Diagnostic marker for neuropsychiatric lupus and detection kit thereof
A marker, spiritual technology, applied in the field of marker identification and use, can solve problems such as lack of consistency in results and lack of clinical basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
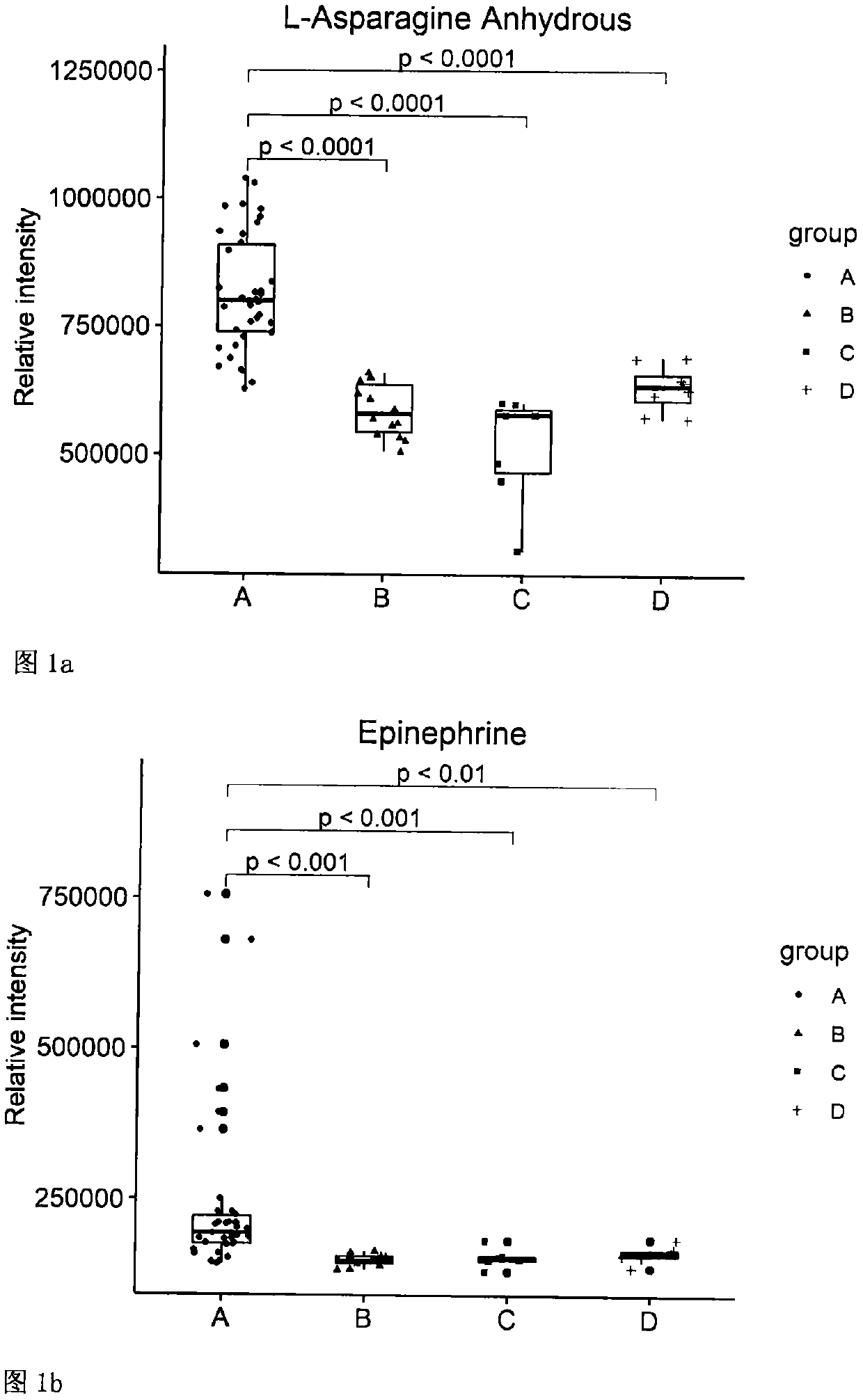
[0047] Example: Detection of metabolites such as L-asparagine by mass spectrometry for diagnosis of neuropsychiatric lupus
[0048] 1. Case and control sample selection criteria
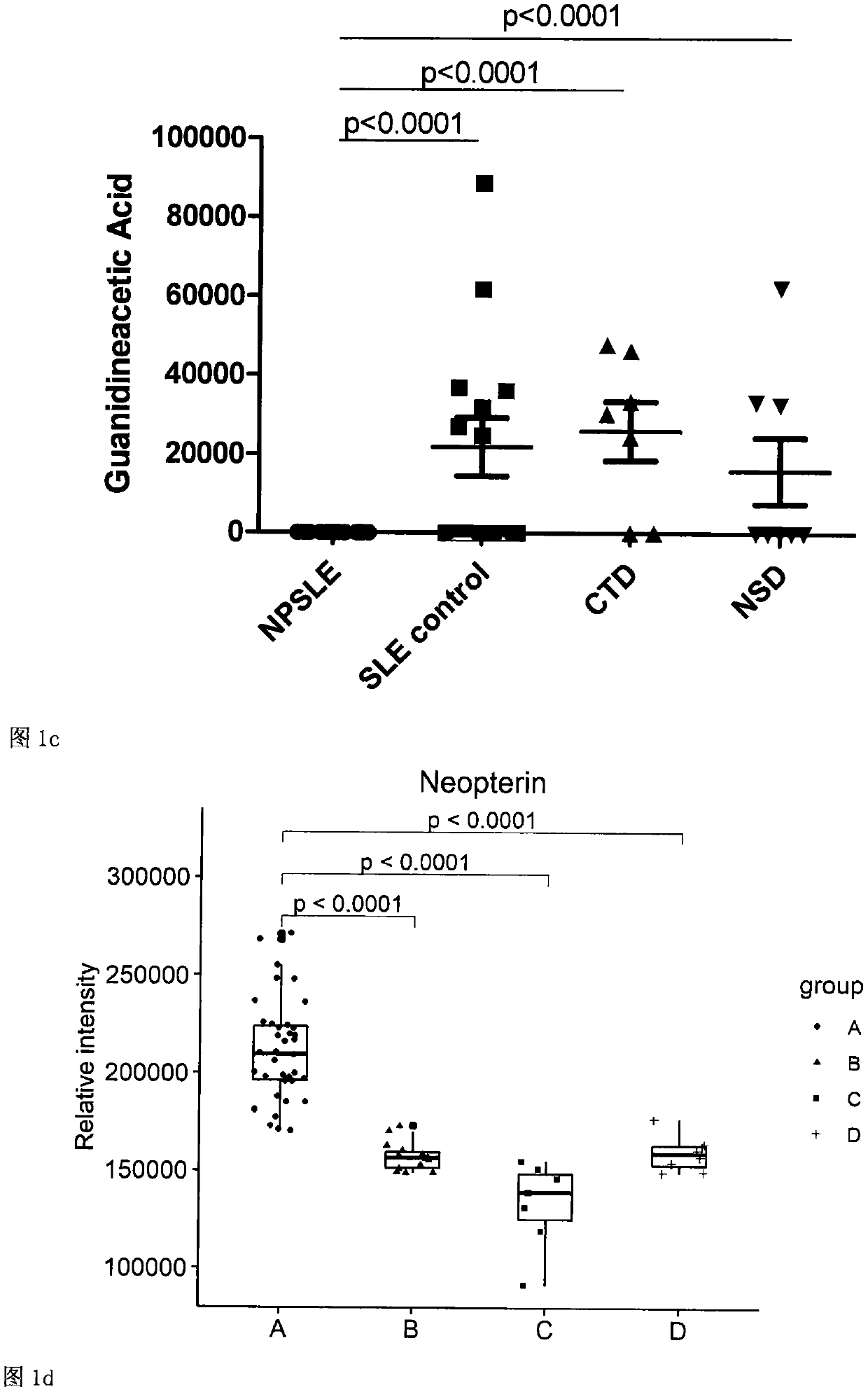
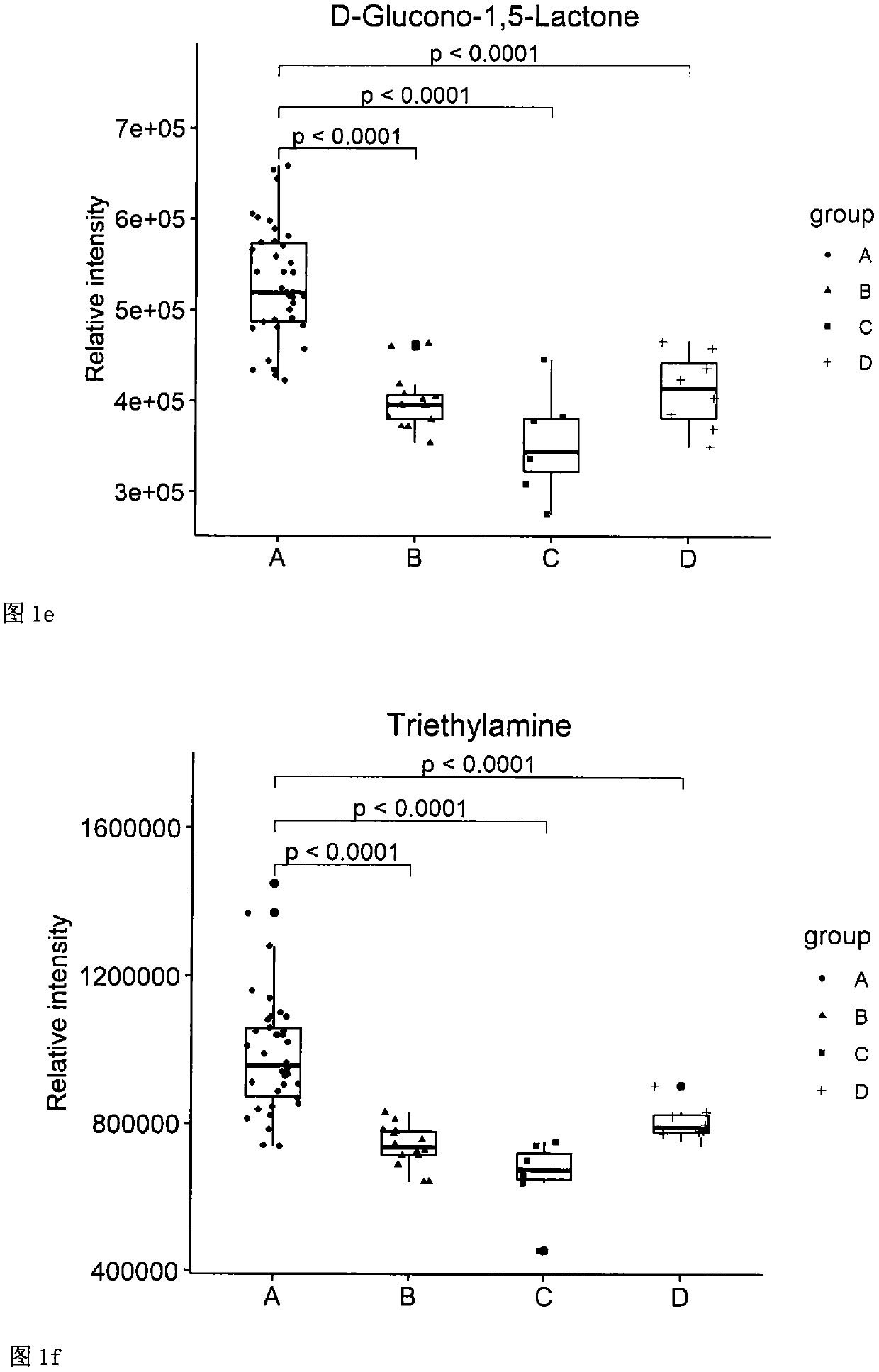
[0049] CSF samples were selected from 38 NPSLE patients, 14 SLE control patients, 7 other connective tissue disease control patients and 8 other neurological disease control patients. All patients in the experimental group met the NPSLE classification criteria established by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) in 1997. All control patients had neuropsychiatric manifestations and were ruled out for NPSLE by an experienced rheumatologist.
[0050] 2. Experimental plan
[0051] (1) Processing of cerebrospinal fluid samples
