A method for removing elemental impurities and pigments in sugammadex sodium refined products
A technology for sodium sugammadex and elemental impurities, which is applied in the field of removing elemental impurities and pigments in refined sodium sugammadex, can solve the problems of unconsidered element impurities, complicated steps, inconvenient operation, etc., so as to reduce the risk of toxicity , the process is simple, the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
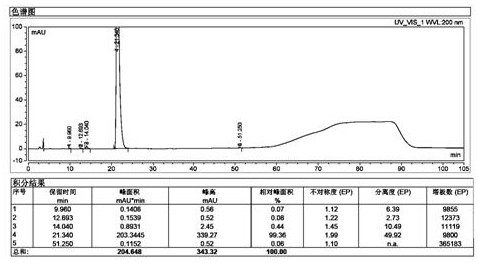
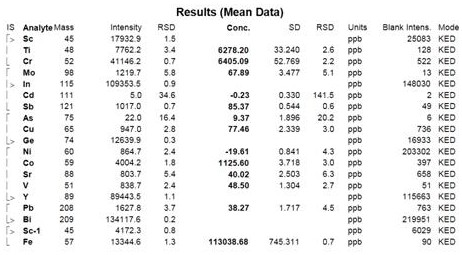
[0063] Take 100g of sugammadex sodium refined product, add 300g of water to dissolve until clear, stir and add 190g of acetone at room temperature, after the addition, the solution becomes slightly turbid. The solution was transferred to a separatory funnel, and the layers were allowed to stand, and an orange-yellow oily substance settled to the bottom. Separate the oil. The supernatant was transferred to the flask, and 1300g of acetone was added with stirring at room temperature, and a white solid was separated out, filtered by suction, and dried to obtain 83g of sugammadex sodium as a white solid, whose purity was 99.78% ( image 3 ), the purity of the product did not change significantly. The Fe content measured by ICP-MS is 4.1ppm, and all the other elemental impurities are less than 1ppm ( Figure 4 ). After detection of orange-yellow oil, its Fe content is 200ppm ( Figure 5 ).
Embodiment 2
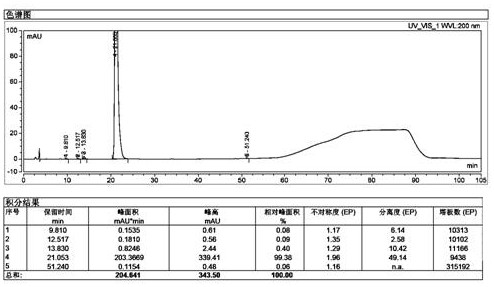
[0065] Take 100g of sugammadex sodium refined product, add 200g of water to dissolve until clear, stir and add 290g of DMF at room temperature, after the addition, the solution becomes slightly turbid. The solution was transferred to a separatory funnel, and the layers were left to stand, and a small amount of oily matter sank to the bottom. The oil was separated, the supernatant was transferred to a flask, and 310 g of DMF was added with stirring at room temperature, a white solid was precipitated, filtered by suction, and dried to obtain 85 g of sugammadex sodium as a white solid, whose purity was 99.78 g by HPLC. %( Image 6 ), the Fe content measured by ICP-MS is 7.1ppm, and the rest of the elemental impurities are less than 1ppm ( Figure 7 )
Embodiment 3
[0067] Take 100g of sugammadex sodium refined product, add 400g of water to dissolve until clear, stir and add 750g of acetonitrile at room temperature, after the addition, the solution becomes slightly turbid. The solution was transferred to a separatory funnel, and the layers were left to stand, and a small amount of oily matter sank to the bottom. The oil was separated, the supernatant was transferred to a flask, and 1600 g of ethanol was added with stirring at room temperature, a white solid was precipitated, filtered by suction, and dried to obtain 73 g of sugammadex sodium as a white solid, whose purity was 99.78 g by HPLC. %( Figure 8 ), the Fe content measured by ICP-MS is 7.0ppm, and the rest of the elemental impurities are less than 1ppm ( Figure 9 )
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com