Dual-rotor expander and using method thereof
An expander and double-rotor technology, which is applied in the field of expanders, fluid motors or pumps, and rotor-type fluid mechanical devices, can solve the problems of no volume expansion process in the expansion chamber, loss of energy transfer process, and inability to adjust the expansion ratio, etc., to achieve structural Simplicity, long service life and no wearing parts effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
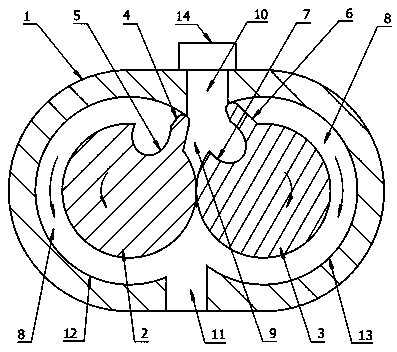
[0040] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, the present embodiment is a rotor expander, a fluid motor, a pump or a compressor, including a cylinder body 1, inside the cylinder body 1 there are two circular and partially overlapping rotor slots 12 and 13, the rotor slot 12 There are first rotor and second rotor respectively in the rotor groove 13, and there are gears driving the first rotor and the second rotor to rotate in opposite directions with a fixed speed ratio outside the cylinder body. Let me repeat. The main bodies of the first rotor and the second rotor are cylinders of equal thickness, and the outer circumferential surfaces are tangent, and the first rotor has protruding sealing teeth 4 extending radially outward from its outer circumference and radially inwardly recessed tooth grooves 5. The second rotor is provided with protruding sealing teeth 6 extending radially outward from its outer circumference and passing tooth grooves 7 recess...
Embodiment 2
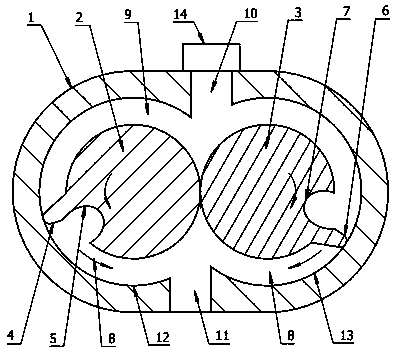
[0047] Such as Figure 5 , Figure 6 As shown, the principle and structure of this embodiment and Embodiment 1 are basically the same, the difference is that this embodiment cancels the air intake control device 14, and sets the inlet 10 on the side of the second rotor, when the first rotor and the second rotor turn to Figure 5 In the position shown, the inlet 10 communicates with the slot 7 on the second rotor, and the high-pressure gas enters the expansion chamber 9 through the inlet 10 and the slot 7. When the inlet 10 is completely blocked by the side of the second rotor, the high-pressure gas no longer Enter the expansion chamber 9 to complete the intake process. Such as Figure 6 In the expansion stage shown, the high-pressure gas cools down in the expansion chamber 9 and performs work externally. The inlet 10 cooperates with the tooth groove 7 to control the amount of gas entering the expansion cavity 9, and replaces the intake control device 14, and adjusts the exp...
Embodiment 3
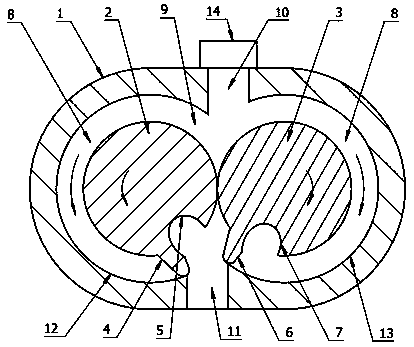
[0049] Such as Figure 7 , Figure 8 As shown, the principle and structure of this embodiment and Embodiment 1 are basically the same, the difference is that this embodiment cancels the air intake control device 14, opens a secondary air intake passage 21 on the first rotor, and opens a secondary inlet on the side of the rotor slot 12 16. Set the inlet 10 on the side of the second rotor, when the first rotor and the second rotor turn to Figure 7 In the position shown, the inlet 10 communicates with the tooth slot 7 on the second rotor, the auxiliary air intake channel 21 communicates with the auxiliary inlet 16, and the high-pressure gas enters the expansion chamber 9 through the inlet 10 and the auxiliary inlet 16. When the inlet 10 is completely filled by the second When the side of the second rotor is blocked and the auxiliary inlet 16 is completely blocked by the side of the first rotor, the high-pressure gas no longer enters the expansion chamber 9, and the intake proce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com