Non-metal heating device for cooking
A heating device, non-metallic technology, applied in the direction of special materials for cooking utensils, applications, kitchen utensils, etc., can solve the problems of low cost, and achieve the effects of increased life cycle, high power, less heat junction and micro-flash discharge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
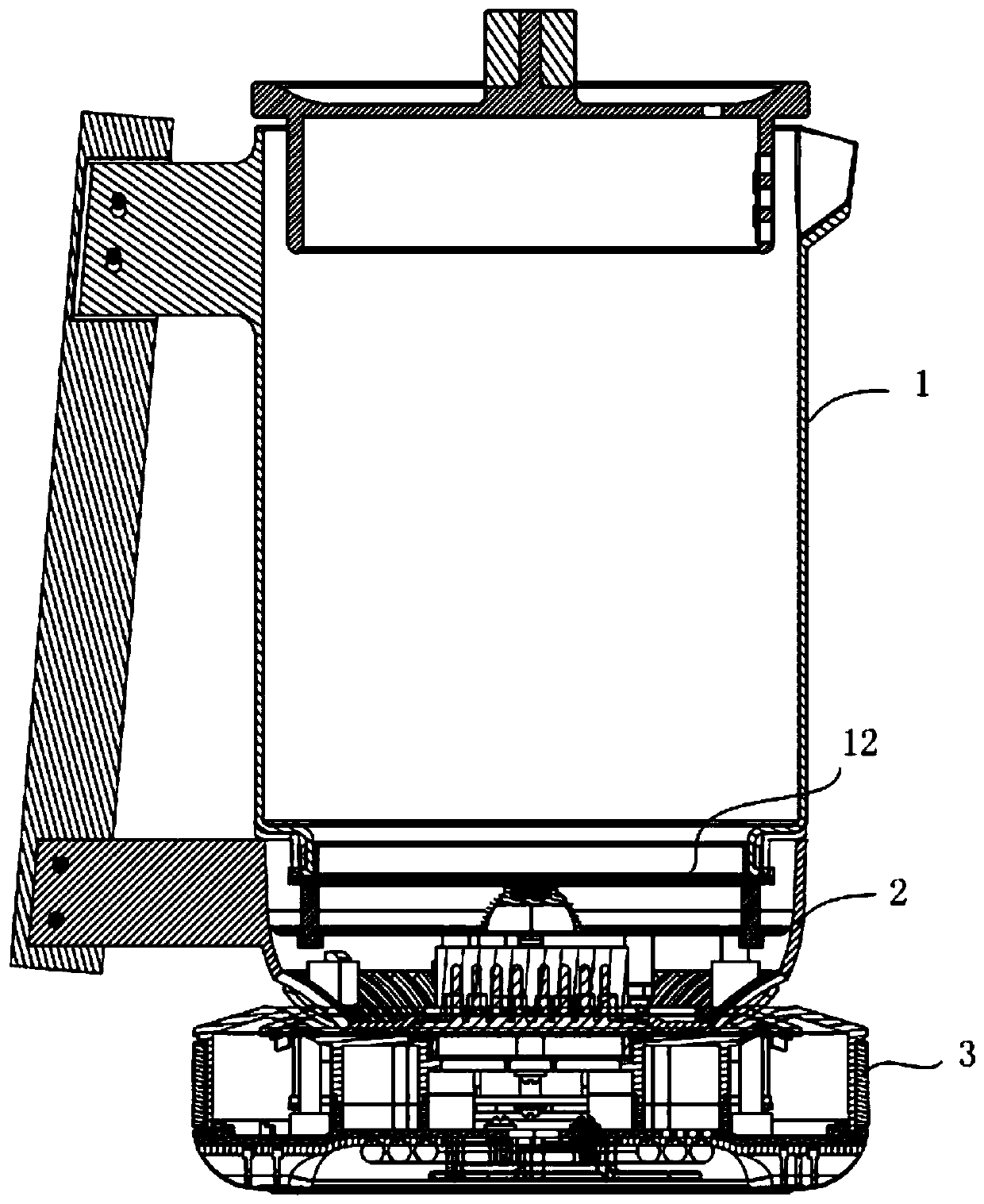
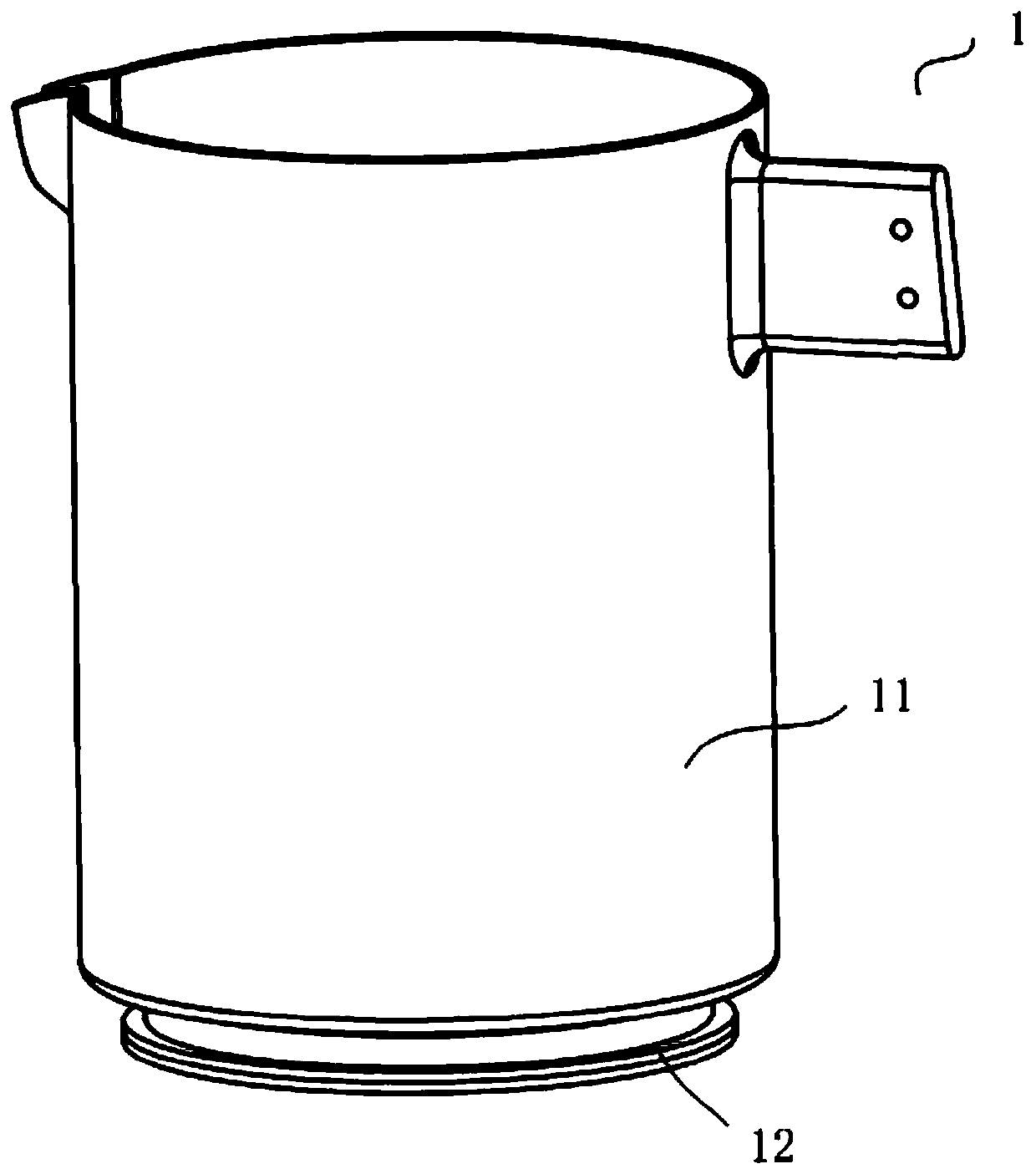
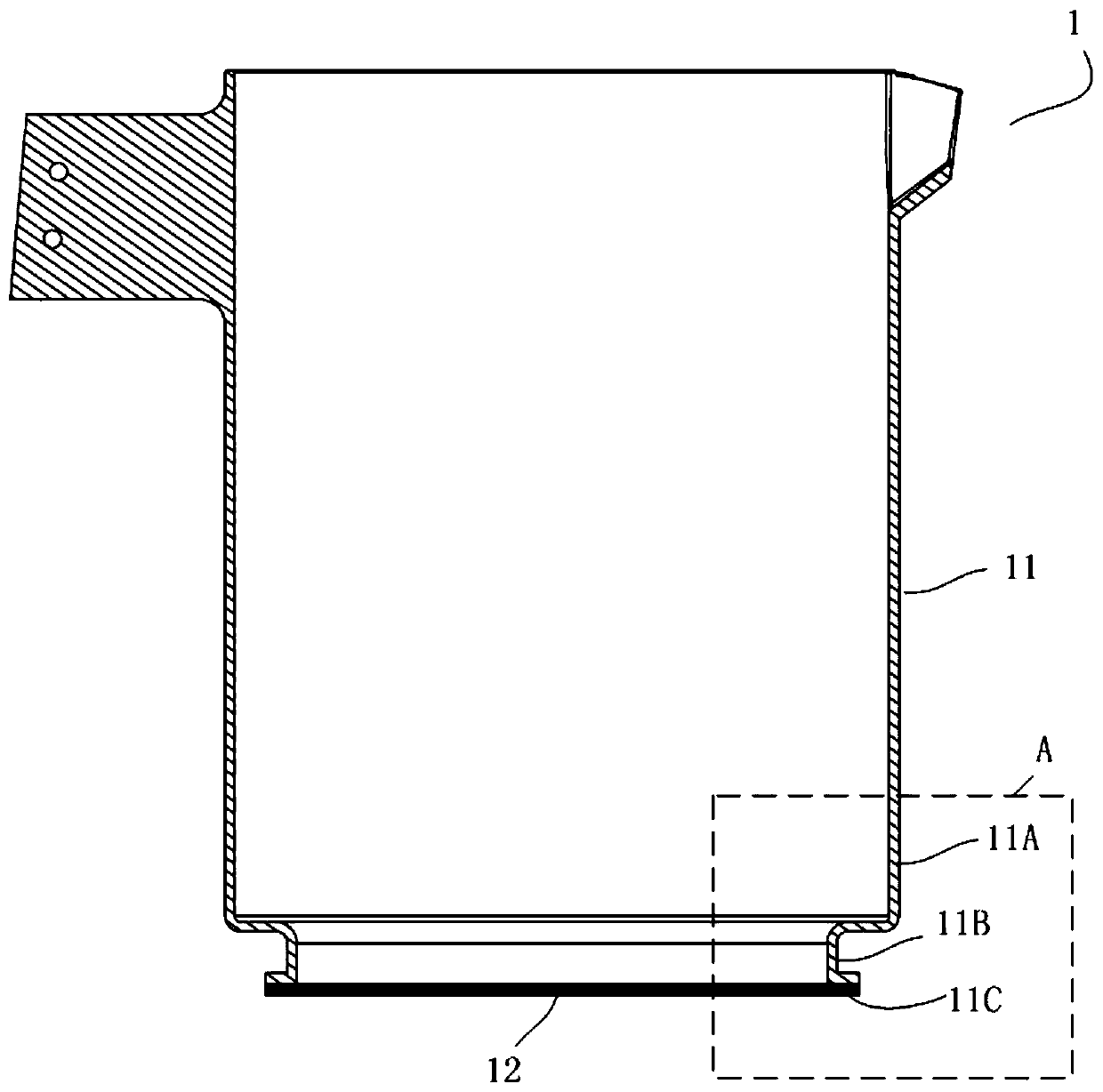
[0074] 1. Make a high borosilicate glass pot with a cut bottom. The pot body includes a pot body and a concave part connected to the pot body. The concave part extends outward to form a flat part;
[0075] 2. Prepare the glass plate and print the heating film on the back of the glass plate;
[0076] 3. Preparation of glass powder coating
[0077] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 30%, Al 2 o 3 10%, B 2 o 3 15%, MgO 5%, ZnO 25%, CaO 15%; the above components were melted uniformly at 1450°C, water quenched, dried, and crushed to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0078] 2. Metal powder: pure silver powder, D 50 <2μm;
