Application of delinearized ubiquitin enzyme family with sequence similarity 105, member B (FAM105B) to liver cancer diagnosis, treatment and prognosis judgment
A FAM105B, ubiquitinase technology, applied in disease diagnosis, biochemical equipment and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve inflammatory factor secretion disorders, ubiquitin chains, abnormal activation of NF-κB and other problems to achieve the effect of increasing proliferation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1: FAM105B is highly expressed in liver cancer tissues
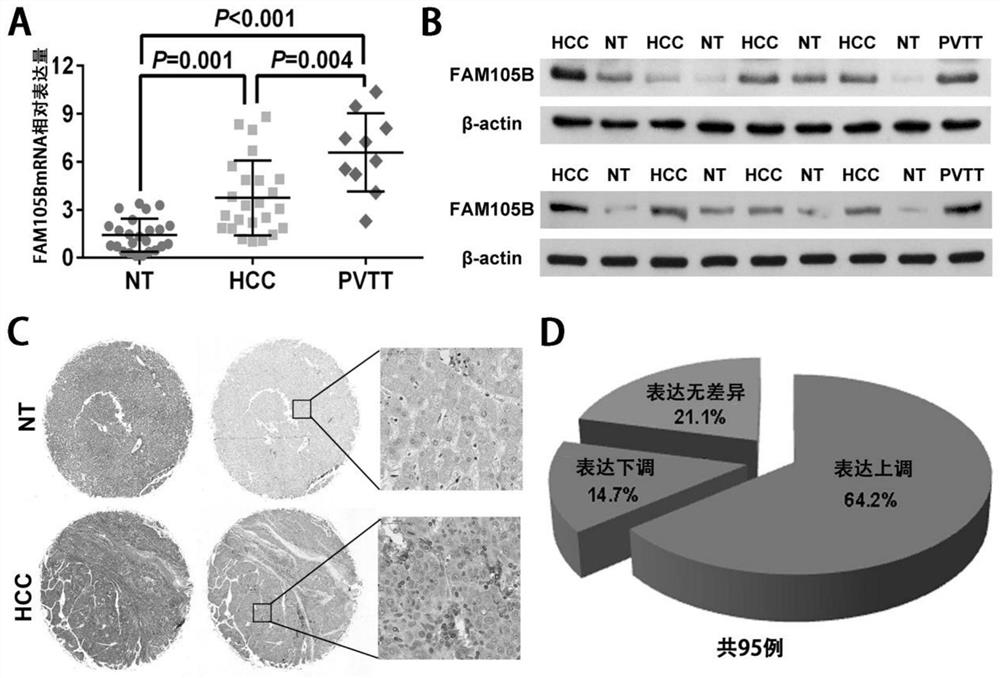
[0103] 24 cases of fresh liver cancer tissues (HCC) and corresponding paracancerous tissues were detected by fluorescent real-time quantitative PCR (see Section 2 of the Experimental Materials and Methods for details) and western blot (see Section 3 of the Experimental Materials and Methods for details). (NT) and the expression levels of FAM105B mRNA and protein in 10 cases of portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT).
[0104] The results showed that the expression levels of FAM105B mRNA and FAM105B protein in fresh liver cancer tissues were significantly higher than those in paracancerous tissues. It is worth noting that, compared with liver cancer tissues and adjacent tissues, the expression level of FAM105B is the highest in portal vein tumor thrombus tissues. For details, see figure 1 A and 1B.
