concrete steps are as follows:
[0057] Use ultrapure water to configure the initial concentration of iopamidol to be 10 μM, use acid and alkali solution to adjust the initial pH of iopamidol solution to 7.0, add NH to the iopamidol solution 2 Cl, the dosage is 200μM, and UV irradiation is carried out at the same time, and the UV intensity is controlled to be 0, 2.43, 4.94, 7.34 and 9.76mW / cm 2 , and the reaction temperature is controlled at 25°C, the degradation of iopamidol after 300s of reaction is detailed in image 3 .
[0058] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the intensity of ultraviolet light directly determines the generation rate of free radicals in the system. With the increase of ultraviolet intensity, the photodegradation rate of iopamidol is gradually accelerated. The UV intensity is 9.76mW / cm 2 , the degradation rate of iopamidol reached 99.12% in only 60s. UV / NH 2 The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com