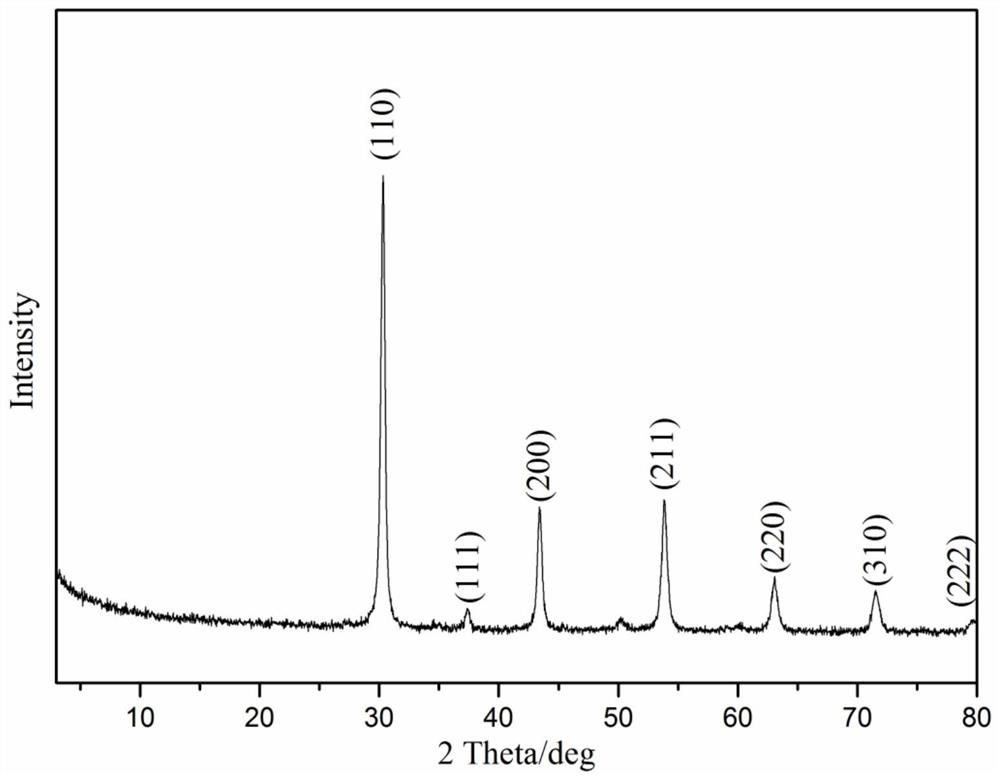
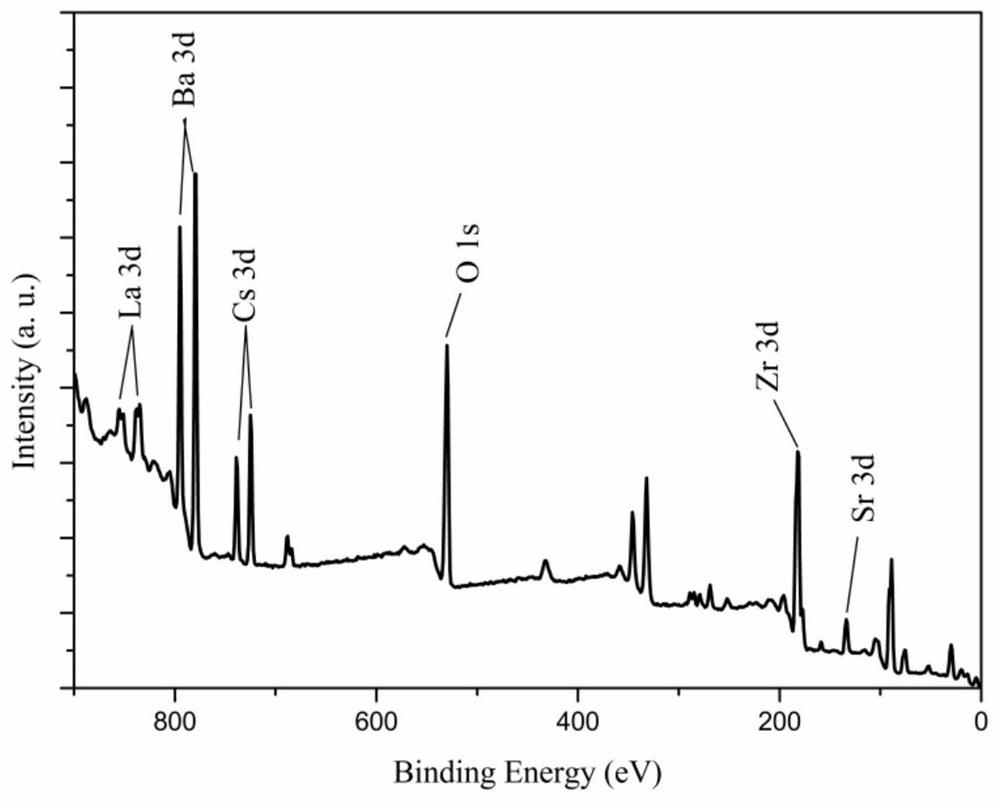
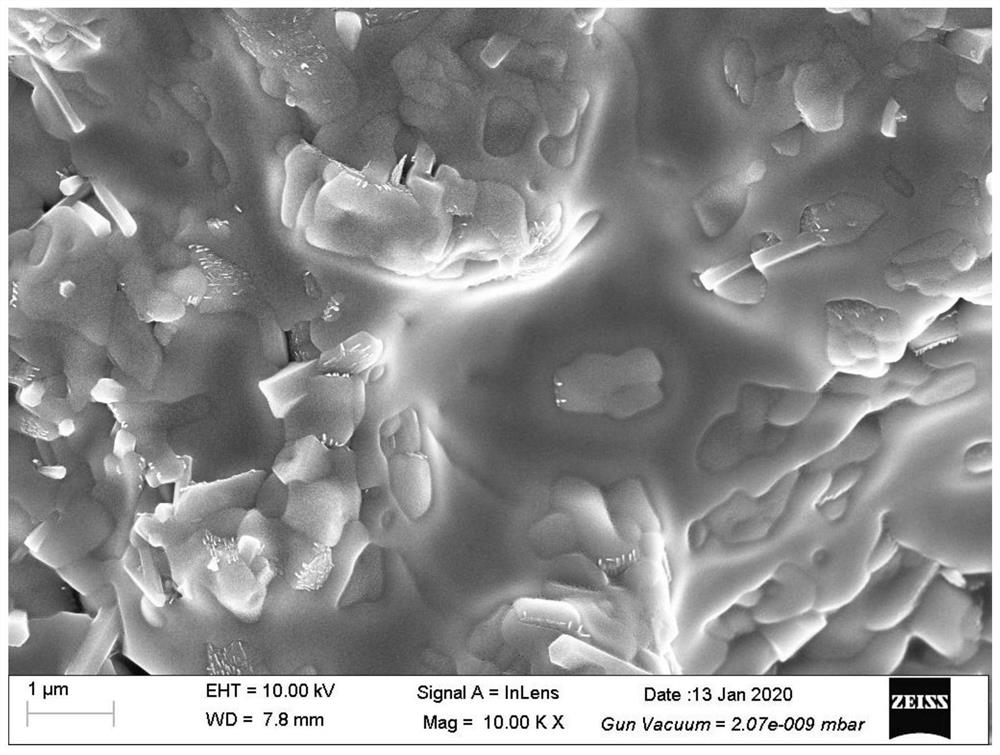
A kind of low temperature preparation method of strontium and cesium glass ceramic co-solidified body
A technology of glass ceramics and solidified body, which is applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of simultaneous solidification of strontium and cesium, does not involve the evaluation of leaching resistance of solidified nuclides, and high cost of industrial application, so as to solve the problem of solidification of ceramics Strong element selectivity, solution to unsatisfactory packaging capacity, and high mechanical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A low-temperature preparation method of strontium and cesium glass-ceramic co-solidified body is characterized in that, comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1, take the Ba(NO 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 O was added to deionized water, and stirred at a speed of 300 r / min until dissolved; the deionized water was mixed with Zr(NO) 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of O is 600:1;
[0029] Step 2: Add citric acid to the stirred solution in step 1, and stir and chelate for 1 hour at a speed of 300 r / min; the citric acid and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of the total cations of O is 3:1;
[0030] Step 3, adding acrylamide to the solution after stirring and chelating in step 2, and then stirring at a speed of 300 r / min at 75° C. to obtain a transparent gel; the acrylamide and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A low-temperature preparation method of strontium and cesium glass-ceramic co-solidified body is characterized in that, comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, take