Nanocage probe, application thereof and nucleic acid detection method
A detection method and nanocage technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem that the pretreatment operation is difficult to meet the sensitivity and accuracy of nucleic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a nanocage probe with nucleic acid recognition function, comprising the following steps:
[0055] Step 1, preparation of silver ball template: dissolve 85mg of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in 20mL of ultrapure water, stir in a round bottom flask and add 85mg of AgNO 3 Let it dissolve completely. Then 200 μL of sodium chloride solution (5M) was added, and AgCl colloid was obtained after stirring for 15 minutes in the dark. In another clean flask, mix 2.5 mL of 0.5 M NaOH solution and 20 mL of 50 mM ascorbic acid solution, and then drop in 2.5 mL of freshly prepared AgCl colloid. The mixture was stirred for 2 hours in the dark, and the silver spheres were collected by washing by centrifugation.
[0056] Step 2. Synthesis of gold / silver nanocages: Dilute the silver nanospheres prepared according to step 1 into 100ml of water, add 200mg of PVP, and heat to boiling for 10 minutes. Then 1.5 mL of HAuCl was added dropwise 4 sol...
Embodiment 2
[0060] This example is the modification of the surface of nanocage particles and its application in dark field imaging monitoring. This embodiment takes microRNA-21 as an example.
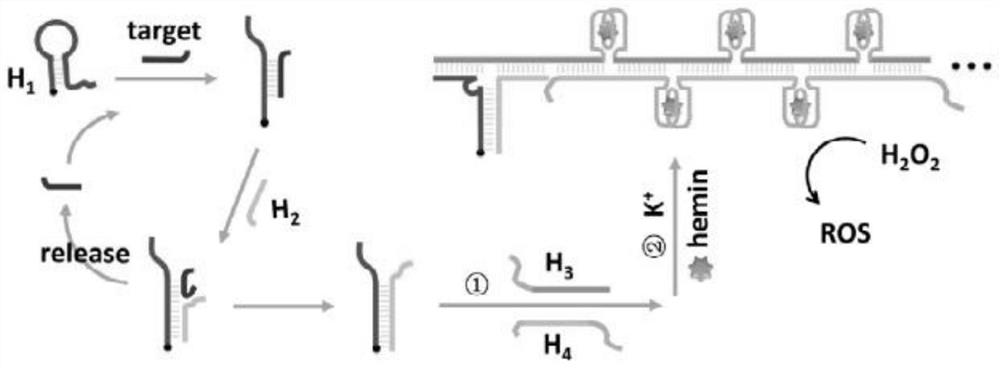
[0061] Step 1. According to Example 1, a nanocage probe with nucleic acid recognition function was prepared, and the plasma probe was dispersed and fixed in a detection cell on a positively charged glass surface, thereby obtaining a detection substrate. Add 20 μL of the solution containing microRNA-21 and H2 to the pool and incubate for 1 h. Then incubate with PBS solution containing H3 and H4. After reacting for 1 h, incubate with PBS solution containing heme (50 μM) and K- (0.1 M). Wherein, after each step of incubation, the reaction pool is washed with PBS buffer; finally, G-quadruplex-heme DNase is formed. Such as figure 1 As shown, after the target strand to be tested is hybridized with the hairpin DNA, the hairpin structure opens to form a straight chain. At this time, H2 in the solution ...
Embodiment 3
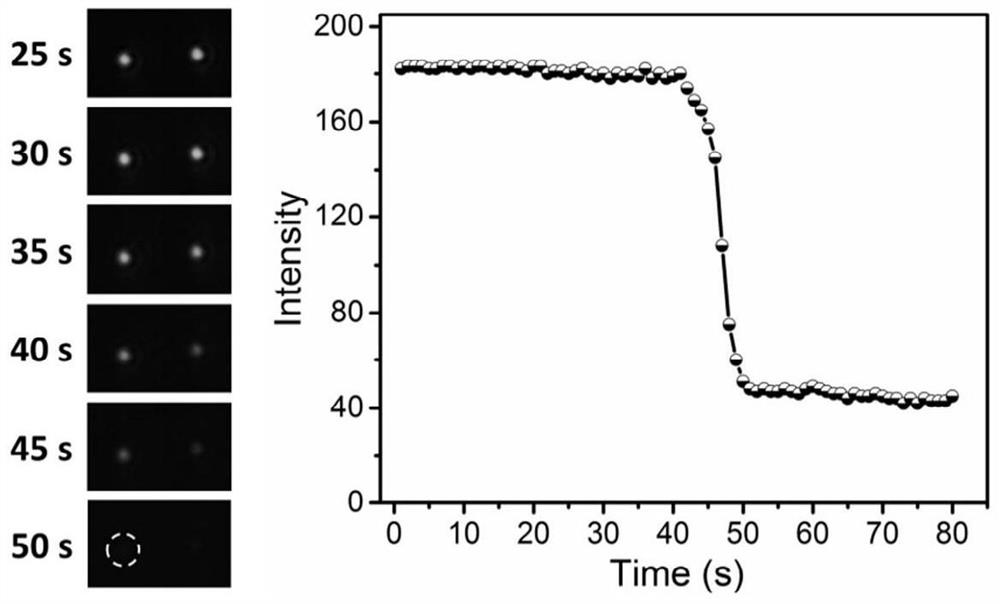
[0070] This embodiment is the application of the quantitative detection and analysis process of microRNA-21. The detection of microRNA and the acquisition of dark-field signals were carried out according to Example 2, wherein the concentration of microRNA-21 added in step 1 was 20 fM, and other experimental operations and signal recording processes were the same. Under this microRNA-21 concentration, the concentration of 133 particles was analyzed. In response to the light-off signal, count the waiting time of each particle, and use Gaussian fitting to obtain an average waiting time of about 41s, such as Figure 4 shown. Repeat the above steps, experiment with different concentrations of microRNA-21, draw the curve between different concentrations of microRNA-21 and the average waiting time, and fit the linear relationship between the two, such as Figure 5 shown. from Figure 5 It can be seen that the optimal detection concentration of microRNA-21 is at 1×10 -16 ~1×10 -1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com