Transfer printing process method for flexible MEMS device
A process method and flexible technology, applied in the field of semiconductor/MEMS manufacturing process, can solve the problems of high requirements for accurate transfer temperature and time, long release time, device structure failure, etc., so as to shorten the release time and improve the transfer rate. Success rate, the effect of enhancing adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
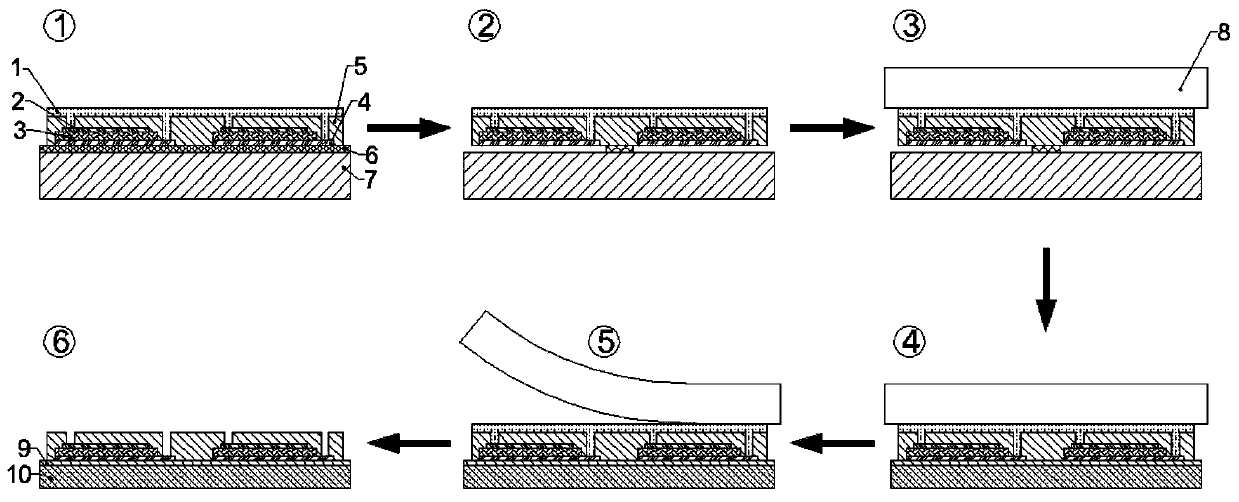
[0021] A transfer printing process method for flexible MEMS devices, the specific steps are as follows:
[0022] Step one, such as figure 1 As shown in step ①, a layer of SiN is deposited on the cleaned 2-inch single crystal silicon wafer by PECVD X sacrificial layer film, where NH 3 and SiH 4 The feeding ratio of the solution is 8:1, the reaction temperature is 450°C, the reaction pressure is 160Pa, and the deposition rate is 1nm / s. Measure its thickness after deposition, in this example SiN X The thickness of the sacrificial layer is 0.8 μm;
[0023] Step two, such as figure 1 As shown in step ①, the SiN X Make bottom electrode Ti(50nm) / Pt(200nm)-PZT(500nm)-top electrode Cr(10nm) / Au(100nm) three-layer device structure on the sacrificial layer, spin coating (low speed 600r / min, gluing time 9s, high speed 3000r / min, gluing time 30s), pre-baking (temperature 120°C, time 3min), nitrogen oven curing (curing by step drying, the temperature is 50°C, 30min, 140°C, 30min, 350...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com