[0105] Tissue chips containing 95 cases of liver cancer specimens were detected by immunohistochemical method (s...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Example 2: High expression of FAM105B indicates poor clinical outcome of patients with liver cancer
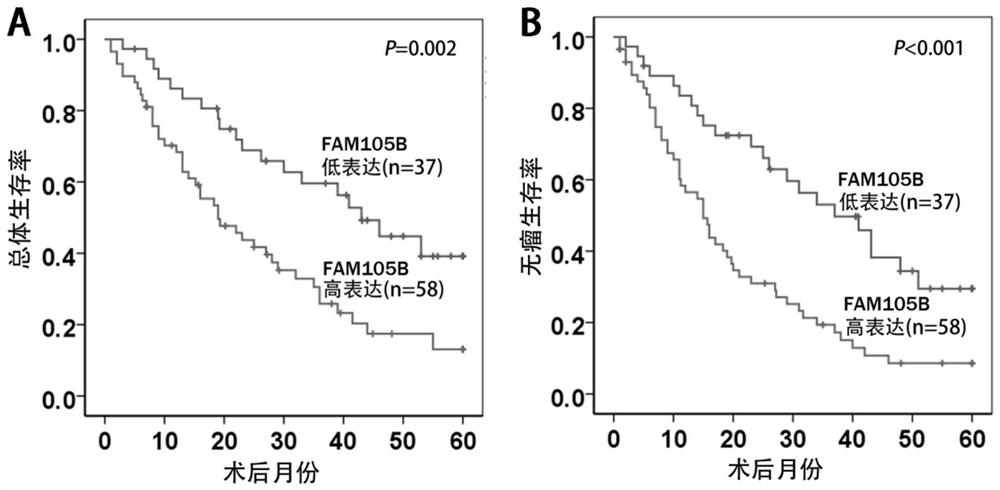
[0110] Combined with clinicopathological data and prognosis follow-up information of liver cancer patients, statistical analysis found that the expression level of FAM105B was correlated with tumor number (P=0.001), tumor capsule (P=0.019), microvascular invasion (P=0.020), and TNM stage (P=0.020). 0.011) and other adverse clinicopathological features were significantly correlated (see Table 1 for details).
[0111] Table 1. The relationship between the expression level of FAM105B in liver cancer tissues and the clinicopathological characteristics of patients
[0112]
[0113] Kaplan-Meier survival curve and Log-rank test were used for prognostic analysis, and the results showed that the overall survival time (Overall Survival, OS) and disease-free survival time (Disease-free Survival, DFS) of the FAM105B high expression group were significantly shorter than those of...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3: In vitro experiments verify that FAM105B can significantly promote the proliferation, migration and invasion abilities of liver cancer cells
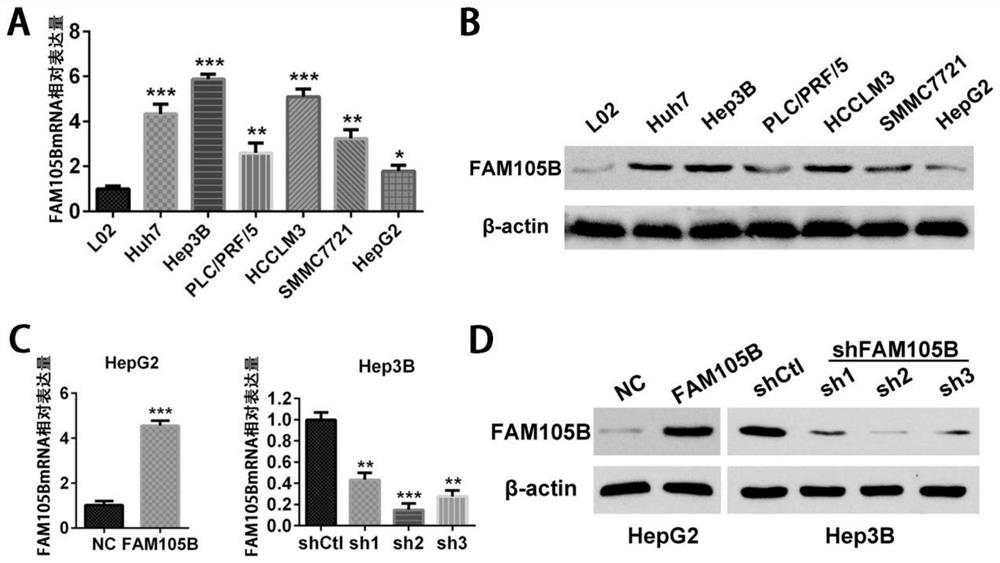
[0119] First, the fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR and western blot methods (see Section 2 and Section 3 of the test materials and test methods for details) were used to detect the effect of FAM105B on the immortalized normal liver cell line L02 and six liver cancer cell lines with different invasion potentials (including Expression levels in Huh7, Hep3B, PLC / PRF / 5, HCCLM3, SMMC7721 and HepG2). The results showed that the expression levels of FAM105B mRNA and FAM105B protein in the liver cancer cell line were significantly higher than those in the normal liver cell line L02 (see image 3 A and 3B).
[0120] Next, the liver cancer cell line HepG2 with low expression of FAM105B and low metastatic potential and the liver cancer cell line Hep3B with relatively high expression of FAM105B and high metastatic potentia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com