Green rust material for fixing anaerobic lake sediment phosphate as well as preparation method and application thereof
A phosphate and lake technology, applied in anaerobic digestion treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of weakening the long-term stable fixation of phosphorus, and achieve the effect of efficiently repairing phosphorus pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
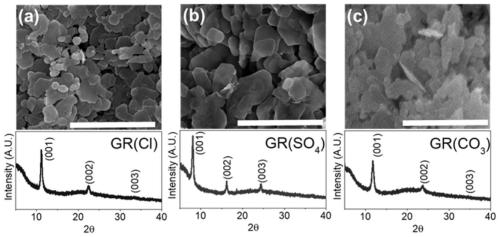
[0035] Embodiment 1: the preparation of three kinds of patina
[0036] 1. Synthesis and preparation of chloride ion intercalation green rust (GR(Cl))
[0037] Step 1): At room temperature, take a 250mL blue cap bottle and add 50mL NaOH (1mol / L) aqueous solution. Weigh 6.96gFeCl 2 4H 2 O (about 0.035mol) was mixed with it, and after putting it into the D8*45 stirring bar, quickly added 150mL of deionized water. Obtain Fe(OH) with a total volume of 200mL 2 Suspension. In this example, the Fe(II) / OH molar ratio was 0.7.
[0038] Step 2): open magnetic stirring to make Fe(OH) 2 Partially oxidized. Adjust the speed to 420-450r / min. Put in a pH meter to check. And press the stopwatch to start timing. When the pH is about 7.3 and the time is about 107 min, stop the reaction.
[0039] Step 3): Immediately put into a 250mL reagent bottle, shake vigorously and then transfer to the glove box to prevent GR(Cl) from continuing to oxidize. Open the lid of the reagent bottle in a...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: different green rust (GR (Cl), GR (SO 4 ), GRCO 3 ) Composite materials to remove phosphate
[0050] Step 1): Prepare a phosphorus solution with a concentration of 10 mg / L, and the solvent is deionized water.
[0051] Step 2): The three green rust composite materials prepared in Example 1 were used for phosphorus adsorption kinetics and isotherms. The green rust dosage was 0.2g / L, the reaction system was 40mL, and the pH was 7.5. React anaerobically in a 50 mL centrifuge tube.
[0052] Step 3): Start timing after feeding, and take samples at specified time points. The sampling times are 0, 2, 5, 10, 30, and 60 minutes respectively. The isotherm samples were all reacted for 60 minutes.
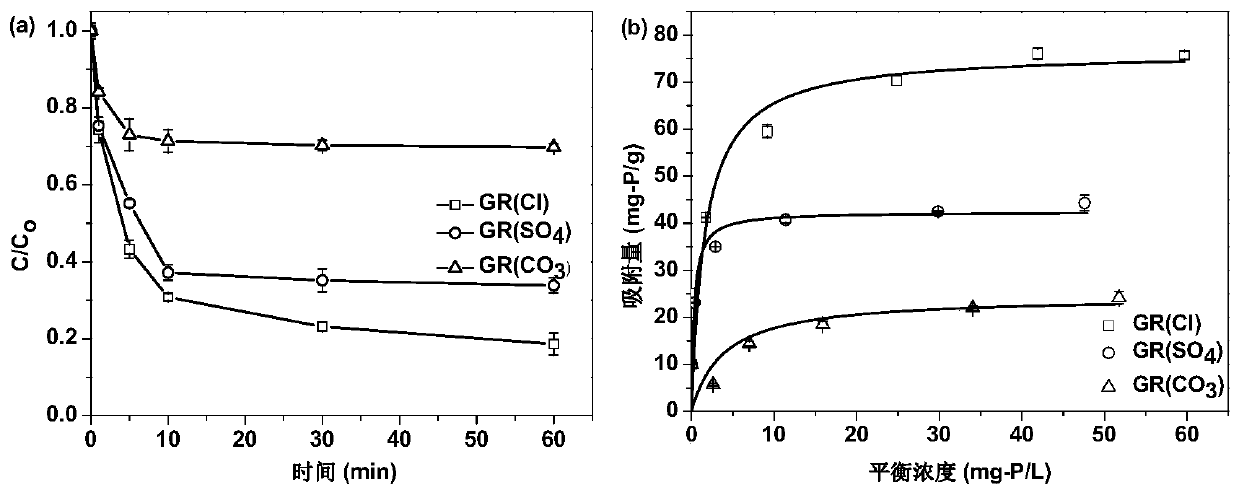
[0053] Step 4): After the reaction, the reaction mixture is passed through a 0.22 μm water film, and the concentration of phosphorus in the filtrate is measured to calculate the removal rate (C / C 0 ) and adsorption capacity, the results are as image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: Different green rusts (GR(Cl), GR(SO) under different pH conditions 4 ), GRCO 3 ) Composite materials to remove phosphate
[0055] Step 1): Prepare a phosphorus solution with a concentration of 10 mg / L, and the solvent is deionized water.
[0056] Step 2): Take the three kinds of patina composite materials prepared in Example 1 for phosphorus adsorption, the dosage of patina is 0.2g / L, and the reaction system is 40mL, adjust the pH to 5.5-9.5 with 0.01M HCl and NaOH respectively, React anaerobically in a 50 mL centrifuge tube.
[0057] Step 3): Start timing after feeding, and take samples after 60 minutes of reaction.
[0058] Step 4): After the reaction, pass the reaction mixture through a 0.22 μm water film, measure the concentration of phosphorus in the filtrate, and calculate the removal rate. The results are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com