[0052] 1. Take the sample out of the -80°C refrigerator and thaw it on ice. After thawing, vortex for 10 seconds to mix.
[0053] 2. Take 50uL of the sample in an EP tube, add 150uL of pre-cooled ice methanol (containing 1ug / mL of 2-chlorophenylalanine as an internal stan...
example 1
[0073] Using individual metabolites as markers for the diagnosis of NPSLE: The levels of 21 metabolites in the NPSLE group were determined, which were significantly different from each control group, and the cut-off required for each metabolite alone was determined. value. Individual determinations of each metabolite could clearly distinguish NPSLE patients (group A) from other control patients. Specifically, any one of the following markers is detected, and the level of the marker is higher than its cut-off value, which can indicate that the patient may be an NPSLE patient (these markers include: L-asparagine, epinephrine, Neopterin, gluconolactone, triethylamine, α-D-glucose, sarcosine, 2-acetylfuran, n-octylal, naphthalene, trans-2-octen-1-ol, β- allanine, spermidine, inositol, steadecatrienoic acid methyl ester, pulerone); correspondingly, detection of any of the other markers at levels below their cut- The off value can indicate that the patient may be an NPSLE patient ...
example 2
[0096] 1. After determining the levels of the above multiple metabolites, multiple metabolites can also be combined to form markers for joint analysis, which can efficiently distinguish NPSLE patients from each control group and obtain ideal sensitivity and specificity. Using the logistic regression method, use the data of these 21 metabolites in 2 groups of 67 samples to fit a logistic regression function. The coefficients of the function are shown in the following table:
[0097]
[0098]
[0099] Note: e+02 means 10 2 , e-04 means 10 -4 .
[0100] Use this model to calculate logistic regression predictors (w) for 67 samples, and use these 67 predictors to plot the ROC curve ( figure 2 ), and calculate the optimal critical value (0.5). The optimal cutoff is the threshold at which the sum of sensitivity and specificity is maximum.
[0101] 2. Among the above metabolites, the content of L-asparagine is positively correlated with the neuropsychiatric injury index (NP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com