Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for deformed pseudomonas plecoglossicida TaqMan and preparation method thereof
A Pseudomonas mutans, real-time fluorescence quantitative technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe-based methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of low accuracy, cumbersome operation, and low sensitivity. Achieve the effect of high practical value, simple operation and complete reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0059] 4. Preparation of positive control
[0060] Extract the constructed pMD18-gyrB plasmid, then use a spectrophotometer to detect the quality and concentration of the plasmid, calculate the copy number of the target gene according to the following formula, and then dilute it with sterilized ultrapure water to a concentration of 1×10 8 Copies / μL of positive gyrB plasmid as a positive standard control
[0061] 5. Design TaqMan probes
[0062] According to the sequencing sequence results of positive clones of recombinant plasmids, use Primer Premier 5 to design probes that meet the following requirements: ①The first letter cannot be "G"; ②Try not to appear consecutive "G"s ≥ 3; ③Generally try to use "C" bases Base content > "G" base, A, T, C, G content is uniform, GC content is 40% to 60%; ④The length of the probe should be ≤27bp, preferably not more than 30bp, and the Tm value should be ≥10ºC than the primer. The needle was synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Co., and its 5' en...
Embodiment 1
[0090] The specificity experiment of embodiment 1 primer
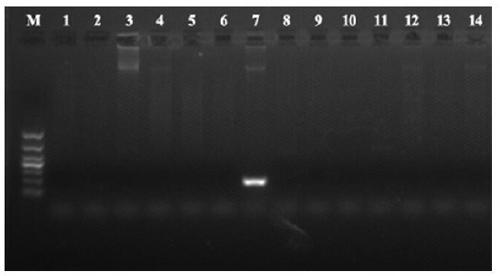
[0091] In order to determine the primer specificity of the TaqMan probe real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit, Vibrio cannellii, Streptococcus agalactiae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Harvey Vibrio, Pseudomonas mutans, Vibrio alginolyticus, Shewanella, Vibrio nocardia, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Pseudomonas putida, Pseudomonas fluorescens DNA as templates, sterile ultra- Pure water was used as a blank control without a template, and the established routine PCR was used for detection. The experimental results showed that only Pseudomonas mutans was detected positive, and all others were negative (such as figure 2 ), which indicated that the designed primers had excellent specificity and could be used for rapid detection of Pseudomonas mutans.
Embodiment 2
[0092] Embodiment 2 Sensitivity detection experiment
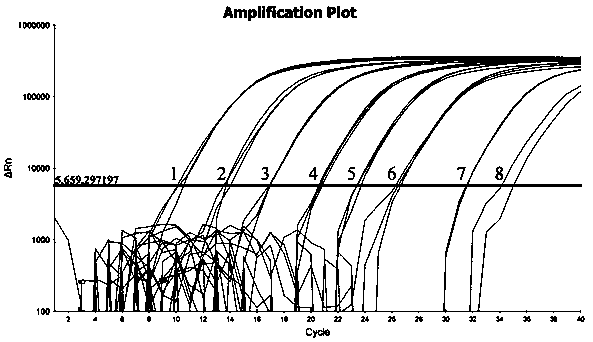
[0093] Dilute the positive control plasmid (pMD18-gyrB) by 1 × 10 8 , 1×10 7 , 1×10 6 , 1×10 4 , 1×10 3 , 1×10 2 , 5×10 1 , 1×10 1 Copy number / μL was serially diluted, and at the same time, the concentration of the original bacterial solution of Pseudomonas mutans was measured by plate counting, and then diluted according to 10-fold gradients, and then 1 mL of bacterial DNA of each gradient was extracted, and 0.2 μL was taken as a template for each, and the samples were tested in a fluorescent PCR instrument. The results showed that the number of cycles (Ct) required for the fluorescent signal in each reaction tube to reach the threshold value and the logarithm of the initial template copy number had an obvious linear relationship (R 2 =0.996) (such as image 3 ), the lower limit of detection for plasmids is 5×10 1 Copy number / μL (eg Figure 4 ), the detection limit for pure bacterial cultures is 50 cfu / mL (such ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com