Dual-target site inverse-transcription fluorescent PCR primers, probes and kits for detection of 2019 new coronavirus
A coronavirus, primer-probe technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve problems such as false negative test results, missed detection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 12019
[0042] Example 1 2019 Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV Gene Sequence Alignment and Target Sequence Determination
[0043] According to the newly published 6 2019-nCoV whole genomes, the nucleic acid sequence was compared through the NCBI database, and the specific nucleic acid sequence in the N gene of the virus was found: W1 (SEQ ID NO.1), W2 (SEQ ID NO.2) and W3 (SEQ ID NO. 3).
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 is aimed at the design of the primer of target sequence and probe
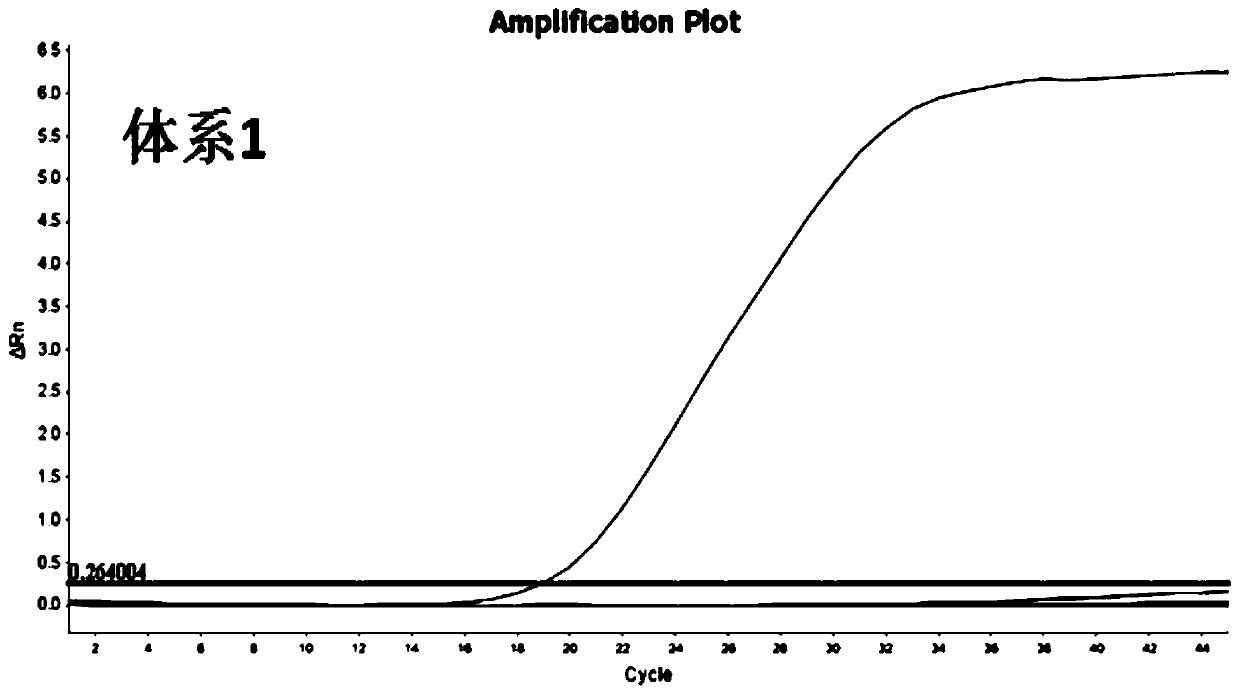
[0045] For the target sequence (SEQ ID NO.1-3) determined in Example 1, the inventors designed multiple combinations of primers and probes. And further, from many primer-probe combinations, 4 groups of MGB probe and primer combinations with better detection effects were selected, as shown in Table 1-Table 4 respectively. System 1 is used to detect target sequence W1, system 2 is used to detect target sequence W2, and systems 3 and 4 are used to detect target sequence W3, respectively.
[0046] Table 1 Primer Probe Sequence of System 1
[0047] 2019-nCoV-F1: TGGCAATGGCGGTGATG (SEQ ID NO.4) 2019-nCoV-R1: AGCTGGTTCAATCTGTCAAGCA (SEQ ID NO.5) 2019-nCoV-P1: TGCTCTTGCTTTGCTG (SEQ ID NO.6)
[0048] Primer probe sequence of table 2 system 2
[0049] 2019-nCoV-F2:GAAGCCTCGGCAAAAACG (SEQ ID NO.7) 2019-nCoV-R2:GCCGAAAGCTTGTGTTACATTG (SEQ ID NO.8) 2019-nCo...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3 Verification of the detection sensitivity and specificity of 4 fluorescent PCR detection systems for 2019-nCoV
[0065] 1. Sensitivity evaluation
[0066] At present, due to the lack of 2019-nCoV strains, the sensitivity experiment uses the RNA sequence of the artificially synthesized 2019-nCoV sequence after in vitro reverse transcription as a positive template, in which the SARS synthetic fragments: S1-S3, respectively correspond to W1-W3 of 2019-nCoV, The sequences of S1-S3 are shown in SEQ ID NO.16-18 respectively; MERS synthetic fragments: M1-M3, respectively corresponding to W1-W3 of 2019-nCoV, and the sequences of M1-M3 are shown in SEQ ID NO.19-21 respectively Show. The synthetic sequences were mixed into 12 normal human throat swabs, and the detection results of 4 sets of RT-qPCR were all positive, with a sensitivity of 100% (12 / 12).
[0067] 2. Specificity evaluation
[0068] Use the 4 sets of RT-qPCR screened and determined in Example 2 to detect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| PCR efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com