[0079] 3. Soldering paste preparation: 15% of organic components, 5% of glass powder, and 80% of metal powder, fully stir the above components, and disperse evenly through a three-roller machine to obtain a paste-like sealing material;
[0080] 4. Apply a uniform layer of glass powder c...
Embodiment 2
[0084] 1. Make a high borosilicate glass pot with a cut bottom. The pot body includes a pot body and a concave part connected to the pot body. The concave part extends outward to form a flat part;
[0085] 2. Prepare the glass plate and print the heating film on the back of the glass plate;
[0086] 3. Preparation of glass powder coating
[0087] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 40%, Al 2 o 3 10%, B 2 o 3 10%, MgO 5%, ZnO 25%, CaO 10%; the above components were melted uniformly at 1450°C, water quenched, dried, and crushed to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0088] 2. Metal powder: pure copper powder, D 50 <2μm;
[0089] 3. Soldering paste preparation: 10% of organic components, 5% of glass powder, and 85% of metal powder, fully stir the above components, pass through a three-roller machine to disperse evenly, and obtain a paste-like sealing material;
[0090] 4. Apply a uniform layer of glass pow...
Embodiment 3
[0094] 1. Making a bottom-cut glass-ceramic pot, the pot body includes a pot body and a concave portion connected to the pot body, and the concave portion extends outward to form a flat portion;
[0095]2. Prepare the glass plate and print the heating film on the back of the glass plate;
[0096] 3. Preparation of glass powder coating
[0097] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 60%, Al 2 o 3 15%, B 2 o 3 10%, MgO 5%, Li 2 O 4%, K 2 O 2%, P 2 o 5 2%, TiO 2 1%, ZrO 2 1%; the above components were melted uniformly at 1550°C, water quenched, dried, and pulverized to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0098] 2. Metal powder: silver powder 95%, palladium powder 5%; D 50 <2μm;
[0099] 3. Soldering paste preparation: 15% of organic components, 5% of glass powder, and 80% of metal powder, fully stir the above components, and disperse evenly through a three-roller machine to obtain a paste-like sealin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com