Cellulose foam capable of visually identifying and removing chromium as well as preparation method thereof and chromium removal method
A technology of cellulose foam and cellulose solution, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, and combustible gas purification, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in reaching, high reactor processing cost, and long time-consuming adsorbent regeneration process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for preparing cellulose foam capable of visually identifying and removing chromium, comprising the following steps:
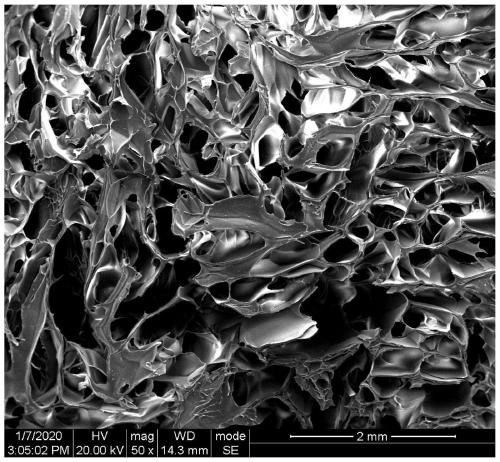
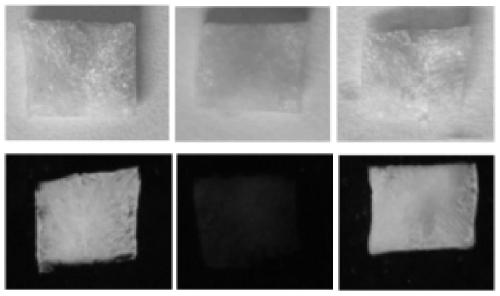
[0026] Take 8.333g of dried cotton, add 145.45ml DMSO solution, then add 42.6mL 40wt% TBAH aqueous solution, mechanically stir to dissolve, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C for 2 hours after standing for defoaming, and obtain a fiber with a mass fraction of 4%. prime solution. Take 10mL of the above solution in a 50ml beaker, add 1mL of epichlorohydrin, stir until the color of the solution becomes lighter, add 0.1mL of 5wt% PEI, stir well, pour it into a mold, put it in a 50°C oven for 60min, take it out to get After replacing the solvent with deionized water, put the hydrogel into the freezer (-18°C) to freeze for 12 hours, and then put it into a freeze dryer at -81°C for 24 hours to obtain cellulose foam (also known as PEI-modified foam). permanent cellulose foam).
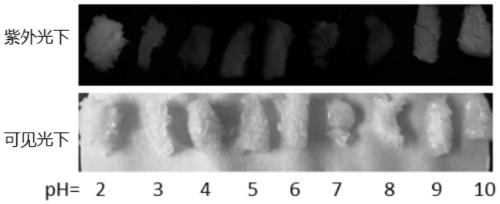
[0027] Take 0.02 g of the prepared cellulose foam, put it into 20 ml of Cr(V...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A method for preparing cellulose foam capable of visually identifying and removing chromium, comprising the following steps:
[0030] Take 10mL of the cellulose solution prepared in Example 1 in a 50mL beaker, add 1mL of epichlorohydrin, stir until the color of the solution becomes lighter, then add 10wt% PEI 1mL, stir well, pour it into a mold, and put it in 50 React in an oven at ℃ for 60 minutes, take out the hydrogel, replace the solvent with deionized water, put it in the freezer of the refrigerator (-18 ℃) to freeze for 12 hours, and then put it in a freeze dryer at -81 ℃ for 24 hours to obtain Cellulose foam.
[0031] Take 0.02 g of the prepared cellulose foam, put it into 20 mL of Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater with a concentration of 100 mg / L and a pH value of 2, and take a sample for analysis after magnetic stirring and adsorption at 25 ° C for 30 min. The removal rate is measured to be 65.57 %.
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for preparing cellulose foam capable of visually identifying and removing chromium, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Take 10mL of the cellulose solution prepared in Example 1 in a 50ml beaker, add 0.5mL of epichlorohydrin, stir until the color of the solution becomes lighter, then add 1mL of 6wt% PEI, stir well, pour into a mold, put in 50 Regenerate in an oven at ℃ for 30 minutes, take out the hydrogel, replace the solvent with deionized water, freeze in the freezer (-18℃) for 12h, and then put it in a freeze dryer at -81℃ for 24h to obtain Cellulose foam.
[0035] Take 0.05 g of the prepared cellulose foam, put it into 25 mL of Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater with a concentration of 100 mg / L and a pH value of 2, take a sample for analysis after magnetic stirring and adsorption at 25 °C for 30 min, and the removal rate is measured to be 95.53 %.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com