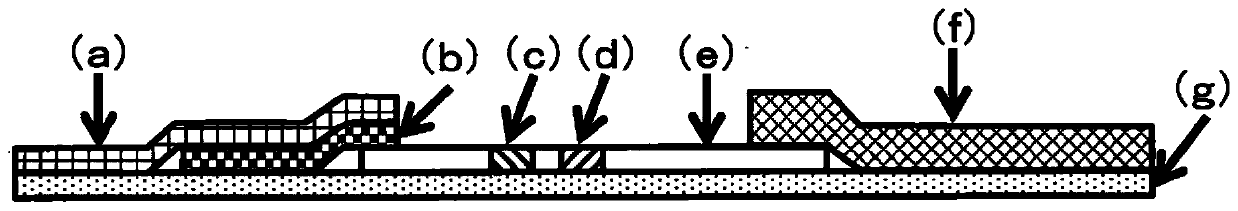
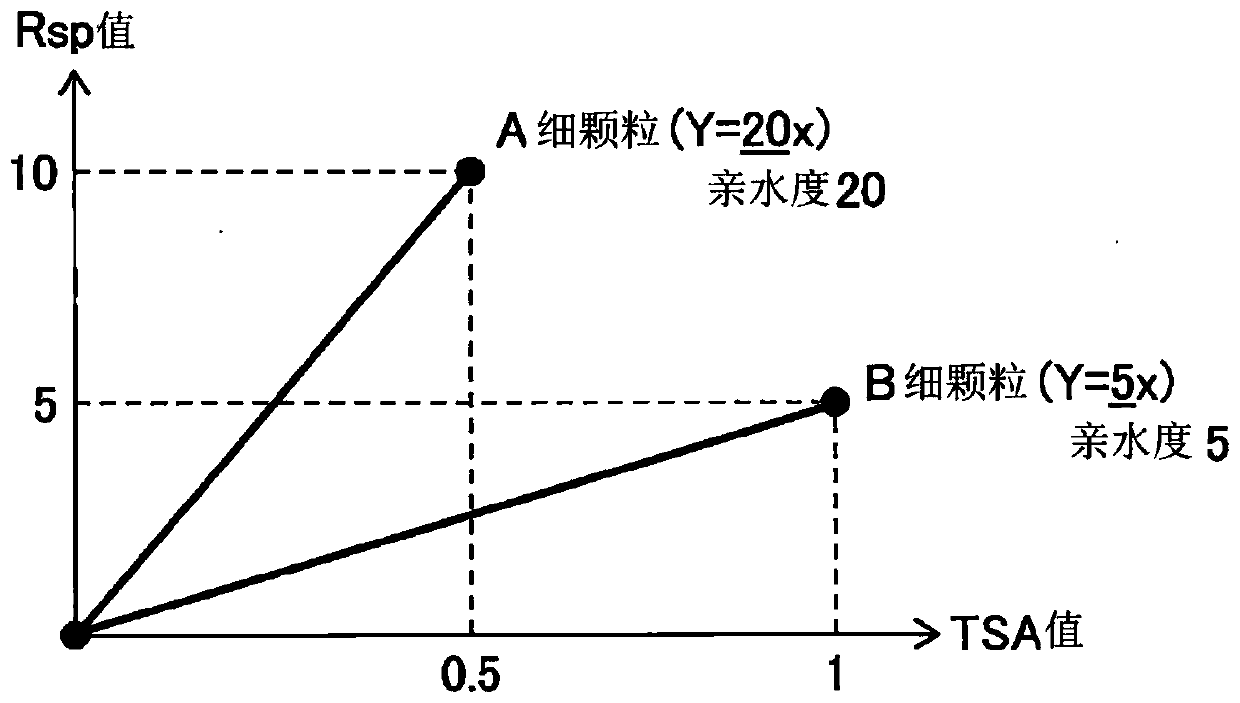
Organic colored microparticles, diagnostic reagent kit, and in vitro diagnosis method
A fine particle, organic technology, applied in the field of organic colored fine particles, can solve the problems of difficult to find TL, poor contrast, misdiagnosis, etc., and achieve the effect of full detection sensitivity and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0164] A cuprocellulose solution having a cellulose concentration of 0.37 wt%, a copper concentration of 0.13 wt%, and an ammonia concentration of 1.00 wt% was produced by a conventionally known method. The obtained cuprocellulose solution was slowly stirred in the presence of air, and the degree of polymerization was adjusted over 12 hours. Furthermore, a coagulation solution having a tetrahydrofuran concentration of 89.00 wt % and a water concentration of 11.00 wt % was produced. While slowly stirring 5000 g of the coagulation liquid using a magnetic stirrer, 500 g of the cuprocellulose solution produced was added. After continuing stirring for about 5 seconds, 1000 g of 10 wt % sulfuric acid was added for neutralization and regeneration to obtain 6500 g of slurry containing cellulose fine particles.
[0165] The resulting slurry was centrifuged at 10000 rpm for 10 minutes. The precipitate was taken out by decantation, poured into distilled water, stirred, and centrifuged ...
Embodiment 2~6
[0180] The chromogenic particles were produced by the same method as in Example 1 except that the degree of polymerization described in the following Table 1 was adjusted to the cellulose fine particles, an immunochromatographic diagnostic kit was produced, and its performance was evaluated. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 7~9
[0182] Reactive dyes having a pyrimidine structure (LevafixRubineCAGR. (Example 7, registered trademark) manufactured by DyStar Ltd., LevafixNavyBlueE-BNACAGR. (Example 8, registered trademark) manufactured by DyStar Ltd., LevafixNavyCA GR manufactured by DyStar Ltd. (Example 8) were used. 9. Registered trademark)) The cellulose fine particles were dyed, and the same method as in Example 1 was used to prepare color-developing particles, and an immunochromatographic diagnostic kit was manufactured, and its performance was evaluated. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com