the Ba(NO 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 O was added to deionized water, and stirred at a speed of 250 r / min until dissolved; the deionized water was mixed with Zr(NO) 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of O is 700:1;
[0037] Step 2. Add glucono-δ-lactone to the stirred solution in step 1, and stir and chelate at a speed of 250r / min for 1.5h; the glucono-δ-lactone and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of the total cations of O is 4:1;
[0038] Step 3, adding polyvinyl alcohol to the solution after stirring and chelating in step 2, and then stirring at a speed of 200 r / min at 80 ° C to obtain a transparent gel; the polyvinyl alcohol and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A low-temperature preparation method of strontium and cesium glass-ceramic co-solidified body is characterized in that, comprises the following steps:
[0044] Step 1, take the Ba(NO 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 O was added to deionized water, and stirred at a speed of 250 r / min until dissolved; the deionized water was mixed with Zr(NO) 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of O is 700:1;
[0045] Step 2. Add glucono-δ-lactone to the stirred solution in step 1, and stir and chelate at a speed of 250r / min for 1.5h; the glucono-δ-lactone and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O and Zr (NO 3 ) 2 ·5H 2 The molar ratio of the total cations of O is 4:1;
[0046] Step 3, adding polyvinyl alcohol to the solution after stirring and chelating in step 2, and then stirring at a speed of 200 r / min at 80 ° C to obtain a transparent gel; the polyvinyl alcohol and Ba(NO) 3 ) 2 , Sr(NO 3 ) 2 , CsNO 3 , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com