Method for selectively protecting restriction enzyme cutting sites in trypsin digestion process
A trypsin and selective technology, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of target protein activity reduction and inactivation, and achieve the effect of reducing affinity and eliminating enzyme cutting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: A method for selectively protecting the enzyme cleavage site during trypsin digestion
[0021] A method for selectively protecting the enzyme cleavage site during trypsin digestion, comprising a polypeptide to be digested by trypsin, the structure of which is: polypeptide 1: SOD fragment 1 + arginine + GLP1 sequence + GCGGGGGG + SOD Fragment 2.
[0022] Among them, the sequence of SOD fragment 1 is:
[0023] ATKAVSVLKGDGPVQGIINFEQKESNGPVKVWGSIKGLTEGLHGFHVHEFGDNTAGSTSAGP;
[0024] The sequence of GLP1 (7-37aa) is: HAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIAWLCKGRG, in which the V at position 33 is mutated to C, in order to cross-link with C in GCGGGGGG to form a disulfide bond. The C-terminus of wild-type GLP1 does not have the sequence GCGGGGGG, which is connected to the back when designing the gene, which can be called a linker.
[0025] SOD fragment 2 sequence is: MATKAVSVLKGDGPVQGIINFEQKESNGPVKVWGSIKGLTEG.
[0026] The arginine of the polypeptide is flanked by cysteines,...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: A method for selectively protecting the enzyme cleavage site during trypsin digestion
[0039] Polypeptide 3: SOD protein fragment 1 + arginine + GLP1 sequence + GCGGGGGG + SOD fragment 2
[0040] The sequence of SOD fragment 1 is ATKAVSVLKGDGPVQGIINFEQKESNGPVKVWGSIKGLTEGLHGFHVHEFGDNTAGSTSAGP;
[0041] The GLP1 sequence is (7-37aa)HAEGTFTSDVSCYLEGQAAKEFIAWLVKGRGC. Among them, the S at the 18th position is mutated to a C, and a C is added after the G at the 37th position.
[0042] SOD fragment 2 sequence is MATKAVSVLKGDGPVQGIINFEQKESNGPVKVWGSIKGLTEG.
[0043] Peptide triple sequence such as Figure 6 shown.
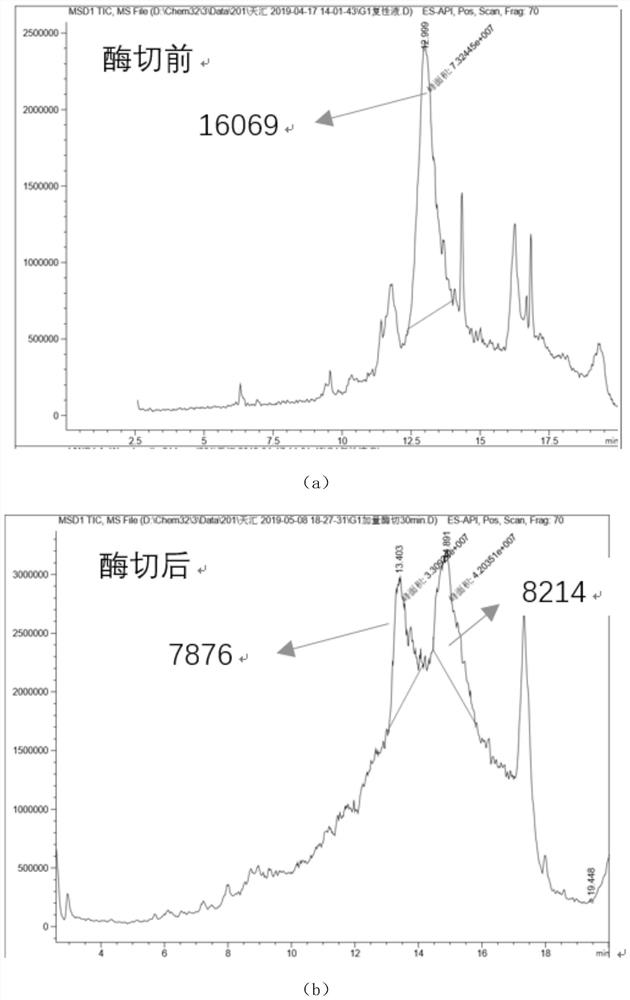
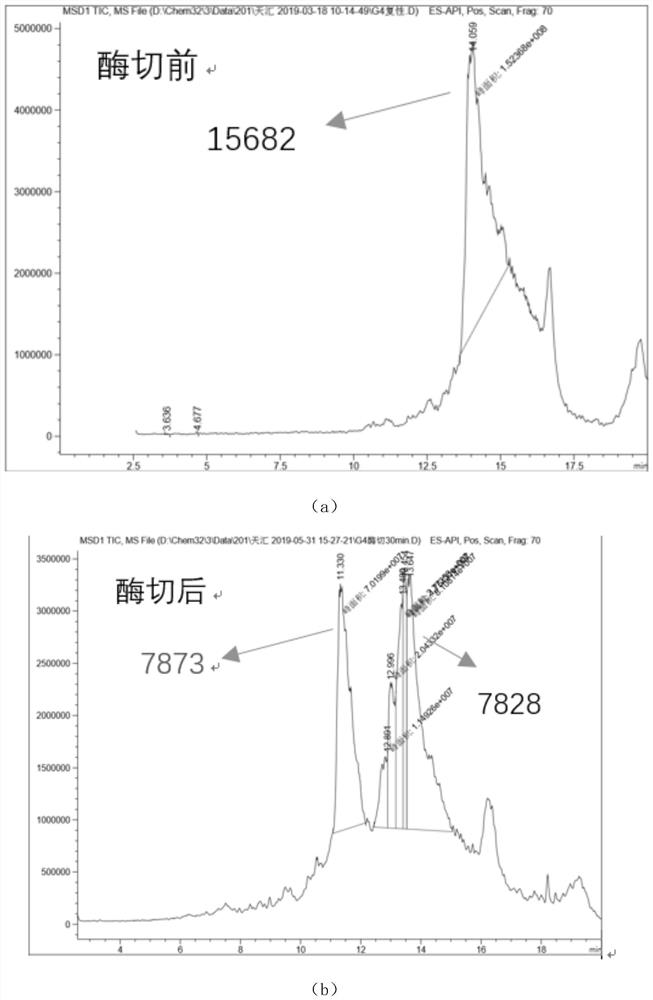
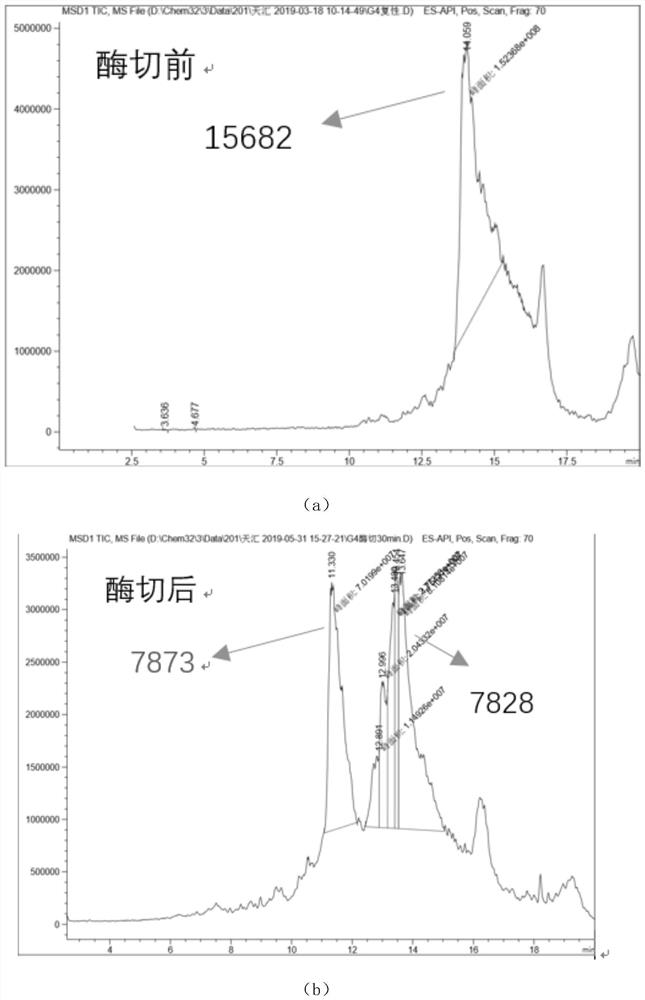
[0044] Check whether the arginine in polypeptide 1, polypeptide 2 and polypeptide 3 can be digested by trypsin according to the following steps.
[0045] Synthetic coding gene: Synthesize the target gene sequence through the gene synthesis company Hefei Jixiang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sequence is as follows:
[0046] Sequence 1:
[0047]CATATG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com